3 minutes
ECOM6013 E-Commerce Payment Systems

Overview
Security, trust, and e-commerce
- e-commerce (by definition) means transfer of value which can be
- resources
- information
- payments
- entertainment
- all of these types of value are desirable and therefore subject to theft
- perhaps, none more than payments (which drives commerce)
- it is all about money
Payment system stakeholders' priorities
- consumers
- low-risk, low-cost, refutable, convenience, reliability
- merchants
- low-risk, low-cost, irrefutable, secure, reliable
- financial intermediaries
- secure, low-risk, maximizing profit
- government regulators
- security, trust, protecting participants and enforcing reporting
Types of payment system
- cash
- most common form of payment in terms of number of transactions (changing quickly)
- instantly convertible into other forms of value without intermediation
- cheque transfer
- second most common payment form in the United States in terms of number of transactions; costly and slowly diminishing in most part of the world
- credit card
- credit card associations
- issuing banks
- processing centers
- stored value
- funds deposited into account, from which funds are paid out or withdrawn as needed, e.g., debit cards, gift certificates, Octopus
- peer-to-peer payment systems (e.g. payme.com)
- accumulating balance
- accounts that accumulate expenditures and to which consumers make periodic payments
- e.g., utility, phone, standing accounts of trusted businesses
- often either with a large deposit, or prepaid

Payment Systems
B2C payment systems
- credit cards
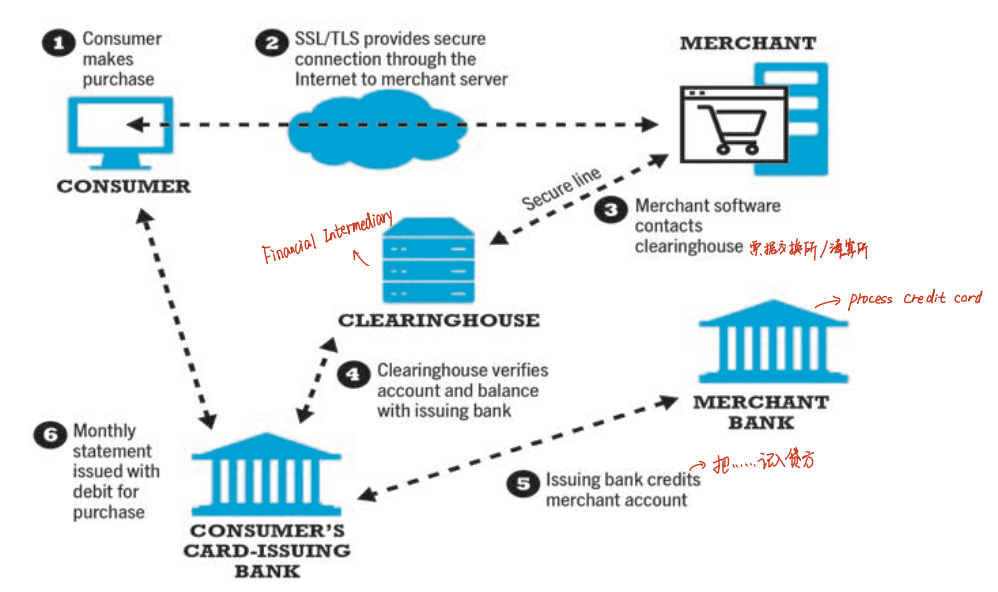
- financial cybermediaries
- on internet-based company that makes it easy for one person to pay another person or organization over the internet
- e.g., Alipay, PayPal, WeChat Pay, Octopus, Obopay
- electronic checks
- electronic bill presentment and payment
- smart cards
- mobile payment
E-commerce payment systems
- credit cards
- limitations of online credit card payment
- security, merchant risk
- cost
- social equity
- limitations of online credit card payment
- debit cards
- digital wallets
- emulates functionality of wallet by authenticating consumer, storing and transferring value, and securing payment process from consumer to merchant
- early efforts to popularize failed
- digital cash
- value storage and exchange using tokens
- most early examples have disappeared
- protocols and practices too complex
- digital checking
- extends functionality of existing checking accounts for use online
- online stored value systems
- based on value stored in a consumer’s bank, checking, or credit card account
- PayPal, Alipay, WeChat Pay
- smart cards
- plastic card (the size of a credit card) that contains an embedded chip on which digital information can be stored and updated
- debit cards are an implementation
- contact -> use card reader
- contactless
- e.g., EZPass, Octopus card (Hong Kong)
- Radio Frequency ID (RFID)
- Near Field Communications (NFC)
- plastic card (the size of a credit card) that contains an embedded chip on which digital information can be stored and updated
B2B payment systems
- for business customers
- make large purchases
- will not pay with credit card or financial cybermediary
- use financial Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) (but on its way out)
- pay for many purchases at once (perhaps the end of the month)
- likely that cloud-based payment gateway (or other Internet-based technology) will eventually take over completely
- Faster Payment System (FPS) (if local in Hong Kong)
The future
- they are attempts to export existing payment systems that work in traditional commerce to e-commerce
- sometimes problems with existing payment systems are magnified when moved to the online world (e.g. credit card theft)
- what is needed is a payment/financial system designed for the online world
- these are defined as cybercurrencies or digital currency