4 minutes
ECOM6013 Mobile Technology and M-Commerce

Mobile Technology
Basic principle
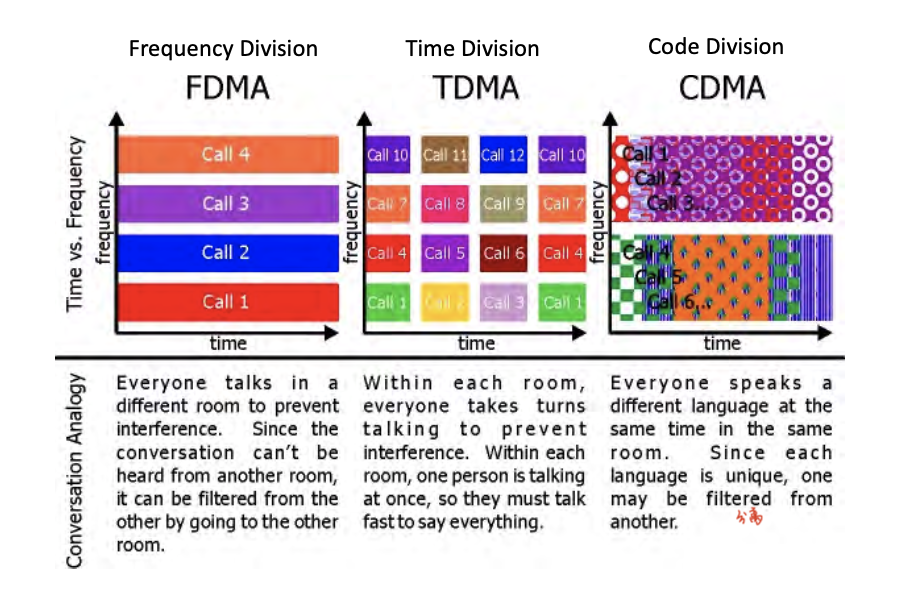
- 3 division methods
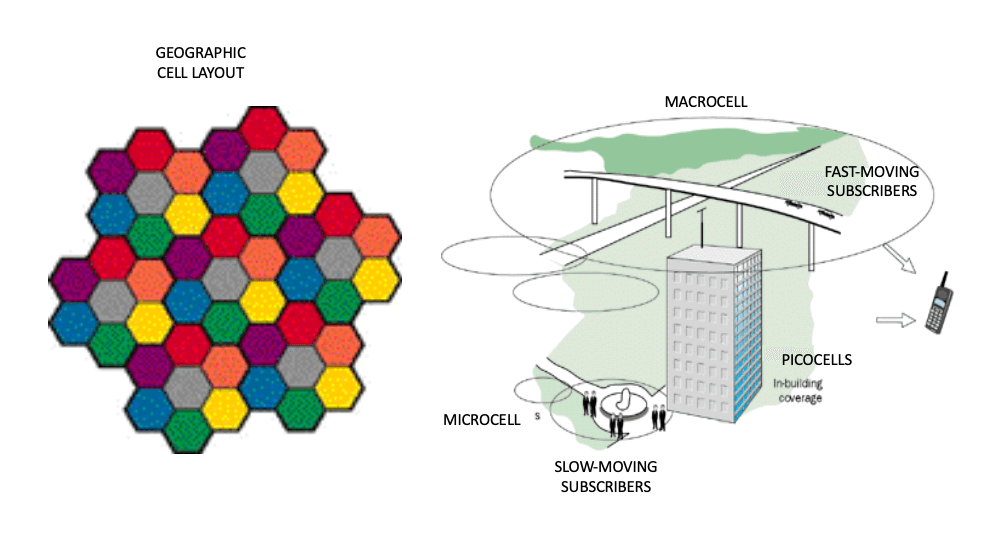
- fundamental mobility: cellphones
- cell handover
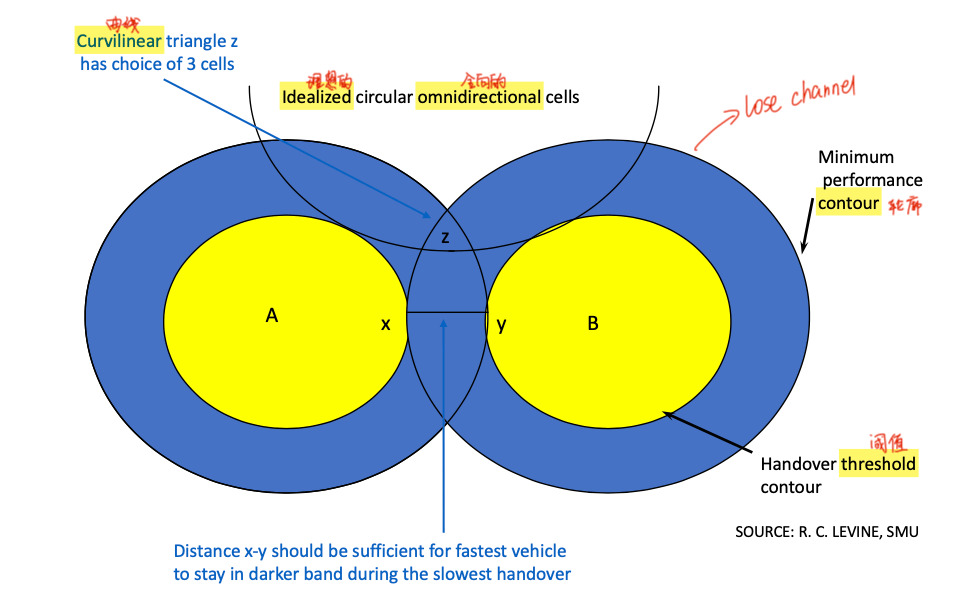
- cell handover
Future and issues
- 5G - the future

- issues with mobile access to e-commerce web sites
- efficiency of mobile device web clients
- broad new range of contextual/accessibility issues, e.g. fingerprint, wearable devices
- screen size – all over the place, unpredictable
- interactivity
- client-side processing requirements
- bandwidth issues
M-Commerce
Overview
- definition
- the buying and selling of goods and services via mobile devices
- mobile devices include (but are not limited to)
- mobile phone/smart phone
- tablet computer
- wearable technology
- mobile devices include (but are not limited to)
- the process of paying for goods and services via mobile devices
- use of any technologies to support the above
- use of mobile devices to
- transact
- communicate
- entertain
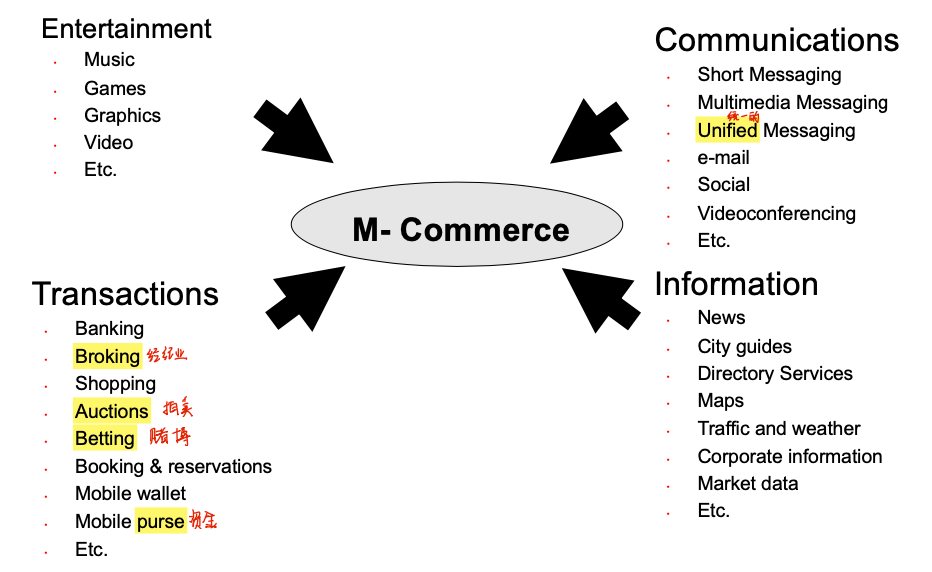
- the buying and selling of goods and services via mobile devices
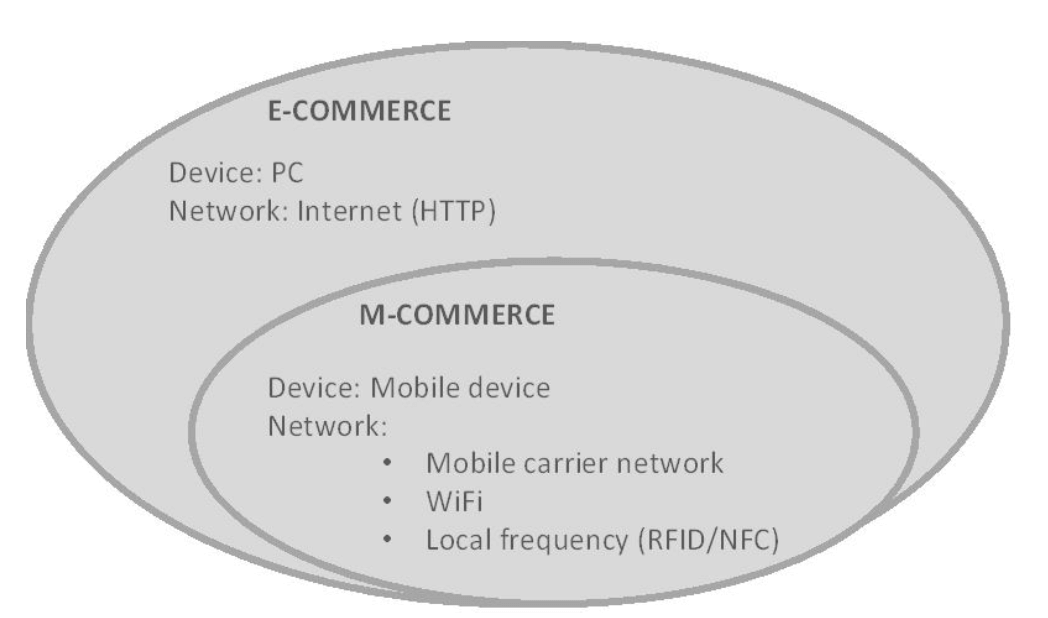
- m-commerce vs e-commerce
- ubiquity
- convenience
- interactivity
- personalization
- localization
- different roles in m-commerce
- user –> individual authorized to use their mobile device
- end user or system user –> the benefit or end result is received by a subscriber
- suppliers –> the benefit or end result is received by an organization that uses m-commerce for increasing productivity and efficiency of its goals
- network operator –> offer the transport facility and network infrastructure
- service providers –> develop new services for and utilize the network infrastructure provided by the network operators
- content providers –> aggregate mobile device content from various sources
- commerce mediators –> provide solutions and services such as payments, security, etc
- finance organizations –> provide framework and infrastructure for payment
- mobile device –> capable of interacting with all other players/roles
- user –> individual authorized to use their mobile device
- services and applications
- mobile ticketing
- mobile money transfer
- content purchase and delivery
- information services
- mobile banking
- mobile browsing
- mobile purchase
- mobile marketing and advertising
Realization
- m-commerce is a special case of IoT-based commerce
- e-commerce via mobile web clients and apps is pretty well understood
- PTDs (Personal Trusted Devices) are full of various sensors that are mediated by the device hardware and can work together
- location and orientation
- multiple types of networking (e.g., NFC, Bluetooth)
- accelerometers
- camera
- common options for mobile website development
- responsive design –> same content as “standard” site + different mobile styling
- automates the inclusion of contextually relevant content based on profiles
- “fluid design” –> layout changes, image resolution changes, interaction changes according to specific device
- advantages
- optimized performance for supported devices
- unpredictable performance for undefined devices –> where use of emulators might come in handy
- disadvantages
- technically complex to implement, maintain, and test new skills required
- higher cost, larger codebase
- example
- all content is stored (in one place) in display-independent XML
- easy to maintain content
- stylesheets are defined for possible display-dependent formats (e.g. extensible stylesheet language transformations – a standard)
- display-dependent content is used to satisfy web request on server-side

- adaptive design –> potentially different content + different styling on different mobile devices
- note: the above are not mutually exclusive
- responsive design –> same content as “standard” site + different mobile styling
- QR codes
- quick response code
- originally designed as a two-dimensional barcode
- not originally intended for mobile use, initailly for camera
- patented, but free license
Other technologies and issues
- GPS/BDS
- widely available on most devices (+)
- great for “geo-location” and “geo-fencing” (+)
- location tracking (-)
- does not work inside buildings (-)
- high battery consumption (-)
- NFC/RFID
- great accuracy for use with payments and product information (+)
- very low cost of RFID sensors/stickers (+)
- not supported on all devices (-)
- 20 cm (7.9 inches) range (-)
- high battery consumption (-)
- obstacles to ambient awareness
- mobile device power
- GPS/BDS and network calls are power hungry
- users feel need to ration battery power
- privacy
- users worry about continuous tracking
- does tracking really provide cost benefit
- network
- bandwidth
- congestion
- processing speed
- but these issues would be addressed by 5G easily
- mobile device power
- mobile web vs mobile apps

- better solution - Progressive Web Apps (PWA) by Google
- make web app have higher capability and higher reach
- features
- reliable
- fast loading, work offline and on flaky networks
- fast
- smooth animation, jank-free scrolling and seamless navigation
- engaging
- launched from the home screen and send push notifications
- reliable
- procedure
