7 minutes
ECOM6013 Internet and E-Commerce Infrastructure
The Internet: Technology Background
Internet and world wide web
- internet
- interconnected network of thousands of networks and hundreds of millions of computers
- links businesses, educational institutions, government agencies, and individuals
- world wide web (web)
- one of the internet’s most popular services
- provides access to billions, possibly trillions, of web pages
The evolution of the internet
- innovation phase (1961 - 1974)
- creation of fundamental building blocks
- institutionalization phase (1975 - 1995)
- large institutions provide funding and legitimization
- commercialization phase (1995 - present)
- private corporations take over, expand internet backbone and local service
Key technology concepts
- internet defined as network that
- uses IP addressing
- supports TCP/IP
- provides services to users, in manner similar to telephone system
- packet switching
- slices digital messages into packets
- sends packets along different communication paths as they become available
- reassembles packets once they arrive at destination
- use routers
- special purpose computers that interconnect the computer networks that make up the internet and route packets
- routing algorithms ensure packets take the best available path toward their destination
- less expensive, wasteful than circuit-switching
- TCP/IP communication protocol
- transmission control protocol (TCP)
- establishes connections among sending and receiving web computers
- handles assembly of packets at point of transmission, and reassembly at receiving end
- internet protocol (IP)
- provides the internet’s addressing scheme
- 4 TCP/IP layers
- network interface layer
- e.g. ethernet, token ring, frame relay, ATM, bluetooth, WiFi
- internet layer
- e.g. IP
- transport layer
- e.g. TCP, UDP
- application layer
- e.g. HTTP, Telnet, FTP, SMTP, BGP
- network interface layer
- OSI, a reference model, has 7 layers
- internet addresses (IP)
- IPv4
- 32-bit number
- four sets of numbers marked off by periods
- class C address: network identified by first 3 sets, computer identified by last set
- IPv6
- 128-bit addresses
- able to handle up to 1 quadrillion addresses (IPv4 can handle only 4 billion)
- IPv4
- domain names
- IP address expressed in natural language
- domain name system (DNS)
- allow numeric IP addresses to be expressed in natural language
- uniform resource locator (URL)
- address used by web browser to identify location of content on the web
- dynamic host configuration protocol (DHCP)
- port number
- for client: 68
- for server: 67
- usually, we do not have a fixed IP address
- port number
- transmission control protocol (TCP)
- other internet protocols and utility programs
- internet protocols
- HTTP
- email: SMTP, POP3, IMAP
- FTP, Telnet, SSL/TLS
- utility programs
- ping
- tracert
- internet protocols
- client/server computing
- powerful personal computers (clients) connected in network with one or more servers
- servers perform common functions for the clients
- storing files
- software applications
- access to printers, etc.
- cloud computing model
- firms and individuals obtain computing power and software over internet
- services
- infrastructure as a service (IaaS)
- software as a service (SaaS)
- platform as a service (PaaS)
- public, private, and hybrid clouds
- radically reduces costs of
- building and operating web sites
- infrastructure, IT support
- hardware, software
- drawbacks
- security risks
- shifts responsibility for storage and control to providers
The mobile platform
- primary internet access is now through
- tablets supplement PCs for mobile situations
- smartphones are a disruptive technology
- new processors and operating systems
- mobile apps
- use of mobile apps has exploded
- most popular entertainment media, over TV
- always present shopping tool
- almost all top 100 brands have an app
- platforms
- iOS
- Android
- app marketplaces
- Google Play
- Apple’s App Store
- Amazon’s Appstore
- use of mobile apps has exploded
Internet Infrastructure
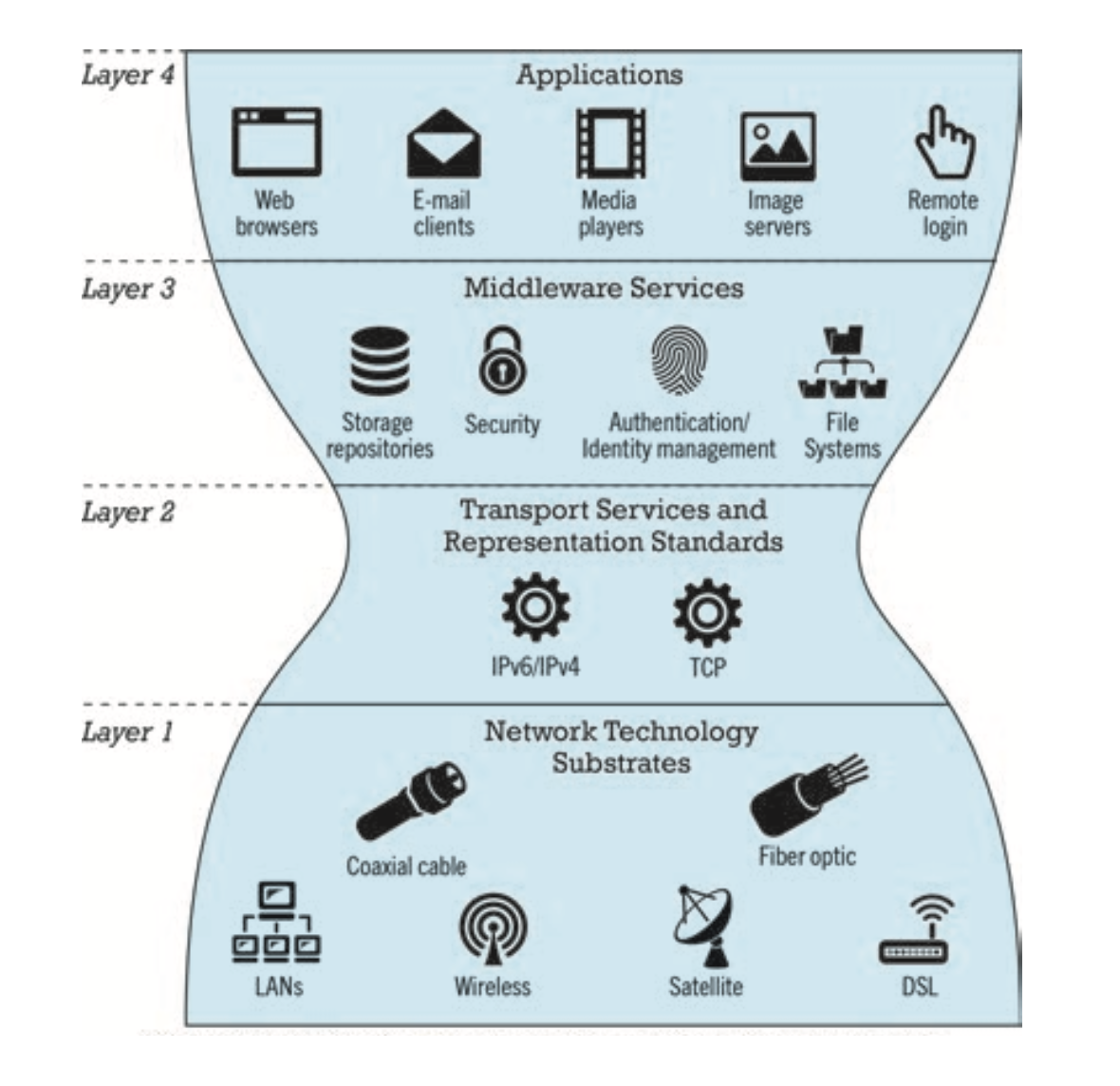
The reason of internet growth has boomed without disruption
- client/server computing model
- hourglass, layer architecture
- network technology substrate
- transport services and representation standards
- middleware services
- applications
Architecture
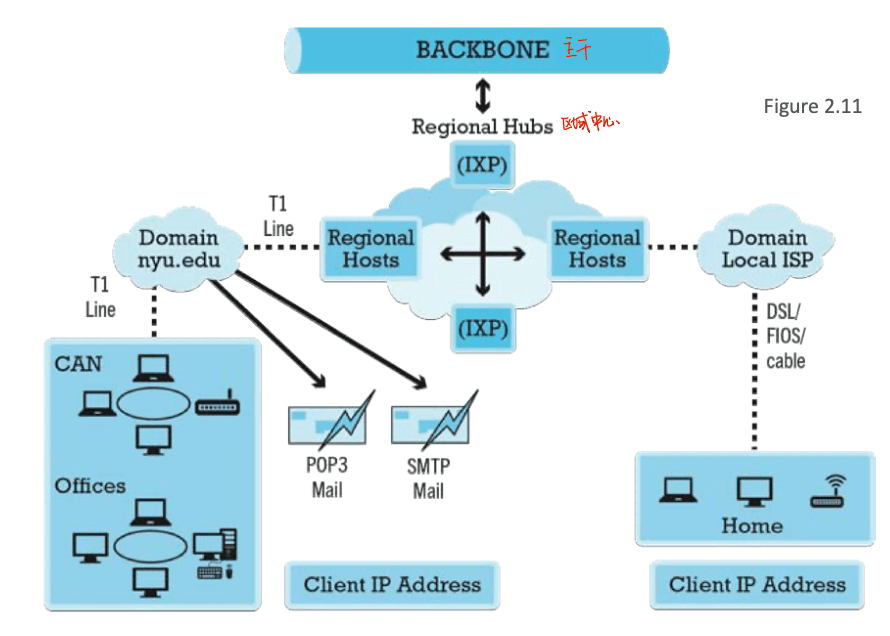
- internet network architecture
- internet backbone
- comprised of fiber-optic cable: hundreds of glass strands that use light to transmit data
- faster speed and greater bandwidth
- thinner, lighter cables
- less interference
- better data security
- tier 1 internet service provider or transit ISPs
- numerous private networks physically connected to each other
- undersea fiber optics, satellite links
- comprised of fiber-optic cable: hundreds of glass strands that use light to transmit data
- internet backbone
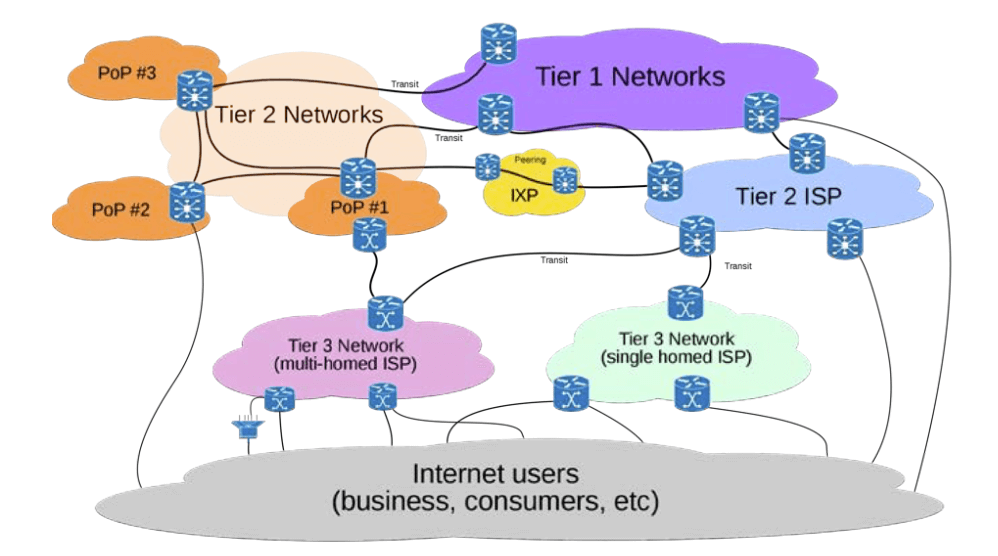
- 3 tiers internet
- internet exchange points (IXPs)
- regional hubs where tier 1 ISPs physically connect with one another and with regional tier 2 ISPs
- tier 2 ISPs provide tier 3 ISPs with internet access
- originally called network access points (NAPs) or metropolitan area exchanges (MAEs)
- e.g. HKIX
- tier 3 ISPs
- retail providers
- lease internet access to home owners, small businesses
- large providers
- Comcast, AT&T, Verizon in US
- PCCW, Hutchison Telecom, HK Broadband in HK
- smaller local providers in most countries
- services
- narrowband
- broadband
- digital subscriber line (DSL)
- cable internet
- satellite internet
- retail providers
- internet exchange points (IXPs)
Area Networks and Internet Access
Campus/corporate area networks
- local area networks operating within single organization
- e.g. HKU, Microsoft Corporation
- lease internet access directly from regional and national carriers
Internet access
- mobile internet access
- two basic types of wireless internet access
- telephone-based
- e.g. mobile phones, smartphones
- computer network-based
- e.g. wireless local area network (WLAN) - based internet access
- WiFi (various IEEE 802.11 standards)
- high-speed, fixed broadband wireless LAN (WLAN)
- wireless access point (hot spots)
- limited range but inexpensive
- Zigbee (for IoT), Bluetooth, BLE
- LoRaWan -> low power WAN
- WiFi (various IEEE 802.11 standards)
- e.g. wireless local area network (WLAN) - based internet access
- telephone-based
- two basic types of wireless internet access
- telephone-based wireless internet access
- currently based on 3G and 4G technologies
- 5G will provide higher bandwidth with speeds reaching 10 Gbps or more, with much lower latency
- intranets
- TCP/IP network located within a single organization for communications and processing
- used by private and government organizations for internal networks
- all internet applications can be used in private intranets
- the internet of things (IoT)
- objects connected via sensors/RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) to the internet
- smart things
- interoperability issues and standards
- security and privacy concerns
- limitations and the current internet
- bandwidth limitations
- slow peak-hour service
- quality of service limitations
- latency
- network architecture limitations
- identical requests are processed individually
- wired internet
- copper and expensive fiber-optic cables
- bandwidth limitations
- governance
- Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN)
- Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF)
- Internet Research Task Force (IRTF)
- Internet Engineering Steering Group (IESG)
- Internet Architecture Board (IAB)
- Internet Society (ISOC)
- Internet Governance Forum (IGF)
- World Wide Web Consortium (W3C)
- Internet Network Operators Groups (NOGs)
The Web
Hypertext
- text formatted with embedded links
- links connect documents to one another, and to other objects such as sound, video, or animation files
- uses Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) and URLs to locate resources on the web
Markup languages
- Hypertext Markup Language (HTML)
- fixed set of pre-defined markup “tags” used to format text
- controls look and feel of web pages
- used in conjunction with Cascading Style Sheets (CSS)
- HTML5, the new version
- eXtensible Markup Language (XML)
- designed to describe data and information
- tags used are defined by user
Web servers and web clients
- web server software
- enables a computer to deliver web pages to clients on a network that request this service by sending an HTTP request
- basic capabilities
- security services
- FTP
- search engine
- data capture
- web server
- may refer to either web server software or physical server
- specialized servers
- database servers
- ad servers
- web client
- any computing device attached to the internet that is capable of making HTTP requests and displaying HTML pages
The internet and web
- features on which the foundations of e-commerce are built
- communication tools
- messaging applications, e.g. instant messaging
- online message boards
- internet telephony, e.g. Voice Over Internet Protocol (VOIP)
- video conferencing, video chatting, telepresence
- search engines
- identify web pages that match queries based on one or more techniques
- keyword indexes
- page ranking
- also serve as
- shopping tools
- advertising vehicles (search engine marketing)
- tool within e-commerce sites
- procedure of Google
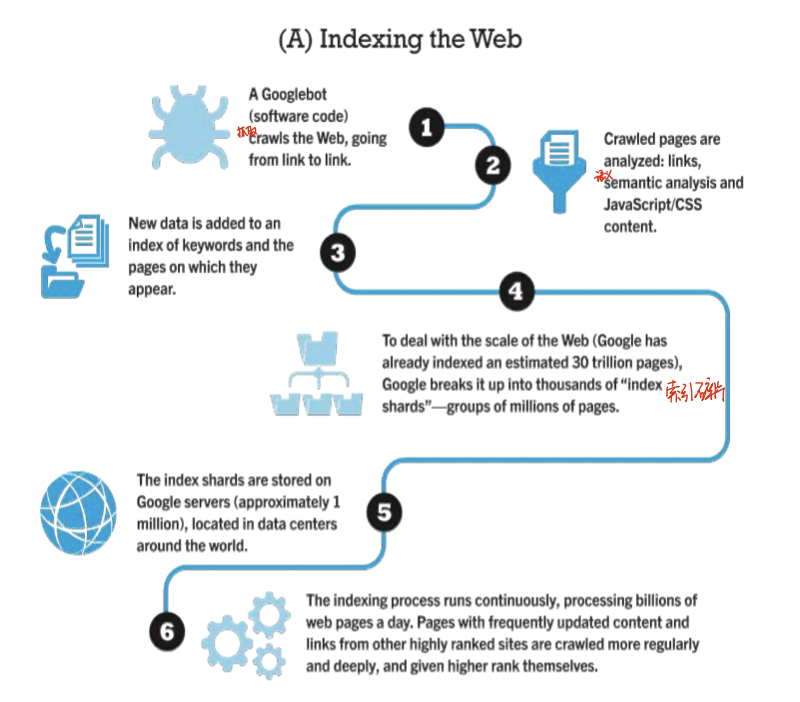
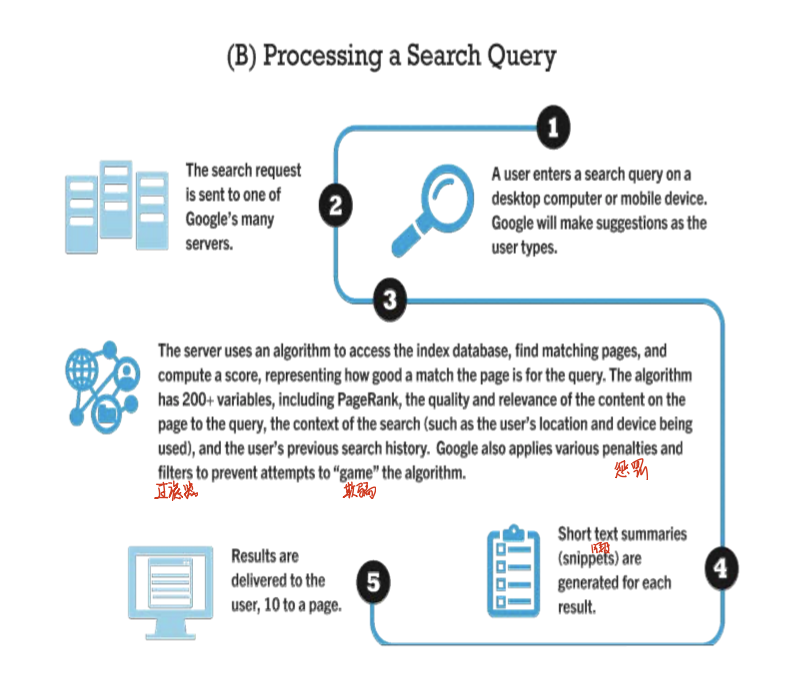
- identify web pages that match queries based on one or more techniques
- downloadable and streaming media
- downloads
- growth in broadband connections enables large media file downloads
- streaming technologies
- enables music, video, and other large files to be sent to users in chunks so that the file can play uninterrupted
- podcasting
- explosion in online video viewing
- downloads
- web 2.0 applications and services
- base on demand of users
- online social networks
- services that support communication among networks of friends, peers
- blogs
- personal web page of chronological entries
- enable web page publishing with no knowledge of HTML
- wikis
- enables doucuments to be written collectively and collaboratively
- virtual reality and augmented reality
- VR
- immersing users within virtual world
- typically uses head-mounted display (HMD)
- e.g. Oculus Rift, Vive, PlayStation VR
- AR
- overplaying virtual objects over the real world, via mobile devices or HMDs
- e.g. Pokémon GO
- VR
- intelligent digital assistants
- computer search engine using
- natural language
- conversational interface, verbal commands
- situational awareness
- can handle requests for appointments, flights, routes, event scheduling, and more
- e.g. Apple’s Siri, Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant
- computer search engine using
- communication tools
Additional Reading
ecom6013 e-commerce technologies internet infrastructure e-commerce infrastructure
1349 Words
2020-12-09 17:16