3 minutes
ECOM7121 The Crowd, How Users Create Value
Google and Two-sided Freemium Business Models
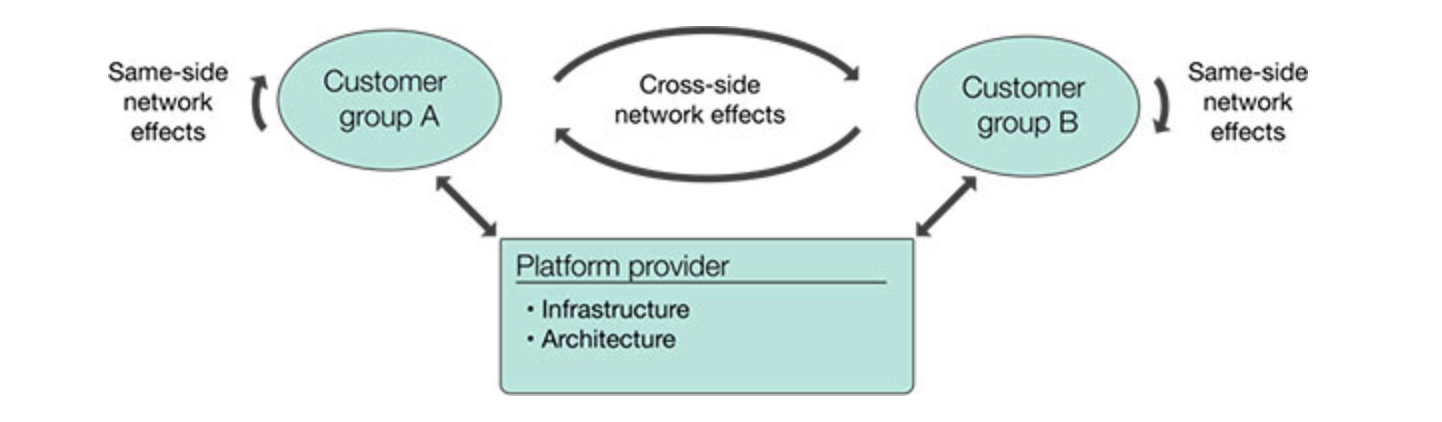
Two-sided markets
- definition
- markets where a platform has two distinct user groups that provide each other with network benefits
- aka. two-sided network
- example
- credit cards on the Visa and MasterCard platform (card holders <-> vendors)
- can be multi-sided
- example
- HMOs (Health Management Organizations) (doctors <-> care facilities <-> patients)
- example
- cross-network effects are typically positive, same-side effects may be positive or negative
Freemium = Free + Premium
- definition
- give your service away for free to acquire a lot of customers
- then offer premium price services or an enhanced version to make money or attract a premium-paying user group
- examples
- Dropbox (cloud storage)
- Linkedln (social media)
- NYTimes.com (print newspaper)
- Spotify (music streaming and downloading)
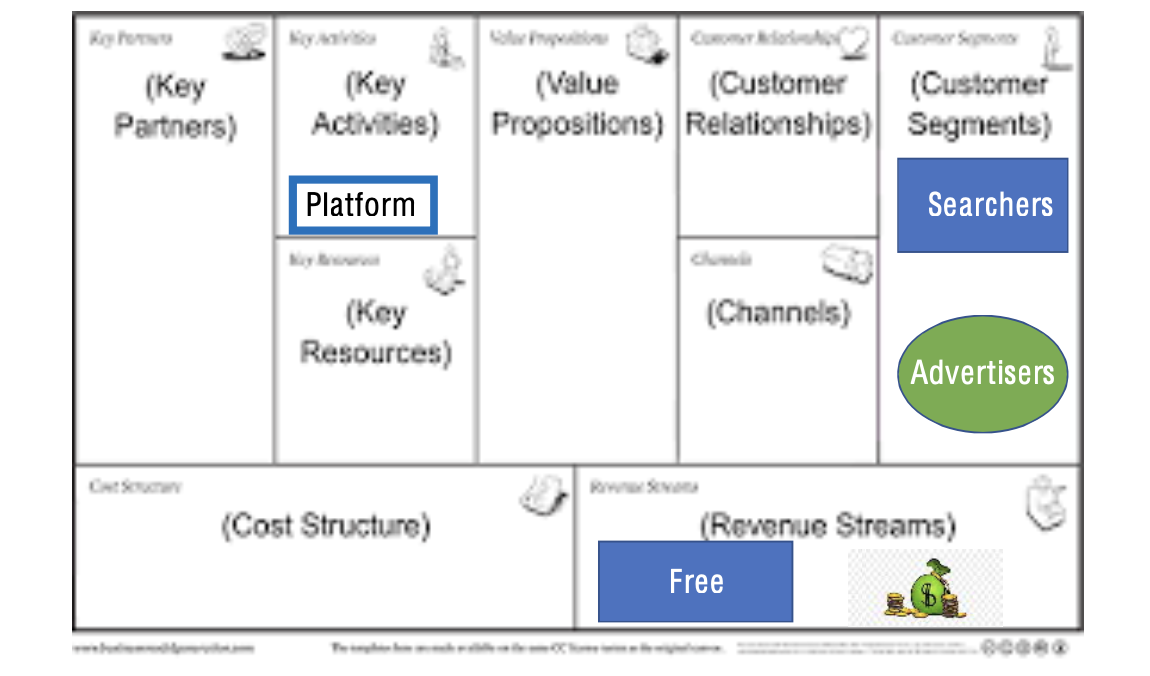
Two-sided freemium model
- example
- Google search (free searchers & premium advertisers)
- your clicks help to develop algorithms
- advertisers pay for best matching
- Google search (free searchers & premium advertisers)
Flickr (Photo Sharing Community) and Multiple Revenue Streams
History
- 2005 marked the crossover between user generated content uploaded and downloaded data from static company websites
- UGC: user generated content
- UGC > downloaded data
- 2007 marked the start of the Mobile App Economy
Common ways to measure mobile businesses
- ARPU: average revenue per user
- DAU: daily active user
- MAU: monthly active user
- DAU/MAU: currently user survival rate
- CPA: cost per action (user action after promotion)
- CAC: customer acquisition cost
- LTV: life time value (value from user)
Common digital and mobile revenue models
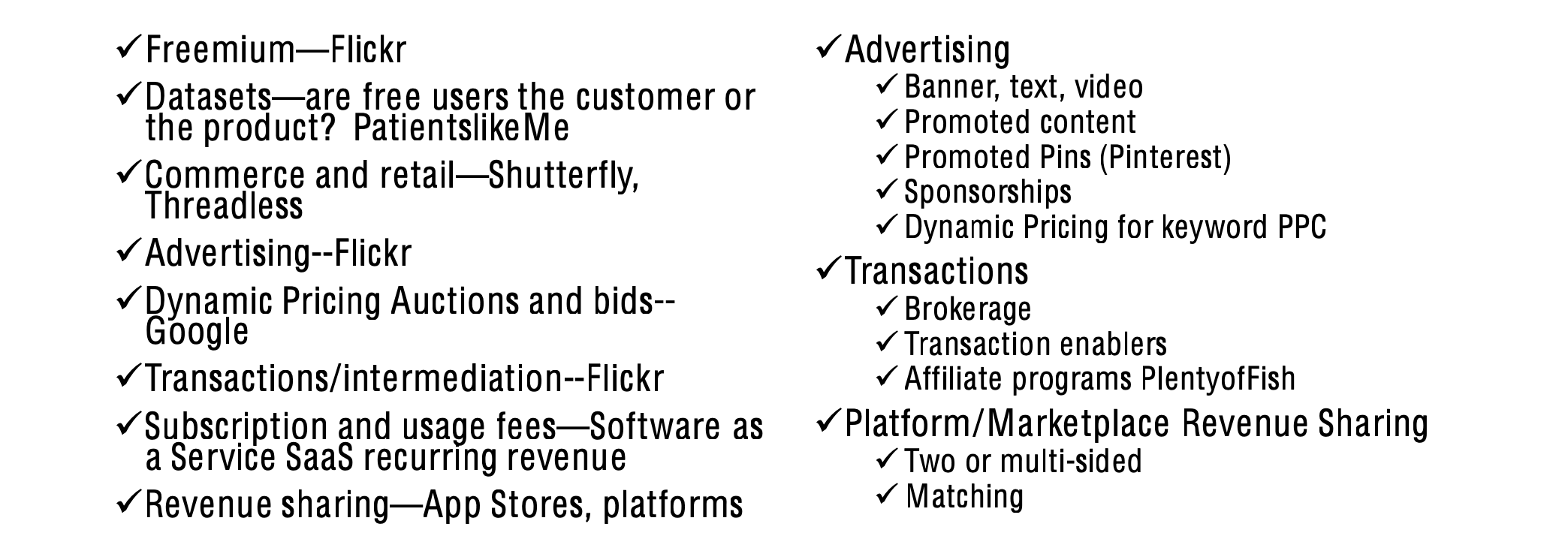
Flickr’s business model and four digital revenue streams
- business model
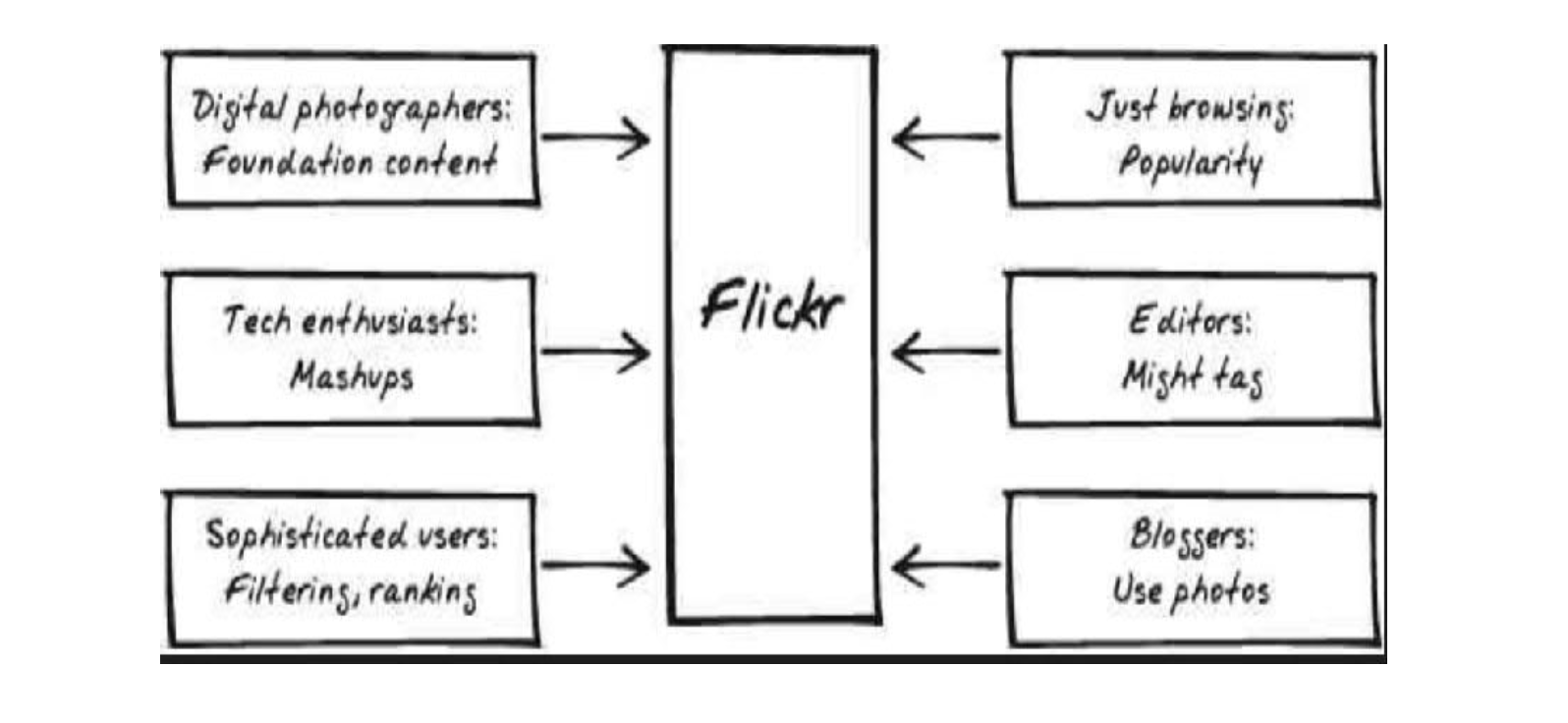
- multiple RPU digital revenue streams
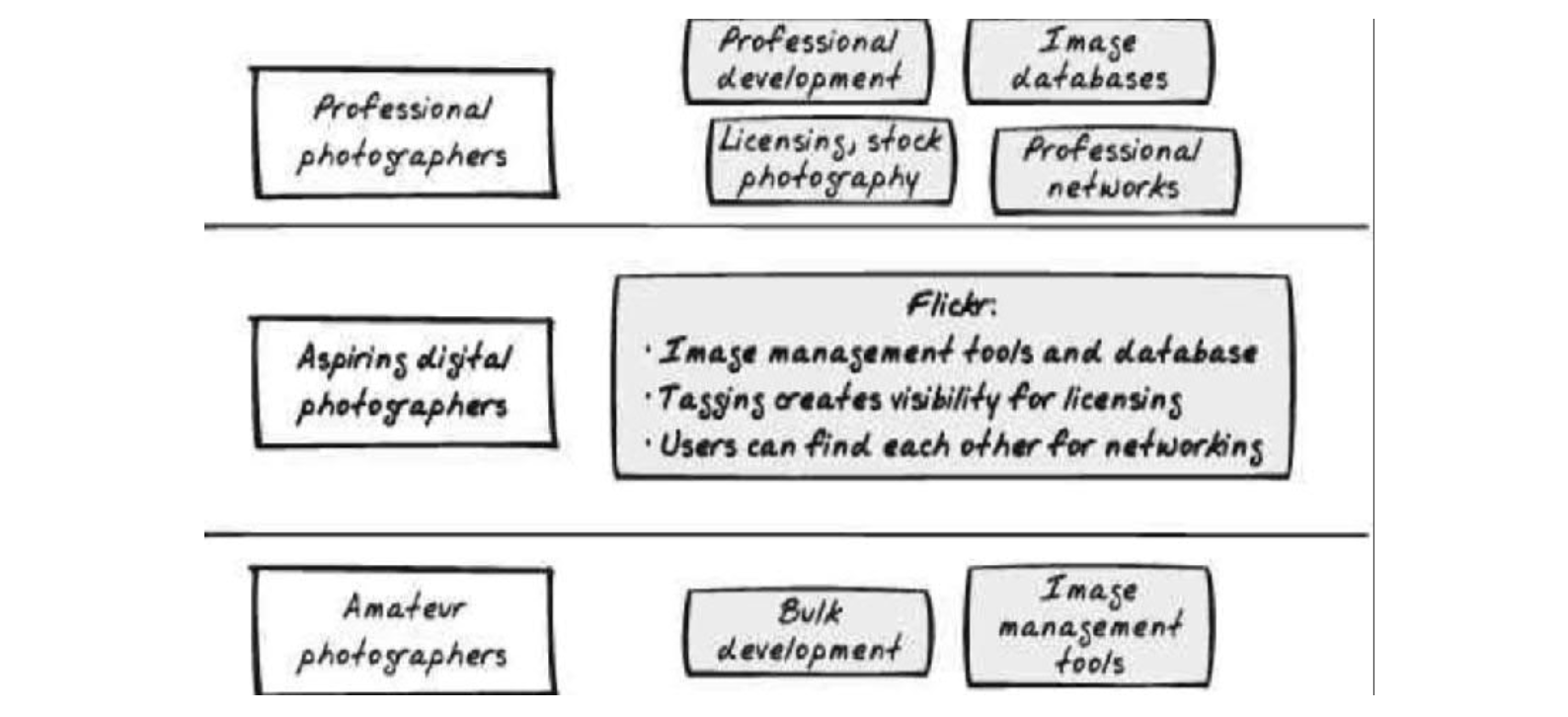
- four digital revenue streams
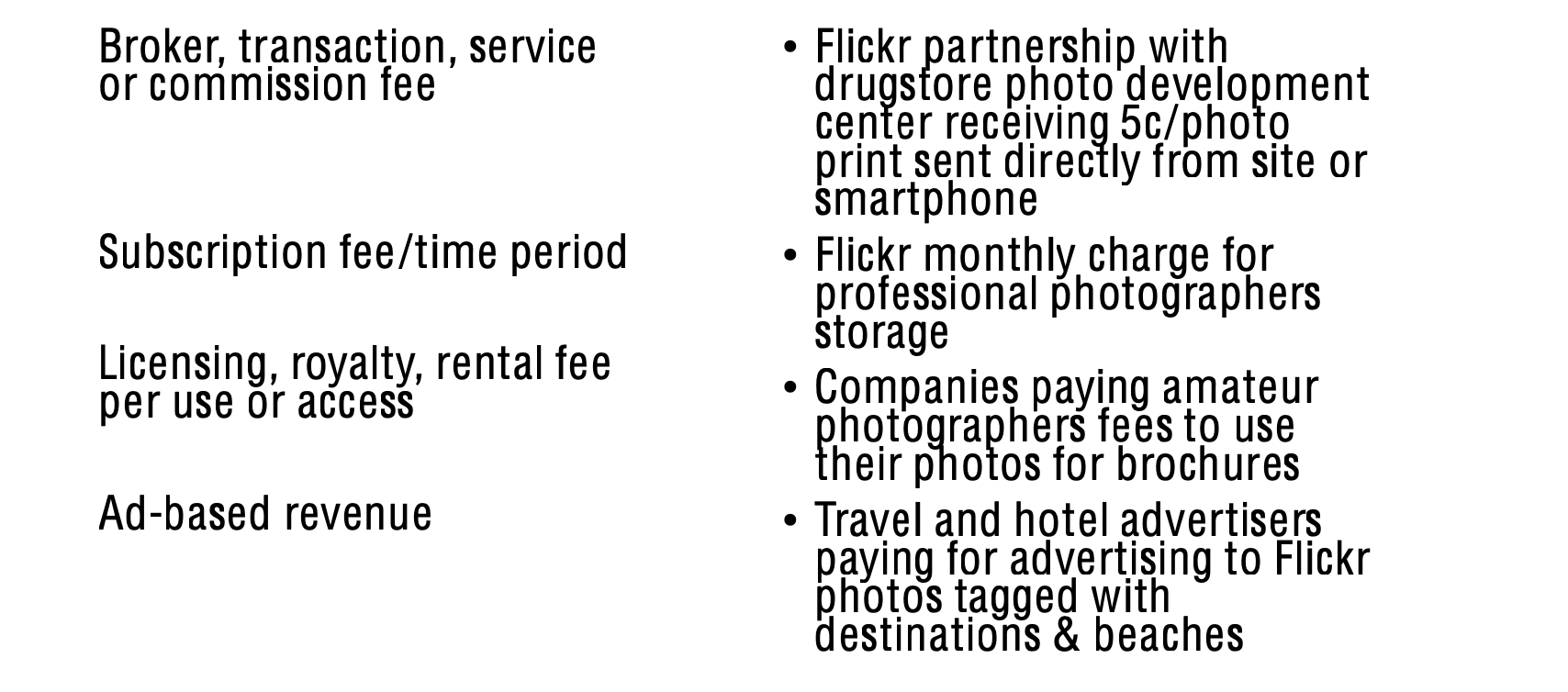
Flickr was compared to Shutterfly and Retail photo online print store
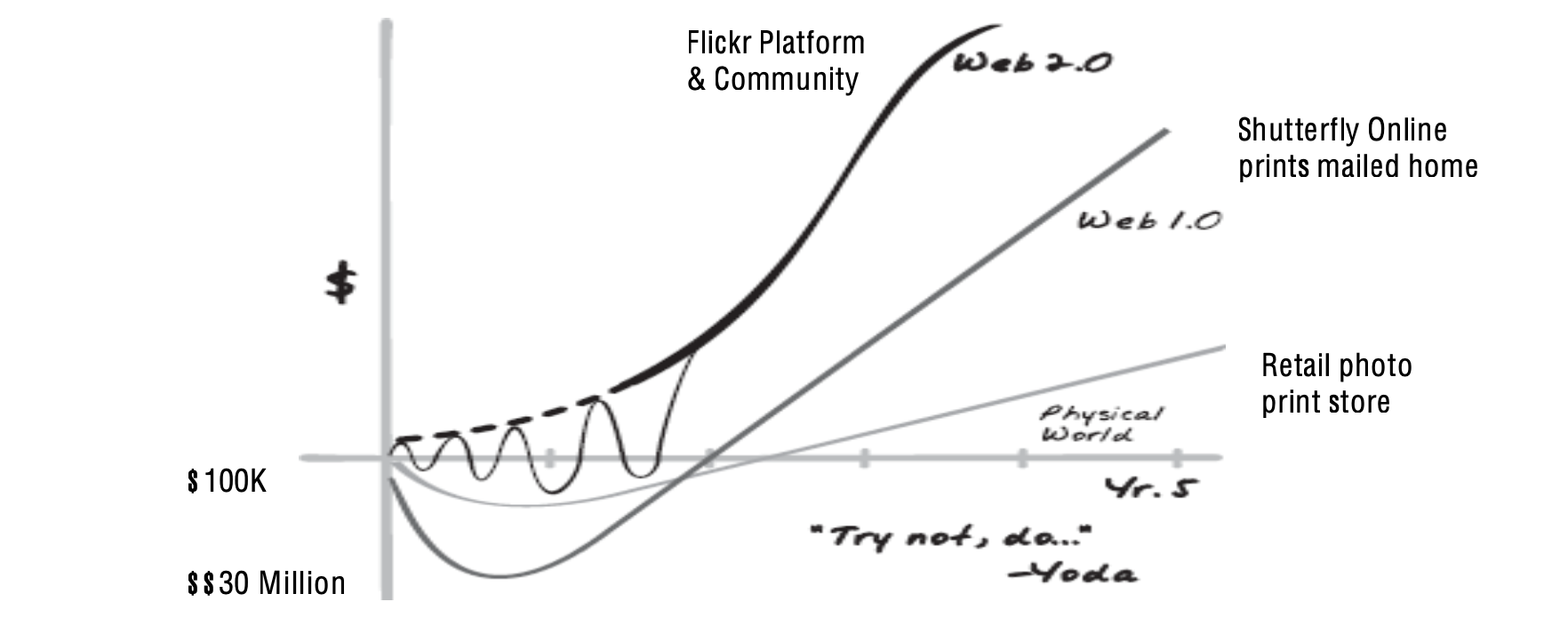
The Digital Stone Soup fable is used to explain how digital businesses can generate multiple revenue streams and RPU from shared digital data while physical goods are “depletive”
- the Stone Soup link
Threadless and Crowdsourcing Competitive Advantage
The Business Model Canvas and the book that introduced it was co-created by 470 crowd-sourcing unpaid contributors
- crowdsourcing = crowd + outsourcing
- is the process of obtaining needed services, ideas, or content by soliciting contributions from a large group of people, especially an online community, rather than from employees or suppliers
- it was coined in 2005 as a portmanteau of crowd and outsourcing
Create a crowdsourced design activity for a bicycle company’s value chain
Often contests are used to ensure that crowd-sourced designs are popular with potential buyers in the market
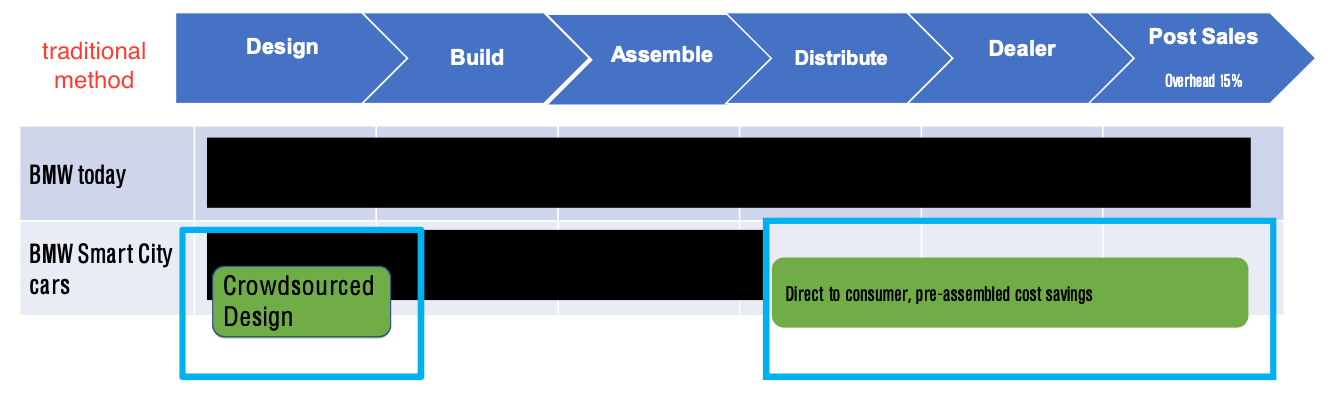
Local Motors and BMW have had success using crowdsourcing contests for auto design
- use crowdsourcing for designing innovative Smart City car designs that address unmet customer needs
- reduce marketing, distribution, retail store, support costs by going online and using social media campaigns
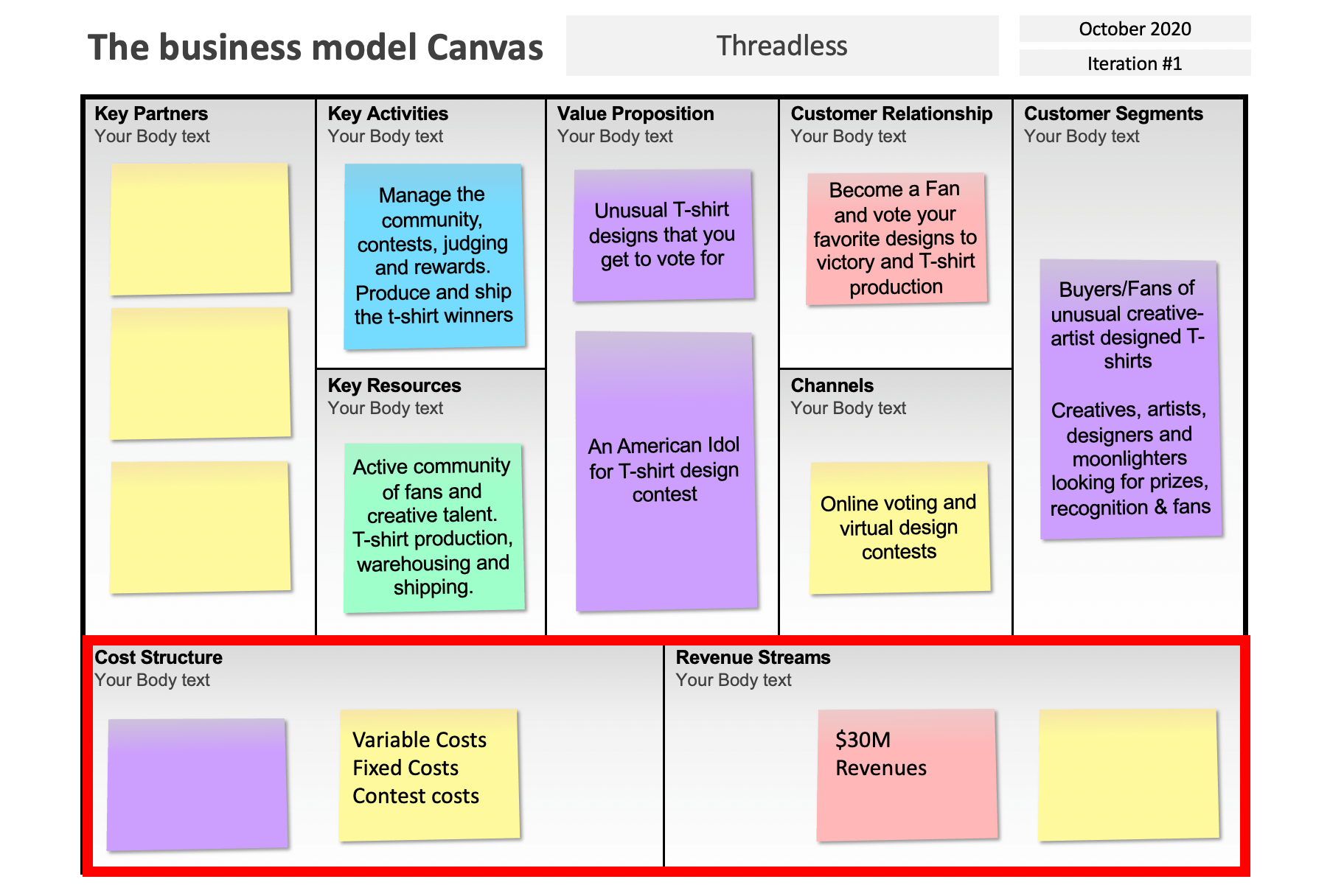
Threadless uses crowdsourcing for t-shirt design and changes the customer relationship with its designers to be more similar to fans of American idol singing contests
- method
- shares cool t-shirt designs
- designers get recognition & reward
- bussiness model
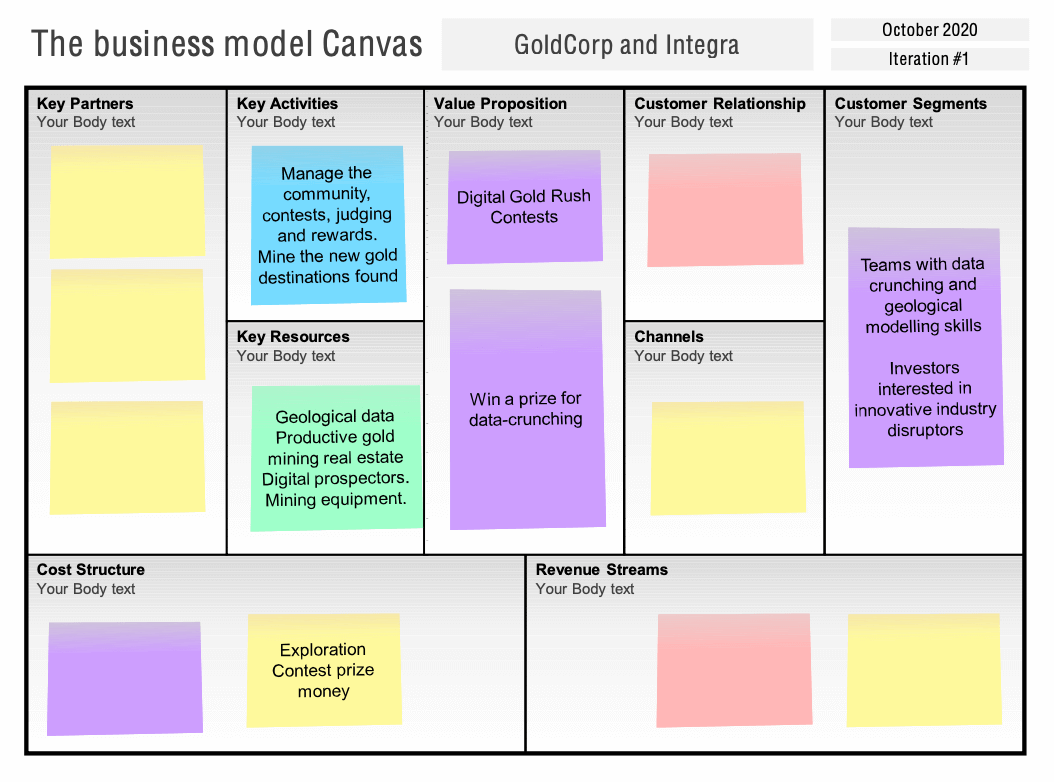
Goldcorp and Gold Mining
Goldcorp uses geologic data analysis crowdsourcing enabled by digital platforms to change the key activities, resources done in-house
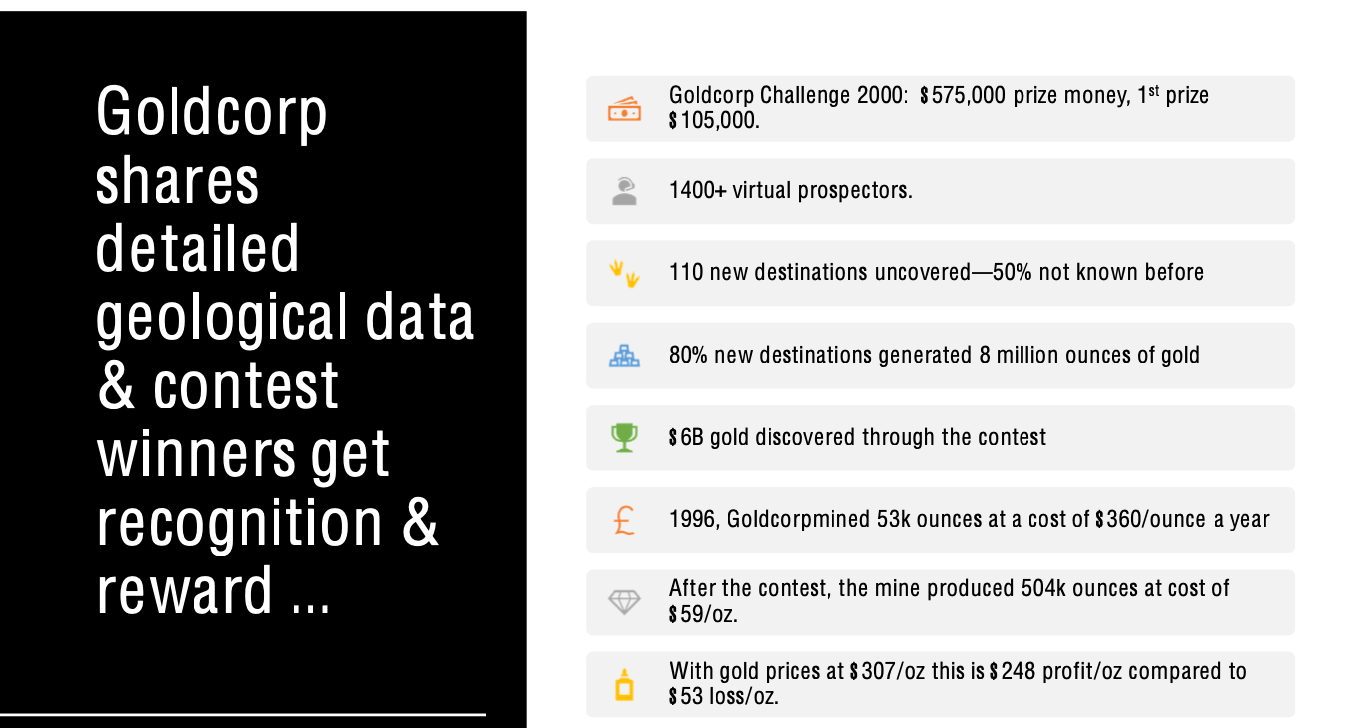
Crowdsourcing increased their revenue by 10 times and their profitability by making it easier to find productive gold mining destinations
Goldcorp’s approach transformed the gold-mining industry, previously a very traditional industry fearful of sharing geologic data
- business model
Many traditional industries, from t-shirt to software, from auto-makers to gold mining, are experimenting with crowdsourcing