3 minutes
ECOM7122 Deep Learning
Deep Learning Image & Voice
Overview
- for applied AI four pillars
- corresponding to unlocking unstructured data
- AI “core” capabilities in language and vision
- natural language processing (NLP)
- corresponding to unlocking unstructured data
- the “core” deep learning breakthroughs
- vision - image recognition
- language - voice recognition
Fastest growing product in history
- result
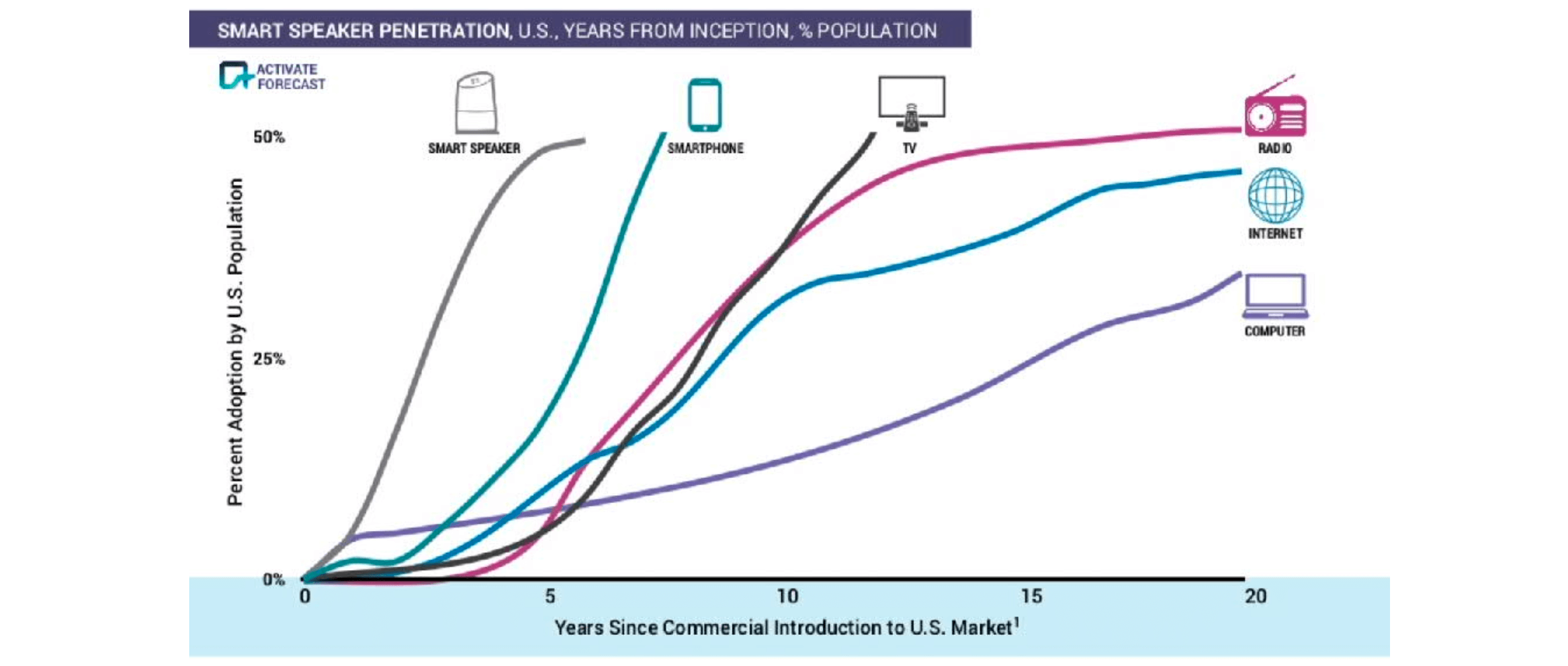
- conclusion
- smart speaker increases the most quickly to 50%
- but smart speaker goes smoothly after 5 years, compared the continuous dramatical growth of smartphone and TV after reaching 50% (growth flatten)
- may due to the loss of freshness
- may due to the loss of practicality
Cases
- vision
- in 2015, the accuracy of human and AI are equal, which is 95% (human accuracy level)
- self-driving is another example
- language
- in 2017, the accuracy of human and AI are equal, which is 95%
- Amazon Alexa (Echo Dot) is an example
- core components of AI/ML applications
- data input - voice
- data (pre)processing - language data for soundbites + NLP
- predictive models - far field voice recognition + understanding of intent and context of voice question or command
- decision rules (rule sets) - use the appropriate Alexa skill to address user intent
- response/output - Alexa voice response
- core components of AI/ML applications
- voice-enabled smart kitchen is another example
Deep Learning & Neural Networks
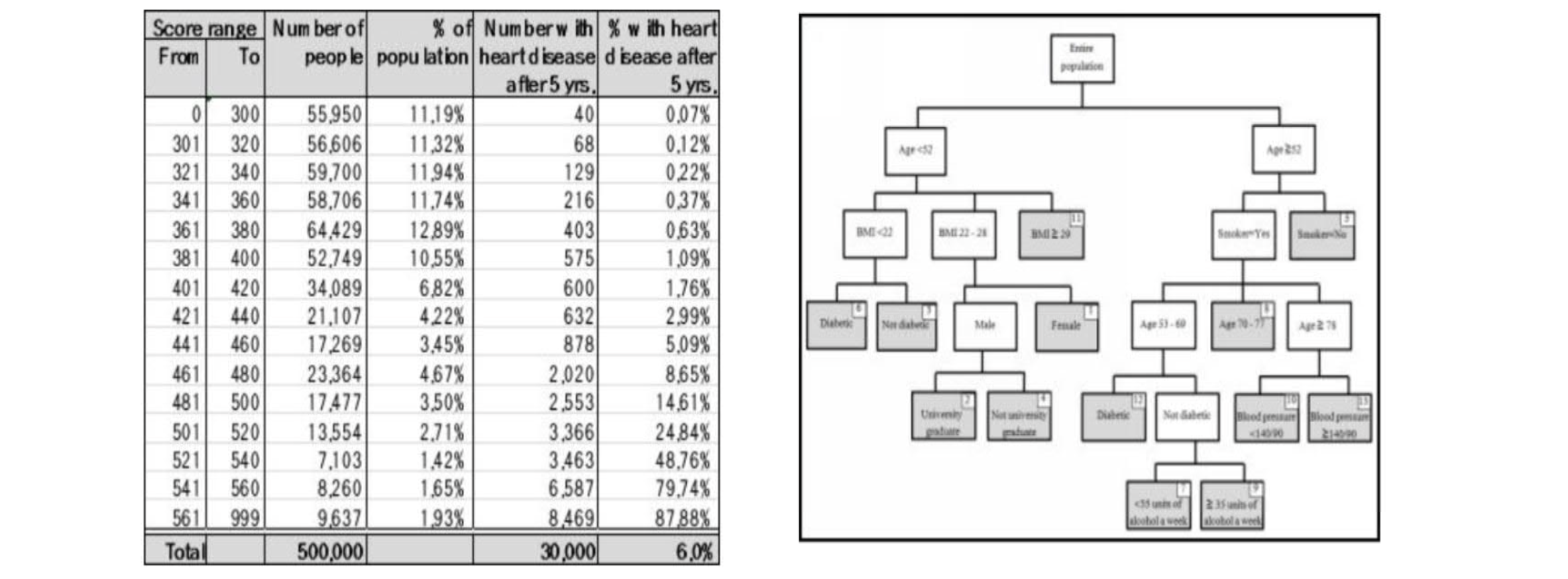
Artificial neuron & neuron network
- from scorecards to decision trees
- an artificial neuron
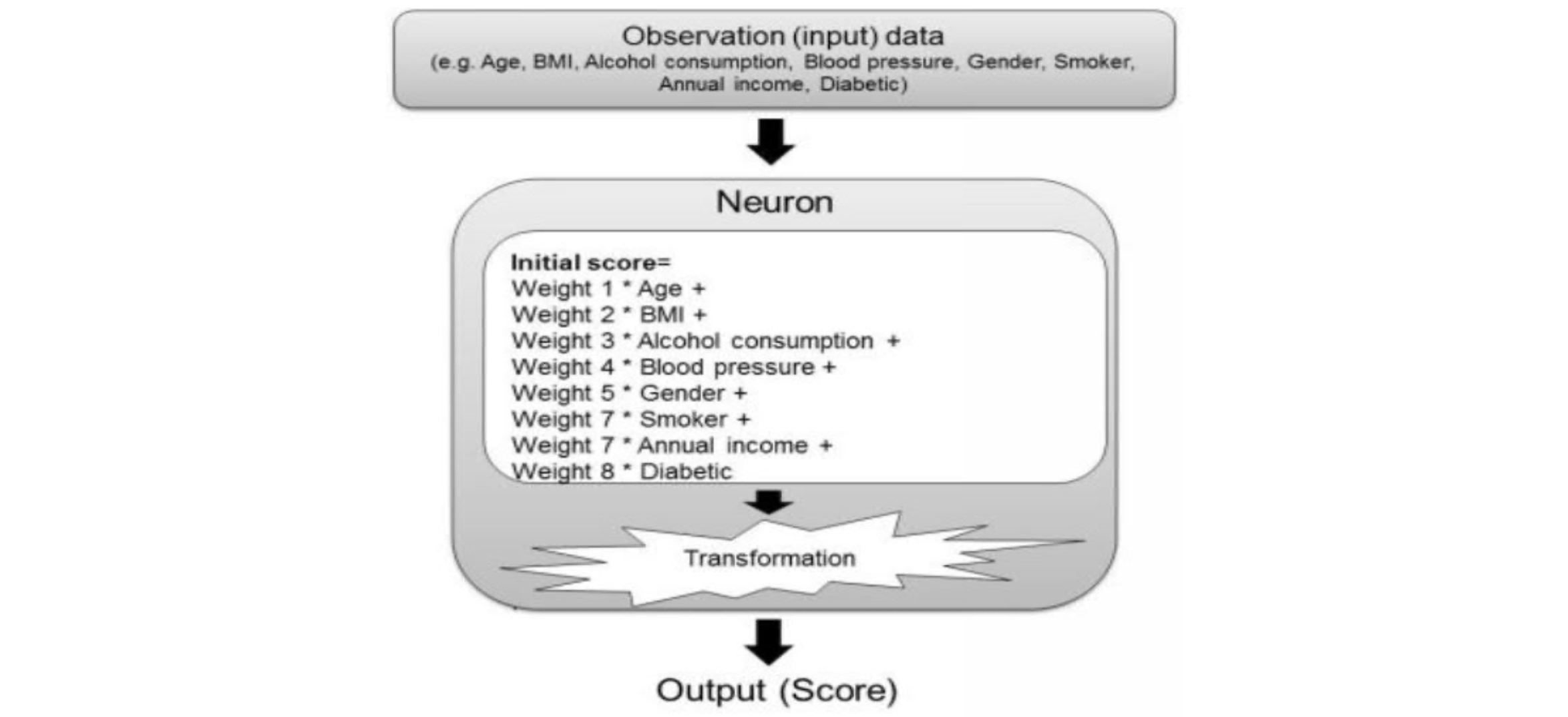
- a neuron network model
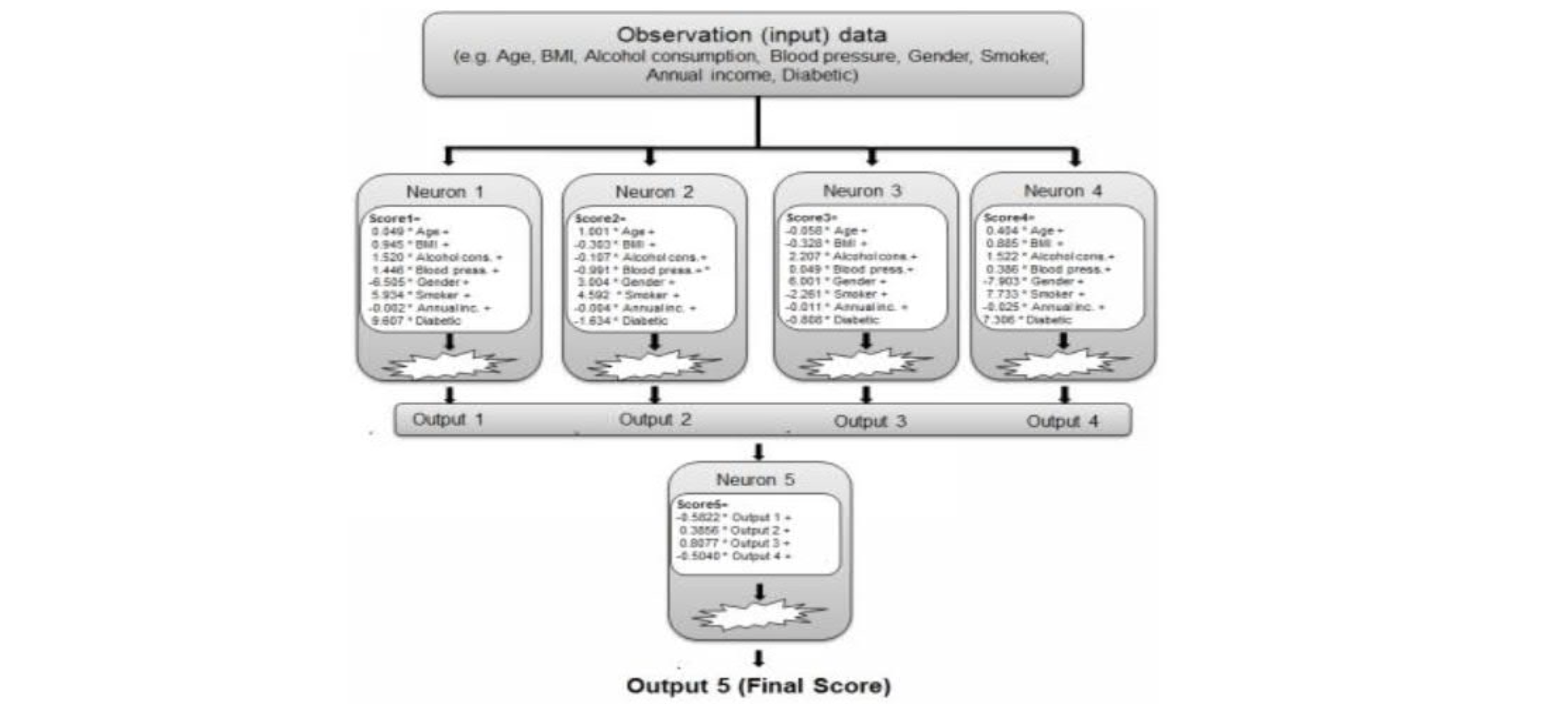
Deep learning
- feature
- the more the layers, the “deeper” the network
- convoluted neural network (CNN)
- not connecting all inputs to all of the neurons in the first layer
- recurrent neural network (RNN)
- create feedback loops where the output of later layers act as inputs to earlier layers
- time latency effect
- basic machine learning paradigms
- supervised learning
- using labelled data
- unsupervised learning
- using unlabelled data
- semi-supervised learning
- using a small amount of labelled data
- and unlabelled data
- reinforcement learning
- concerned with how intelligent agents ought to take actions in an environment in order to maximize the notion of cumulative reward
- supervised learning
White Box & Black Box AI
Create a common sense baseline first
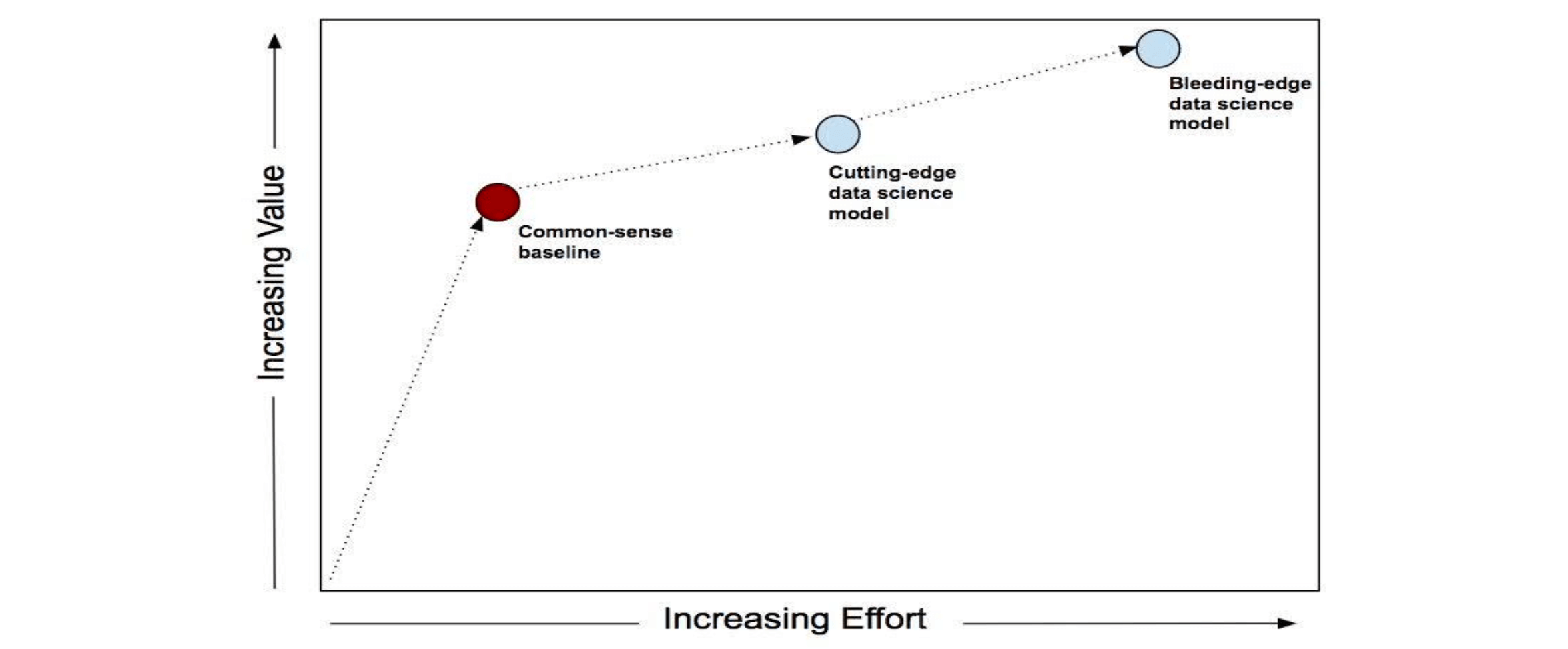
White box vs. black box AI
- white box
- simple models - scorecards, decision trees
- easy to understand how a score and prediction about someone is arrived
- which data items are important, which less
- easy to code
- still produce pretty good predictions
- black box
- complex models - neural networks, object recognition, language translation, game playing
- requires multiple machine learning approaches - autonomous robots, cars, digital personal assistants
The ethics of applied AI & deep learning
- can do with AI -> should do with AI
Additional Reading
- Computer Vision Leader Fei-Fei Li on Why AI Needs Diversity
- Pony.AI Launches China’s First Robotaxi Service
- A Good Blog
- Why Is Google’s Go Win Such a Big Deal?
- Inside Amazon’s Artificial Intelligence Flywheel
- Alibaba: Chinese Photo-Estimating AI Handles 12 Claims in 6 Seconds
- Scan-Reading AI Systems Are Helping Doctors Diagnose COVID-19
- Exclusive: Laser Scans Reveal Maya “Megalopolis” Below Guatemalan Jungle
- How AI Detectives Are Cracking Open the Black Box of Deep Learning
- Black-Box Versus White-Box Models
ecom7122 entrepreneurship development and fintech ventures in asia entrepreneurship fintech deep learning
489 Words
2021-03-31 11:57