6 minutes
ECOM6013 E-Commerce Presence
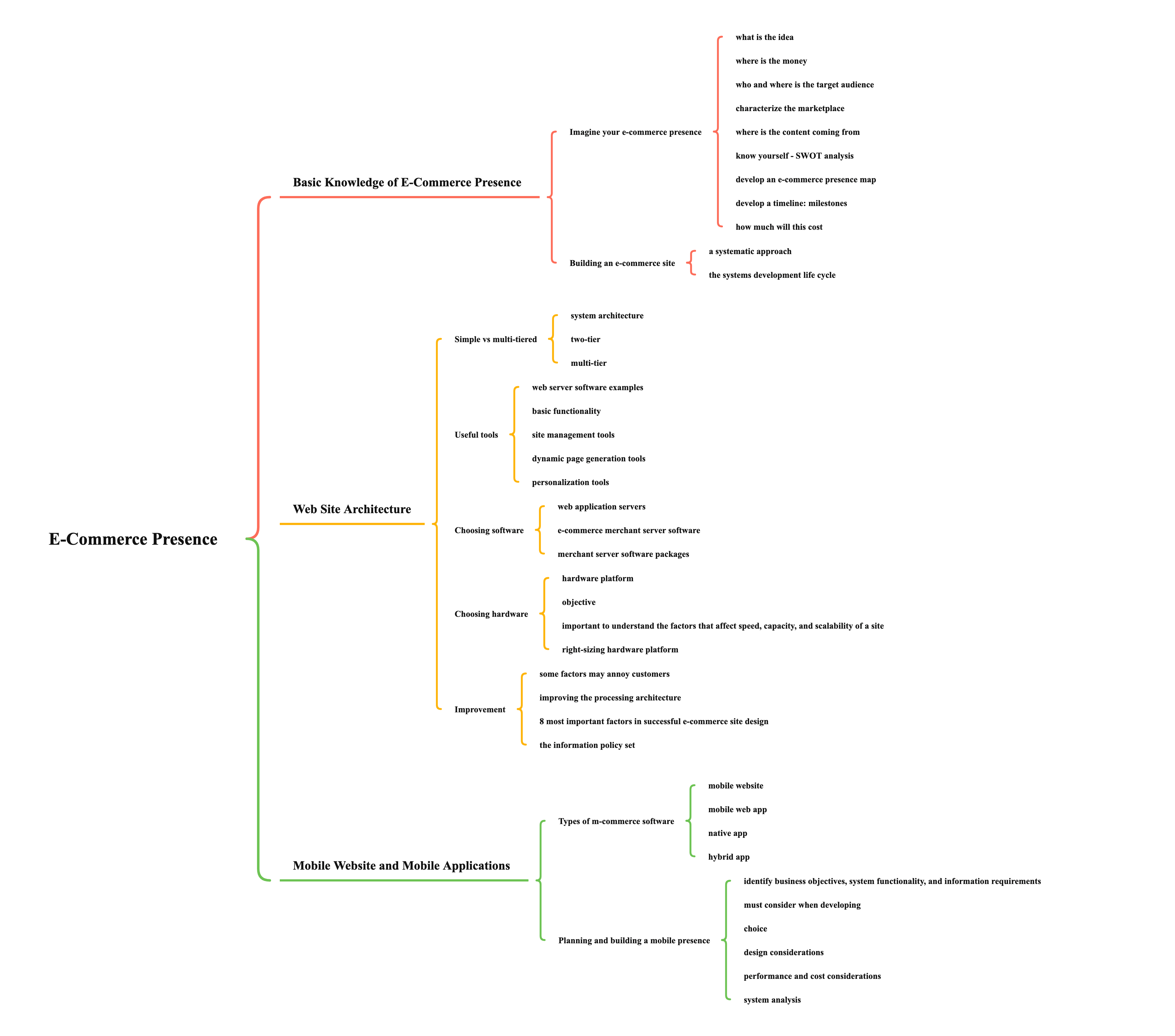
Basic Knowledge of E-Commerce Presence
Imagine your e-commerce presence
- what is the idea
- your mission
- target audience
- intended market space
- strategic analysis
- marketing matrix
- development timeline
- preliminary budget
- where is the money
- business model
- revenue model
- who and where is the target audience
- demographics
- lifestyle
- consumption patterns
- characterize the marketplace
- size
- growth
- demographics
- structure
- where is the content coming from
- know yourself - SWOT analysis

- develop an e-commerce presence map
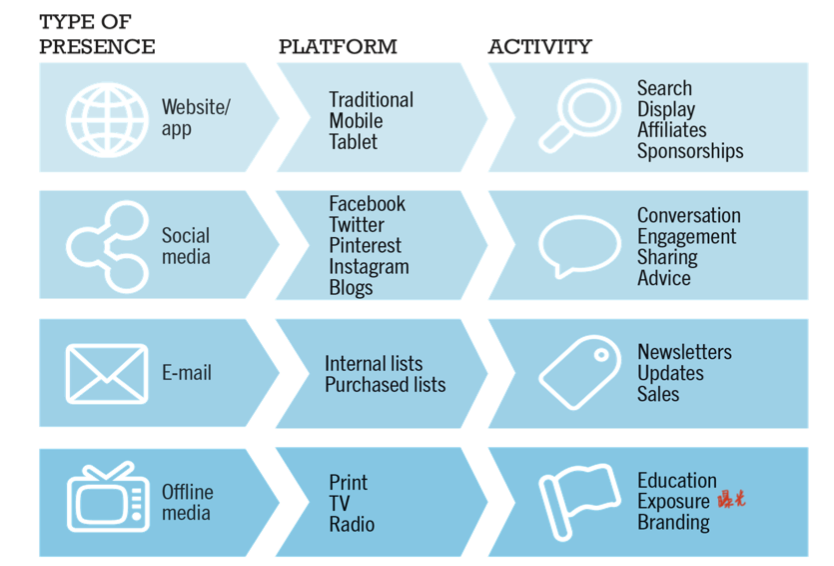
- develop a timeline: milestones
- how much will this cost
- e.g. US estimate, different in other countries
- small website: up to US$5000
- small setup: US$25,000 to US$50,000
- large corporate website: US$100,000+ to millions
Building an e-commerce site
- a systematic approach
- most important management challenges
- developing a clear understanding of business objectives
- knowing how to choose the right technology to achieve those objectives
- main factors to consider
- management
- hardware architecture
- software
- design
- telecommunications
- human resources
- most important management challenges
- the systems development life cycle
- methodology for understanding business objectives of a system and designing an appropriate solution
- five major steps
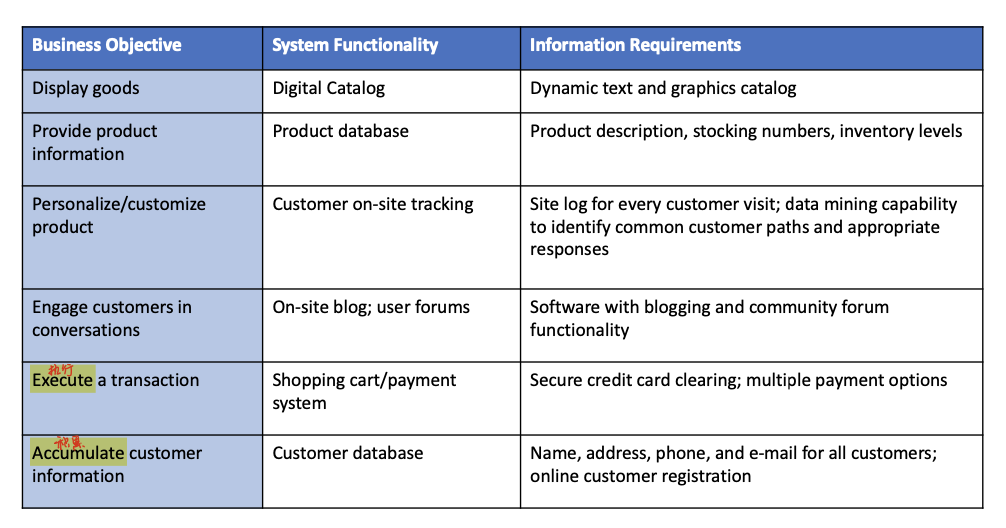
- system analysis/planning
- business objectives
- list of capabilities you want your site to have
- system functionalities
- list of information system capabilities needed to achieve business objectives
- information requirements
- information elements that system must produce in order to achieve business objectives
- example
- consideration for quality
- navigation
- accessibility, e.g. payment
- scalability
- reliability
- maintainability
- usability
- compatibility and interoperability
- security
- readability
- business objectives
- system design
- definition
- description of main components of a system and their relationship to one another
- 2 components
- logical design
- data flow diagrams, processing functions, databases
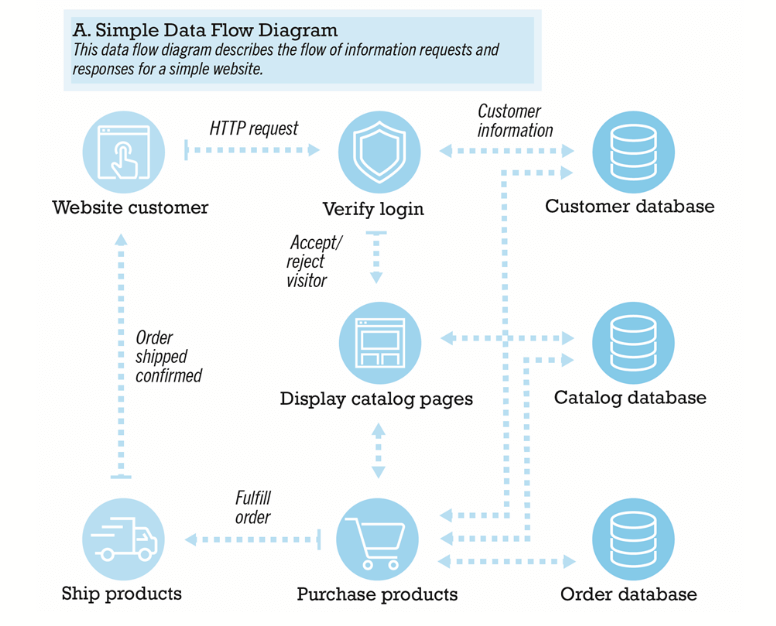
- data flow diagrams, processing functions, databases
- physical design
- specifies actual physical, software components, models, etc.
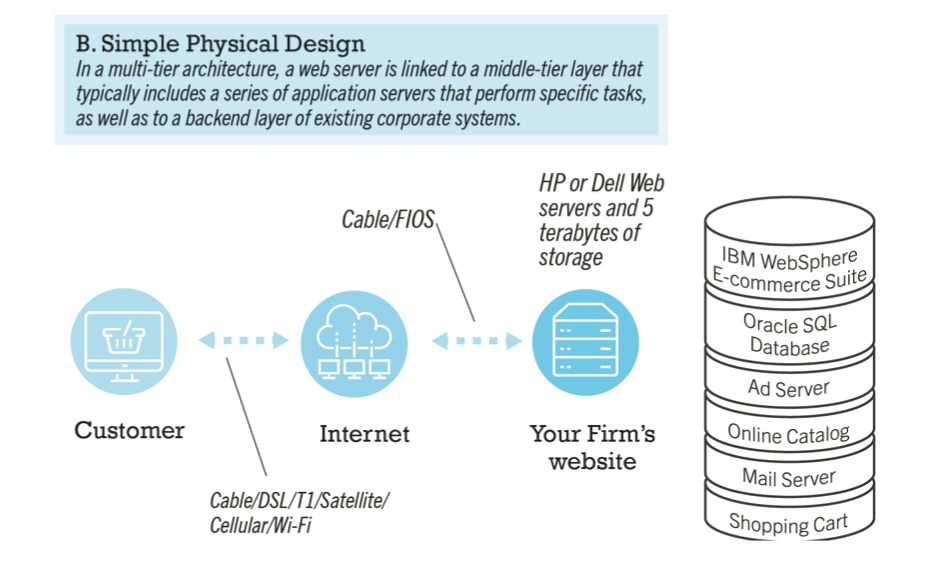
- specifies actual physical, software components, models, etc.
- logical design
- definition
- building the system
- building
- build own
- outsourcing
- requires team with diverse skill set
- choice of software tools
- both risks and possible benefits
- hosting
- host own
- outsourcing
- hosting company responsible for ensuring site is accessible 24/7, for monthly fee
- firm purchases or leases web server (with control over its operation), but server is located at vendor’s facility (co-location)
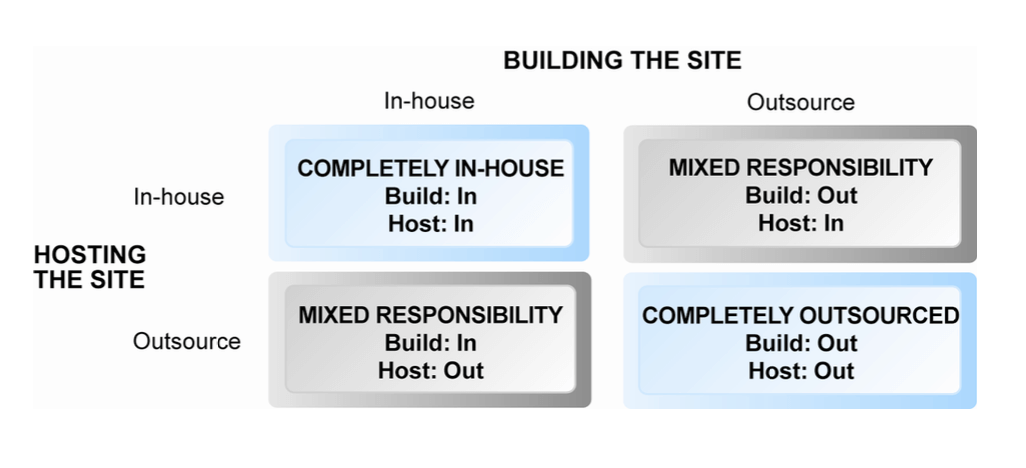
- building
- testing
- unit testing
- system testing
- acceptance testing
- A/B testing (split testing)
- multivariate testing
- implementation -> the first step, a circle
- maintenance
- systems break down unpredictably
- maintenance is ongoing
- maintenance costs are similar to development costs
- benchmarking
- optimization
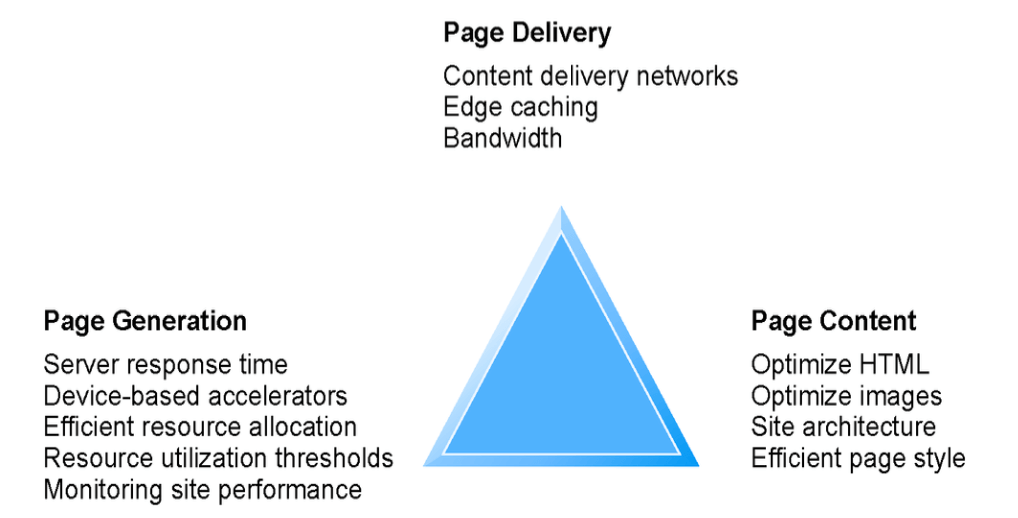
- maintenance
- system analysis/planning
- best practices
- continuous availability 99%
- design for scalability
- build in management for end-to-end delivery
- plan for growth
- design system for high-speed performance
- understand and optimize workload on system
Web Site Architecture
Simple vs multi-tiered
- system architecture
- arrangement of software, machinery, and tasks in an information system needed to achieve a specific functionality
- two-tier
- web server and database server
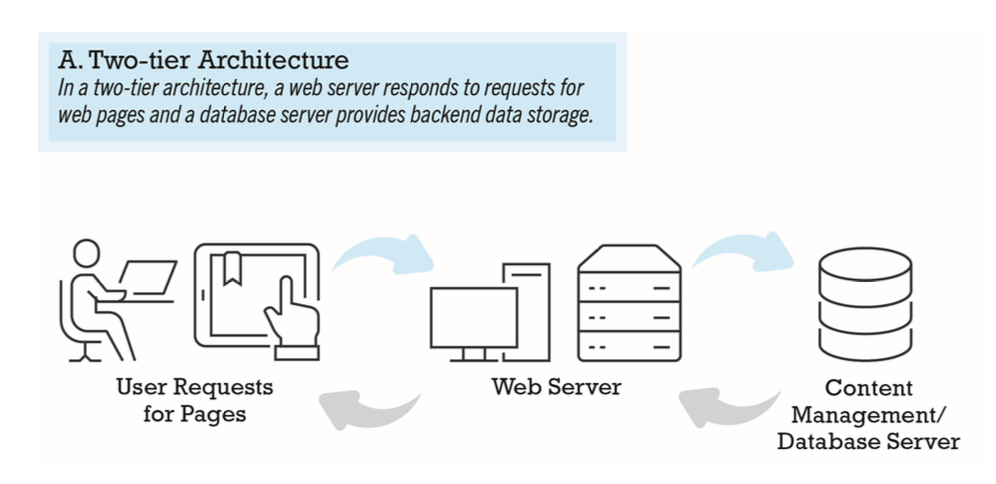
- web server and database server
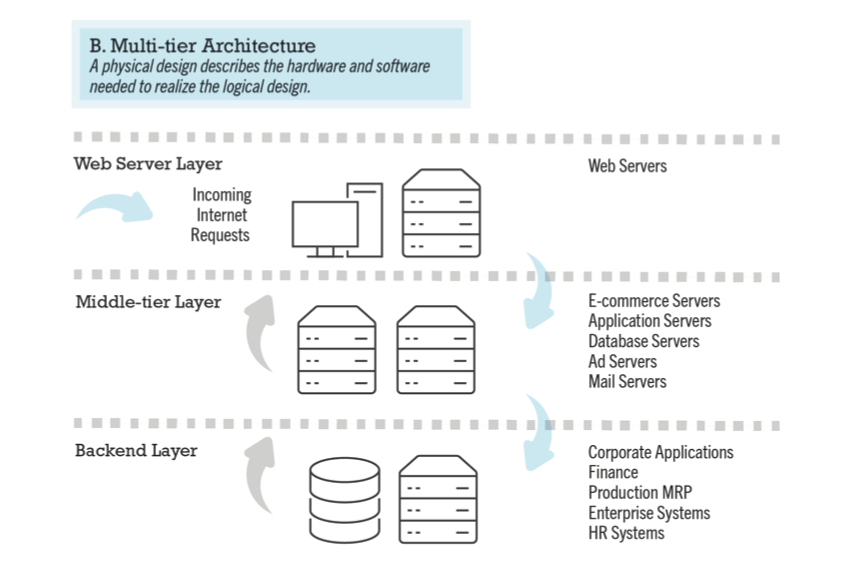
- multi-tier
- web application servers
- backend, legacy databases
Useful tools
- web server software examples
- Apache
- leading web server software
- works with UNIX, Linux operating systems
- reliable, stable, part of open software community
- Microsoft’s Internet Information Server (IIS)
- second major web server software
- windows-based
- integrated, easy-to-use
- Apache
- basic functionality
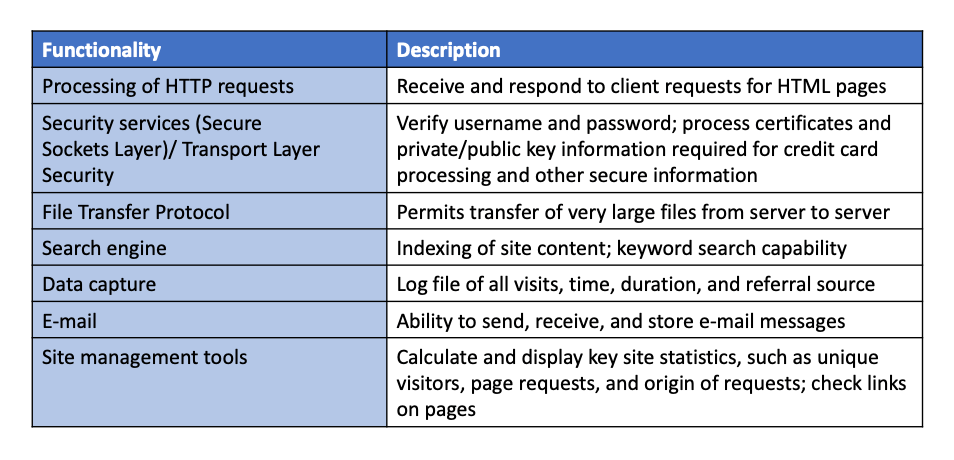
- site management tools
- basic tools included in all web servers
- verfify that links on pages are still valid
- identify orphan files (no links to the page)
- third-party software for advanced management
- monitor customer purchases
- marketing campaign effectiveness
- keep track of hit counts and other statistics
- e.g. Webtrends Analytics 10
- basic tools included in all web servers
- dynamic page generation tools
- dynamic page generation
- contents stored in database and fetched when needed
- common tools
- CGI, ASP, JSP, ODBC, JDBC
- advantages
- lower menu costs
- permits easy online market segmentation
- enables cost-fee price discrimination
- enables content management system (CMS)
- dynamic page generation
- personalization tools
- personalization
- ability to treat people based on personal preferences and prior history with site
- customization
- ability to change the product to better fit the needs of the customer
- cookies
- primary method to achieve personalization
- personalization
Choosing software
- web application servers
- provide specific business functionality required for a website
- type of middleware
- isolate business applications from web servers and databases
- single-function applications being replaced by integrated software tools that combine all functionality needed for e-commerce site
- e-commerce merchant server software
- provides basic functionality for sales
- online catalog
- list of products available on website
- shopping cart
- allows shoppers to set aside, review, edit selections, and then make purchase
- credit card processing
- typically works in conjunction with shopping cart
- verifies card and puts through credit to company’s account at checkout
- online catalog
- provides basic functionality for sales
- merchant server software packages
- also called e-commerce software platform
- integrated environment that includes most of functionality needed
- shopping card
- merchandise display
- order management
- different options for different-sized businesses
- small and medium-sized businesses
- Yahoo Small Business
- open-source solutions
- mid-range
- IBM Web Sphere Commerce Express
- Sitecore Experience Commerce
- high-end
- IBM Web Sphere Professional/Enterprise
- SAP Hybris
- Oracle ATG Web Commerce
- many now also available as cloud-based SaaS solutions
- key factors in selecting a package
- functionality
- support for different business models, including m-commerce
- business process modeling tools
- visual site management and reporting
- performance and scalability
- connectivity to existing business systems
- compliance with standards
- global and multicultural capability
- local sales tax and shipping rules
- small and medium-sized businesses
Choosing hardware
- hardware platform
- underlying computing equipment needed for e-commerce functionality
- objective
- enough platform capacity to meet peak demand without wasting money
- important to understand the factors that affect speed, capacity, and scalability of a site
- right-sizing hardware platform
- the demand side
- customer demand
- most important factor affecting speed of site
- factors in overall demand
- number of simultaneous users in peak periods
- nature of customer requests (user profile)
- type of content (dynamic versus static web pages)
- required security
- number of items in inventory
- number of page requests
- speed of legacy applications
- customer demand
- the supply side
- scalability
- ability of site to increase in size as demand warrants
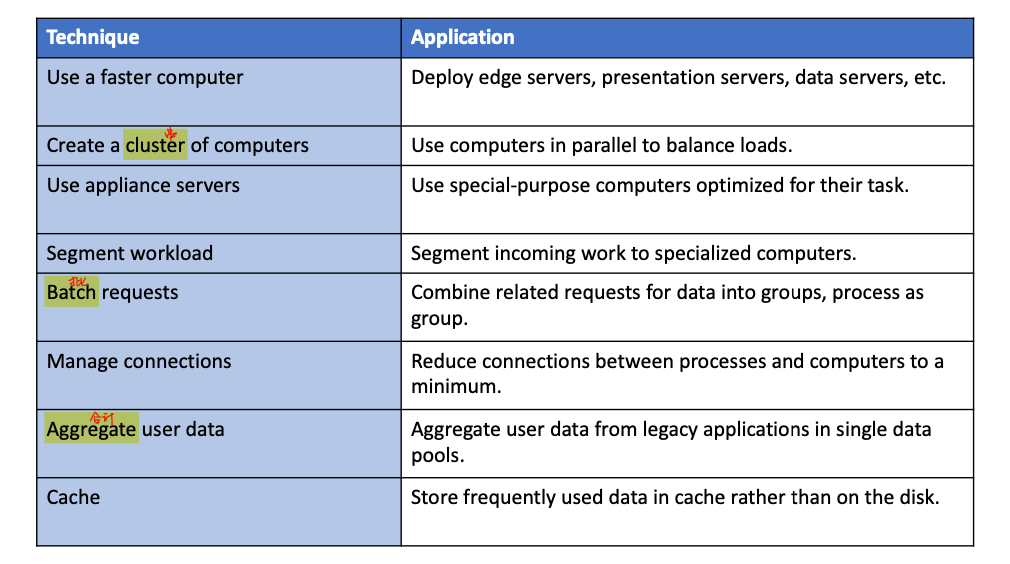
- ways to scale hardware
- vertically
- increase processing power of individual components
- horizontally
- employ multiple computers to share workload
- improve processing architecture
- outsource hosting, use content delivery network
- vertically
- scalability
- the demand side
Improvement
- some factors may annoy customers
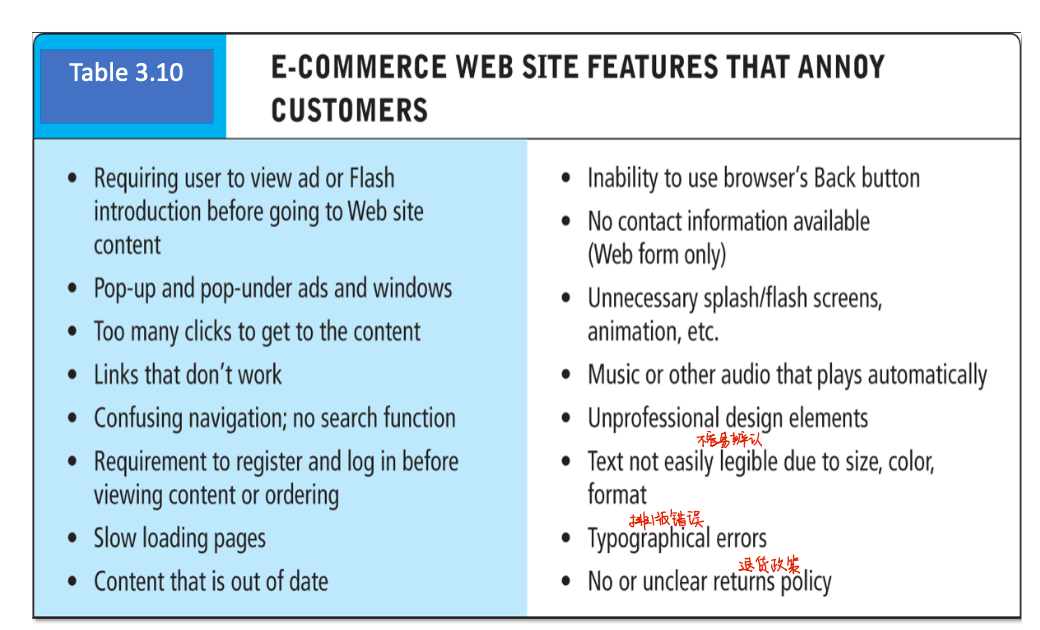
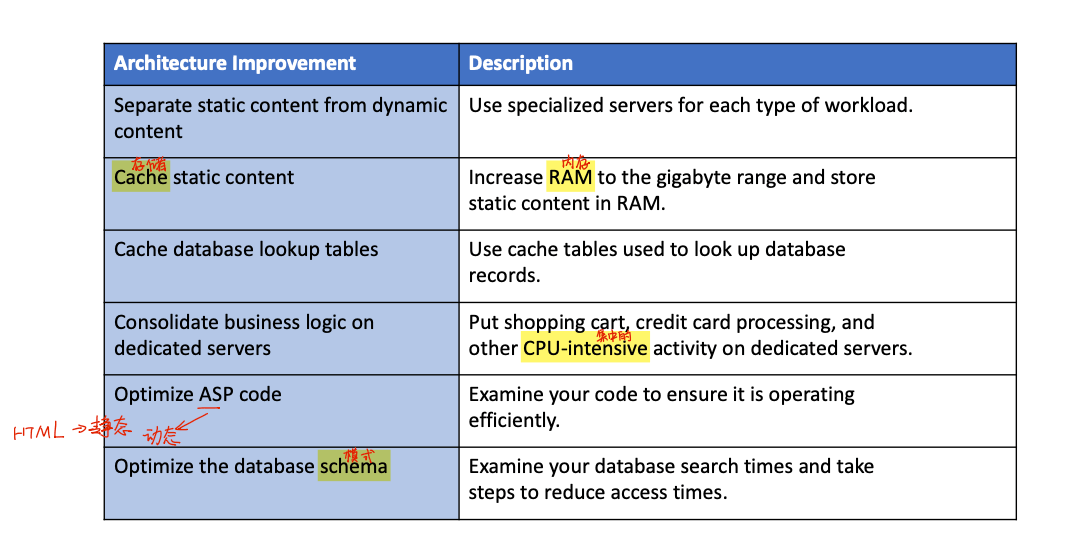
- improving the processing architecture
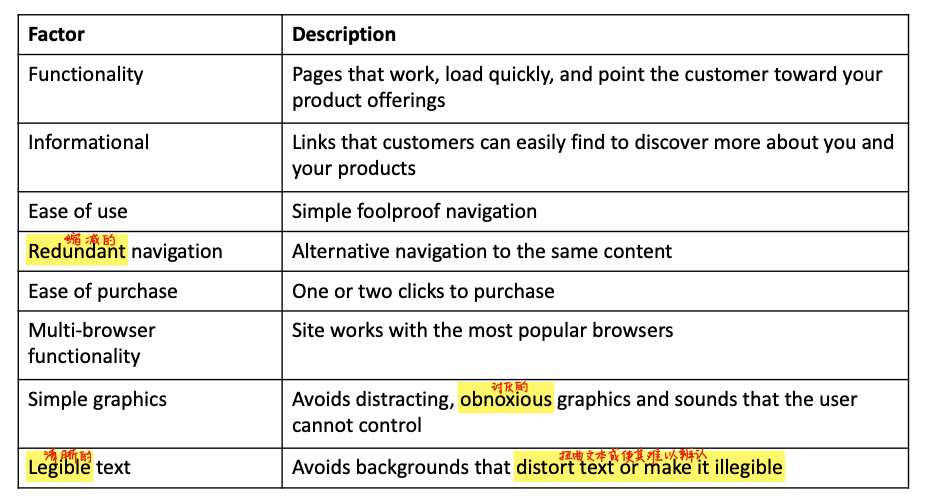
- 8 most important factors in successful e-commerce site design
- the information policy set
- privacy policy
- set of public statements declaring how site will treat customers’ personal information that is gathered by site
- accessibility rules
- set of design objectives that ensure users with disabilities can effectively access site
- privacy policy
Mobile Website and Mobile Applications
Types of m-commerce software
- mobile website
- responsive web design
- mobile web app
- can be used in browsers on mobile phone
- the speed is faster than mobile website, but slower than native apps
- rely on OS, screen size, finger navigation, etc.
- can use camera and other components of mobile phone
- native app
- hybrid app
- runs inside native container
- app distribution
- based on HTML5, CSS, JavaScript
Planning and building a mobile persence
- identify business objectives, system functionality, and information requirements
- must consider when developing

- choice
- mobile website or mobile web app
- less expensive
- native app
- can use device hardware, available offline
- mobile website or mobile web app
- design considerations
- platform constraints
- graphics, file sizes
- mobile first design
- desktop website design after mobile design
- responsive web design (RWD)
- CSS site adjusts layout of site according to device screen resolutions
- adaptive web design (AWD)
- server delivers different templates or versions of site optimized for device
- platform constraints
- performance and cost considerations
- mobile first design
- most efficient
- mobile website
- resizing existing website for mobile access is least expensive
- mobile web app
- can utilize browser API
- native app
- most expensive
- requires more programming
- progressive web app (PWA)
- latest and likey to become most popular (more later)
- mobile first design
- system analysis
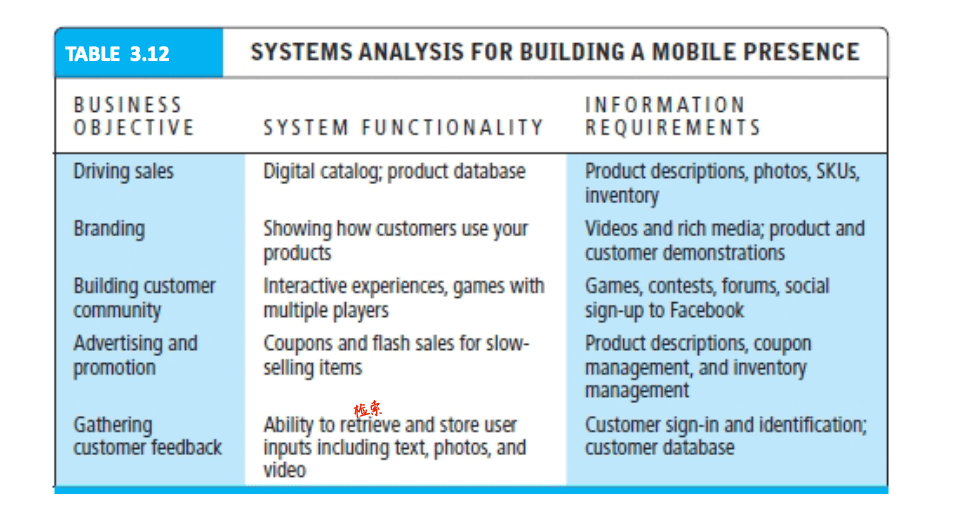
ecom6013 e-commerce technologies e-commerce presence website design website testing website maintenance
1167 Words
2020-12-10 09:54