3 minutes
ECOM7121 Mobile Smart Cities, IoT, Big Data Systems
Smart Cities 7 Dimensions Scenario Planning
Smart city
- definition
- a crowd-sourced innovation concept that came out of IBM’s Innovation Jams
- a city full of smart, innovative, creative knowledge workers in a area similar to Silicon Valley
- a sustainable “greener” city
- a densely populated urban environment with ubiquitous and pervasive computing technology infrastructure
- cities that use advanced IT and mobile technology to solve urban problems
- cities that use AI Data-driven Smart Cloud SaaS government services and IoT infrastructure
- major growth
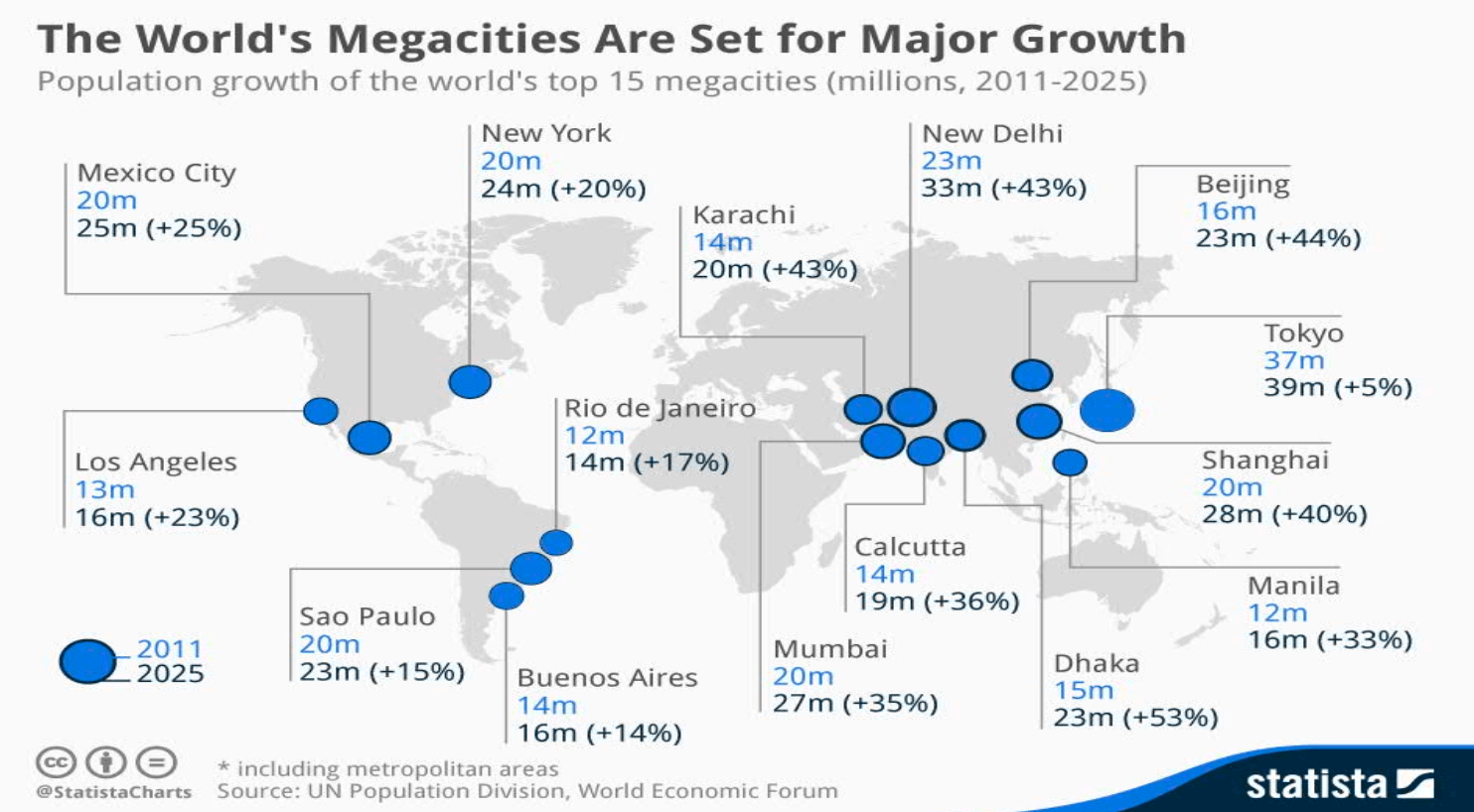
- unprecedented scale of urban problems
- traffic
- pollution
- overcrowding
- infrastructure breakdowns
- emergency and disaster prevention
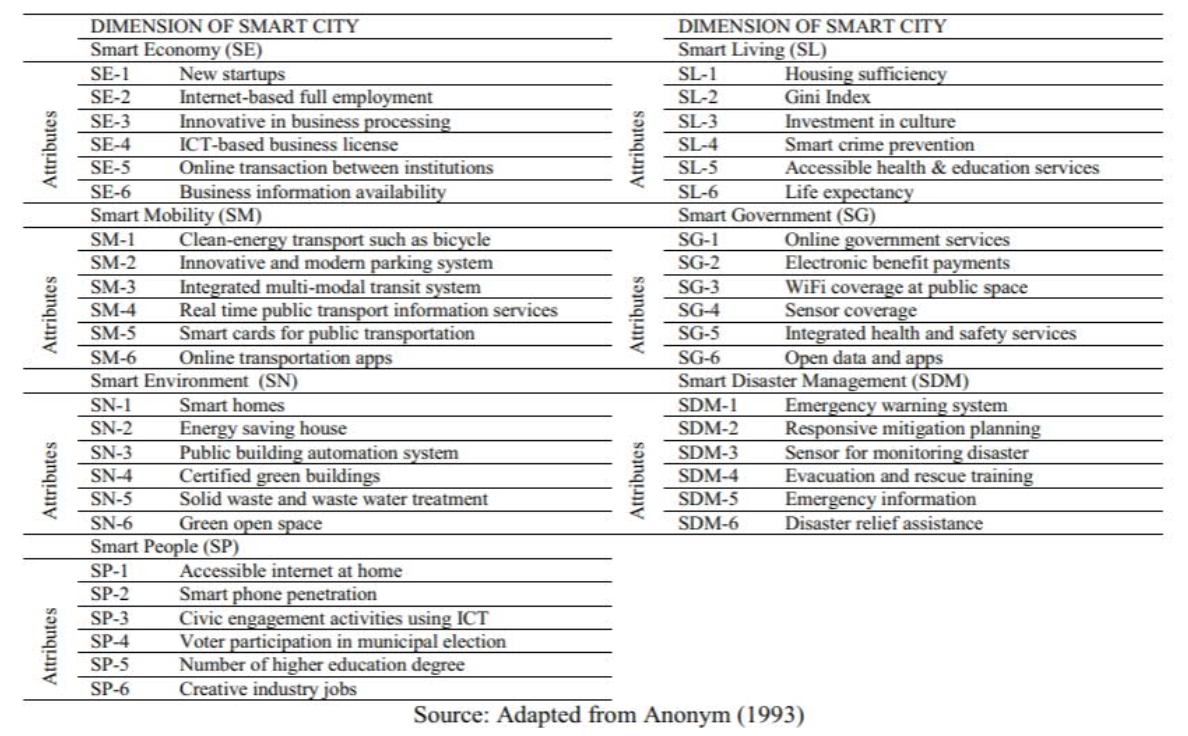
7 dimensions
- overview
- smart economy (SE)
- smart people (SP)
- smart governance (SG)
- smart mobility (SM)
- smart environment (SN)
- smart living (SL)
- smart disaster management (SDM)
- details
Scenario planning
- step 1 - build from scratch
- what are the top 3 things you like
- don’t like or key areas you find missing in the picture
- how will the covid-19 pandemic change this 2030 future scenario
- step 2 - take the list you wrote in step 1 and add the smart city dimension by letter
- example

- example
- step 3 - determine the details
- which dimensions are priorities for you
- example

- example
- look back at the above table to get ideas on the ways in which your smart city smartphone app can improve dimensions with integrated IT and IoT technology
- example

- example
- which dimensions are priorities for you
Internet of Things M2M Networks Smartphones
Overview
- background
- we have experienced the exponential growth of networked devices, products and services due to network effects
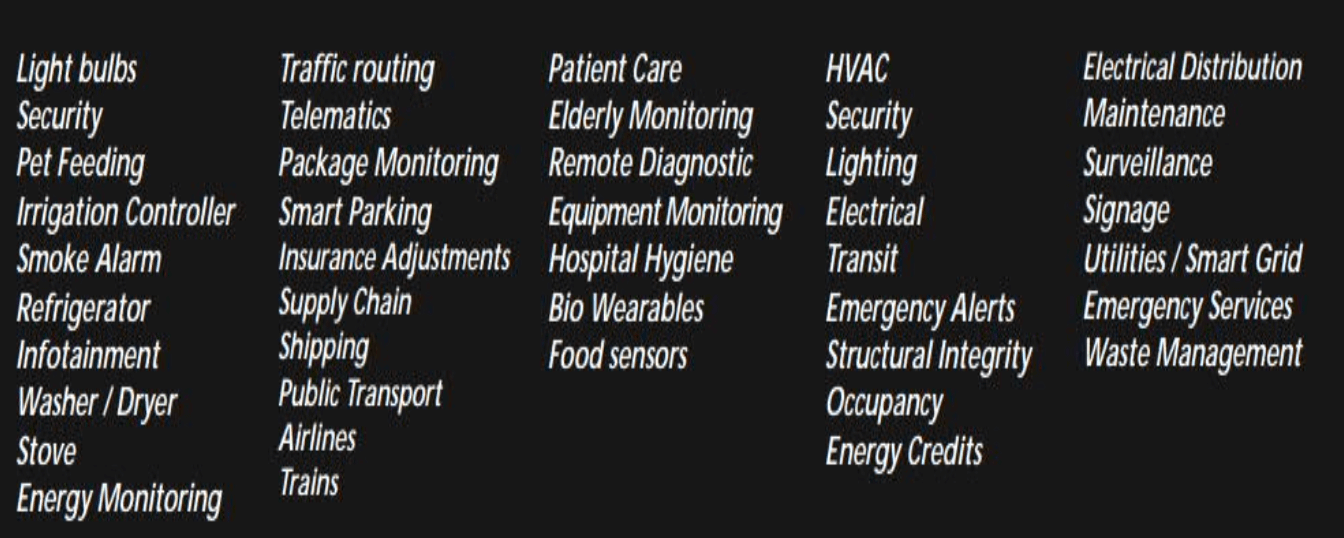
- what could you connect in this industry
- home (consumer)
- transport (mobility)
- health (body)
- buildings (infrastructure)
- cities (industry)
- big data and networked real-time systems
- reason
- reason
- some details
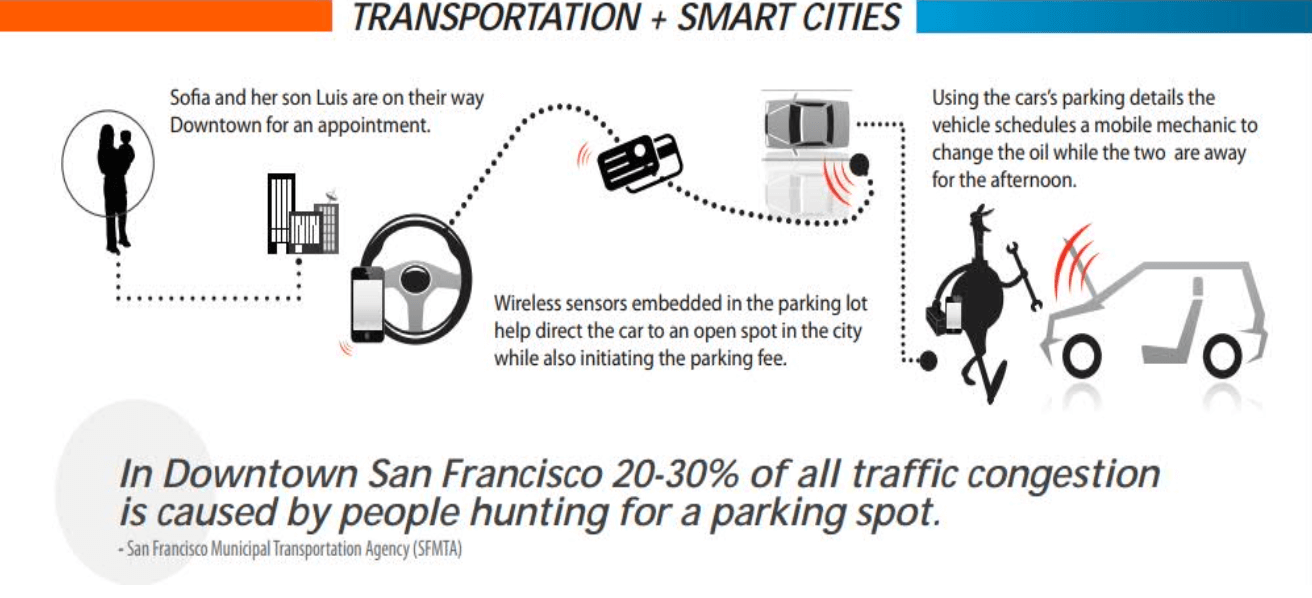
- smart mobility (SM)
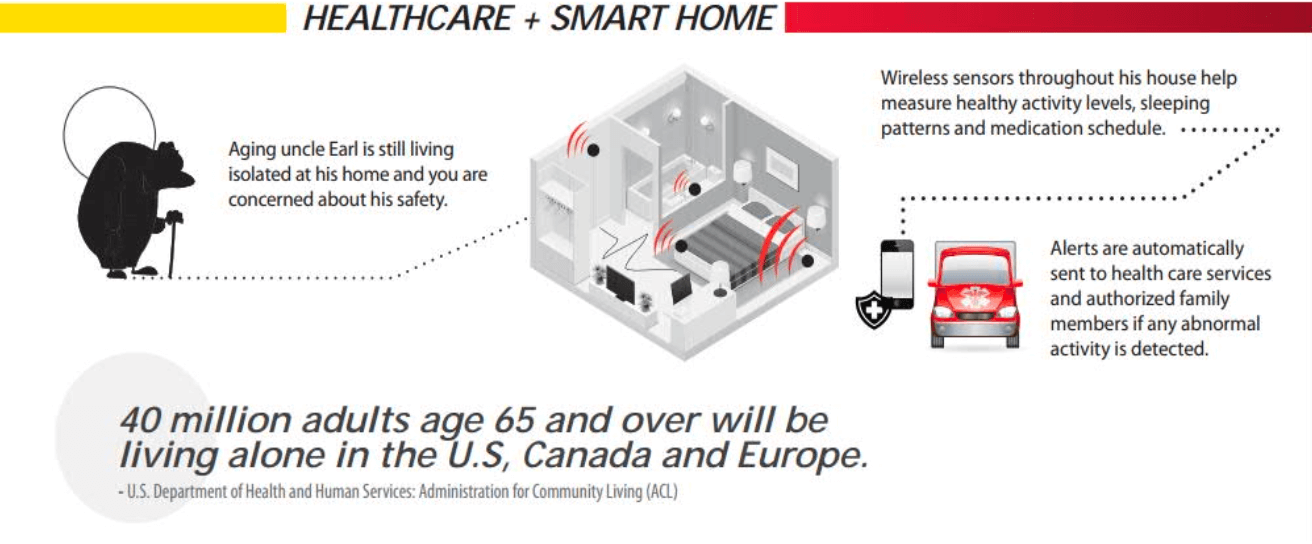
- smart healthcare & smart home (SG + SL)
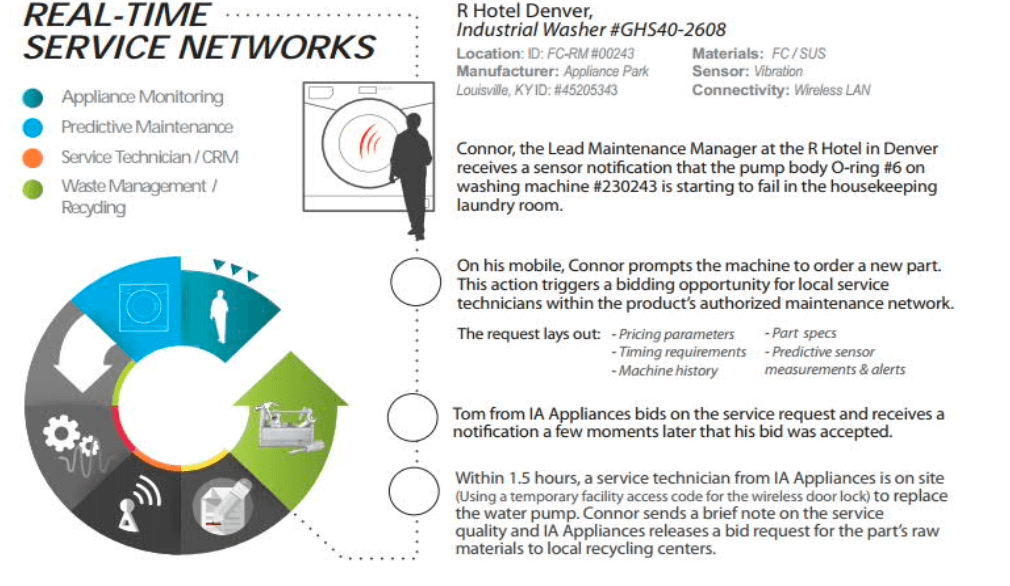
- smart environment via smart buildings (SN)

- smart living and environment (SL + SN)
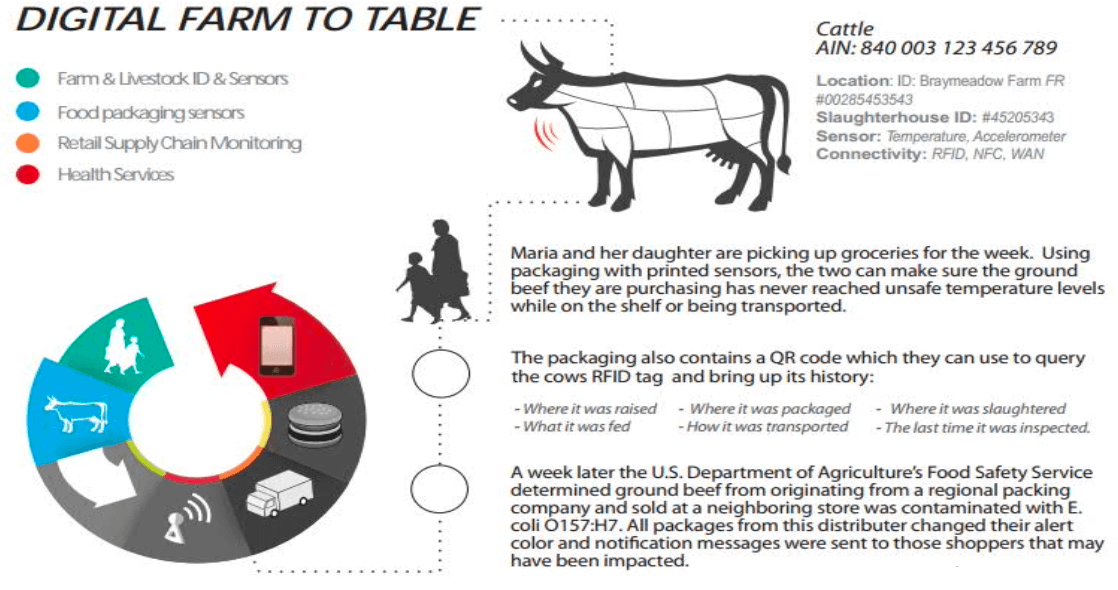
- smart living food tracing QR code (SL)
- smart mobility (SM)
Smart cities: a complex system
- crowdsensing and crowdsourcing with smartphone apps could enable individuals to contribute to and benefit from improving their cities
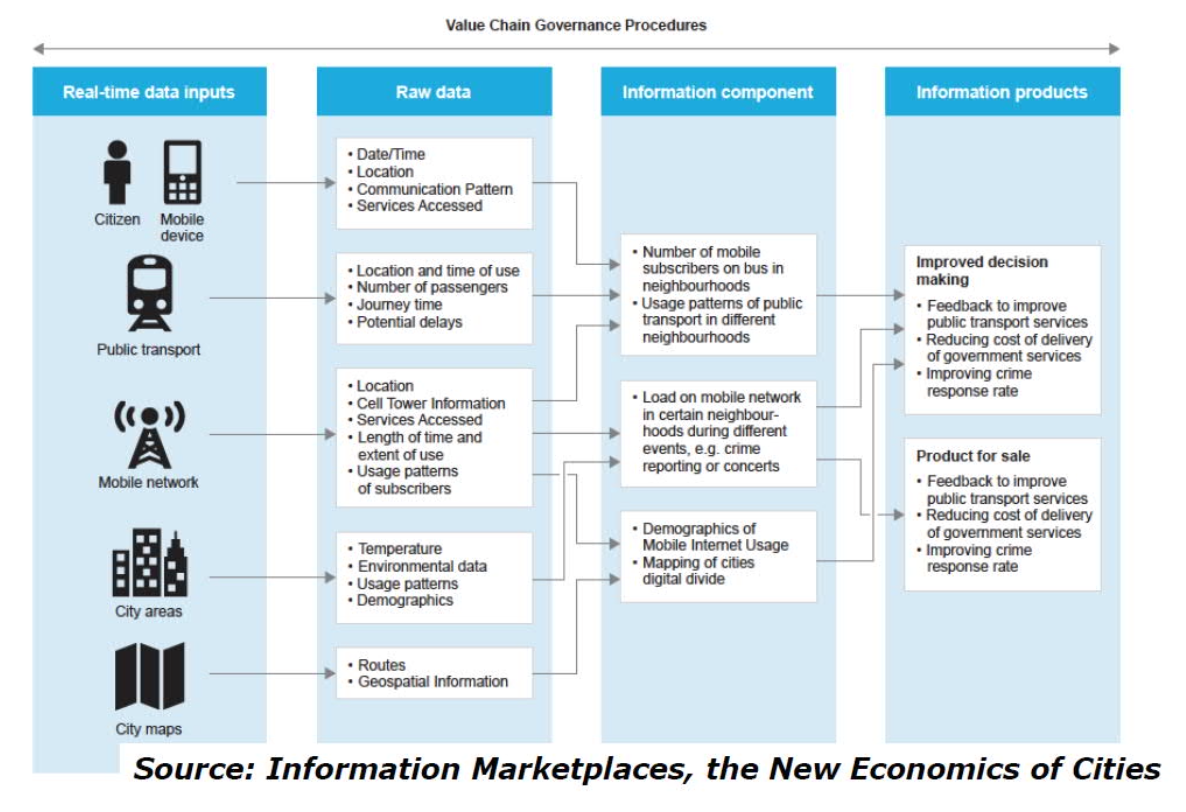
The Smart Cities' Examples
2018 AI and smart cities in China
- Hangzhou “city brain”
- 2016 Alibaba -> 128 intersections, emergency support
- Zhang Yijang, China’s first AI-partnered traffic policeman
- cloud platforms/smart parking in Shanghai
- 7m users have 100 government services
- data exchange platform where companies purchase “open” data
- Huawei has embedded chips in parking spaces of 300 parking los
- cashless in Beijing with Huawei pay in 2017
- Guangzhou — regional health app and digital education city
- Xian — rural to urban migration and public service provisioning
Utopia or dystopia
- details
- linggang Shenzhen -> 7000 cameras -> theft & robbery cases halved
- jaywalking in Shenzhen -> public embarrassment & repeat offenders
- social credit—reward high scores, financial inclusion vs black mirror
- Europe privacy concerns -> policymakers w. memories of WWII
- system engineering — engineering complex systems, crowds, communities