5 minutes
ECOM7122 Machine Learning, InsurTech and Ethical Considerations
Machine Learning & Heart Attack Risk
Overview
- traditional medical systems
- treat illness when people are already sick
- the reason of using machine learning
- more accurate
- 20% - 30% better performance (means better prediction)
- “unbiased”
- statistical vs prejudicial bias
- fast
- automated decision making system
- but some decision making system may generate risks
- cheap
- predictive models work 24/7
- can provide medical services all the time
- more accurate
Scorecard
- features
- easy to understand and fits with our common sense and intuition
- it is “explainable” or “white-box”
- scenario - predicting heart disease

- predicting heart disease with scorecard

- likelihood of heart attack in the next 5 years
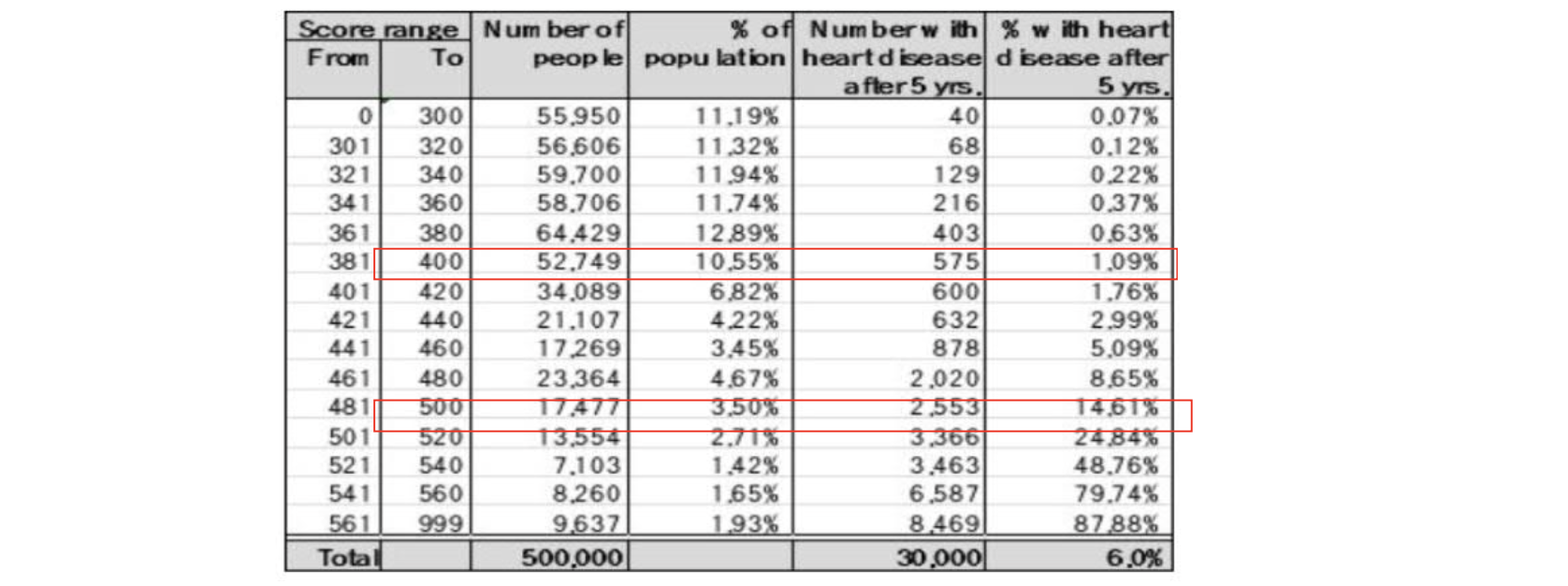
- decision rules & cutoffs
- if this was a Covid-fatality risk calculator, who would you vaccinate first & why
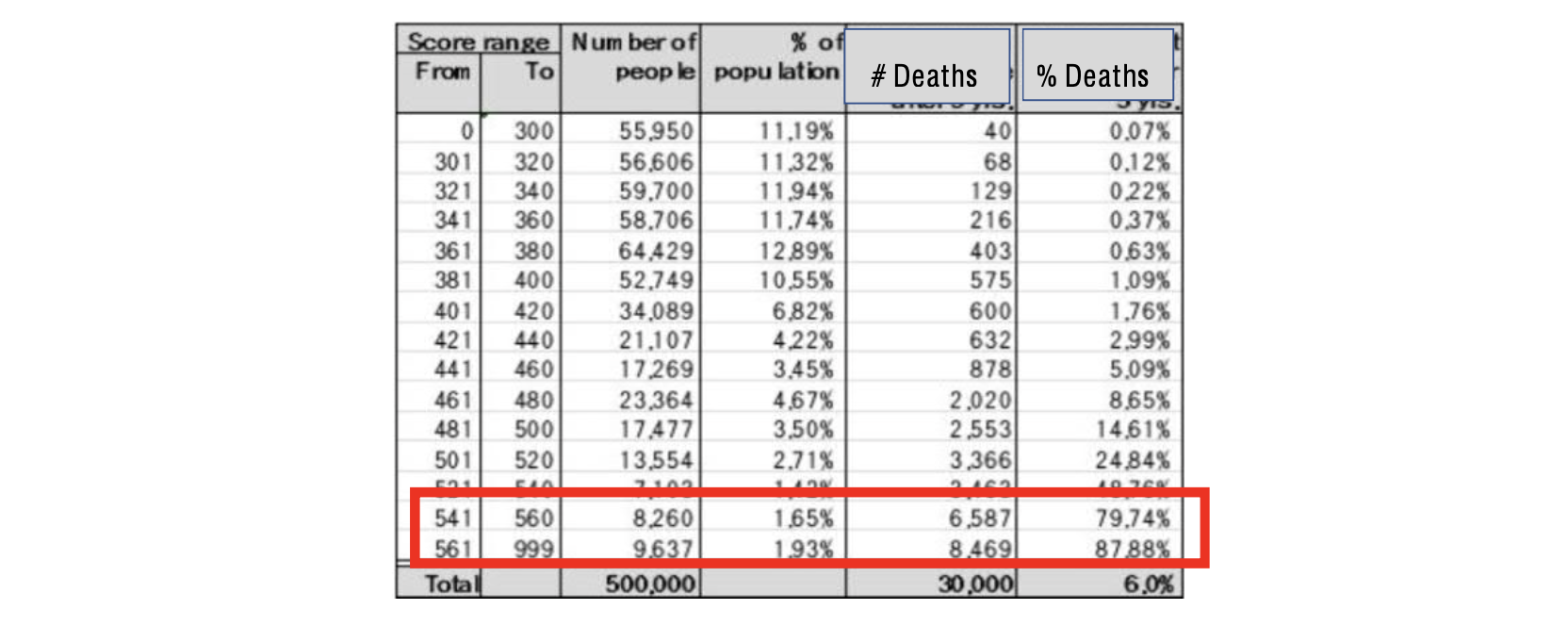
- if this was a default risk calculator, who would you deny credit to, who would you loan to
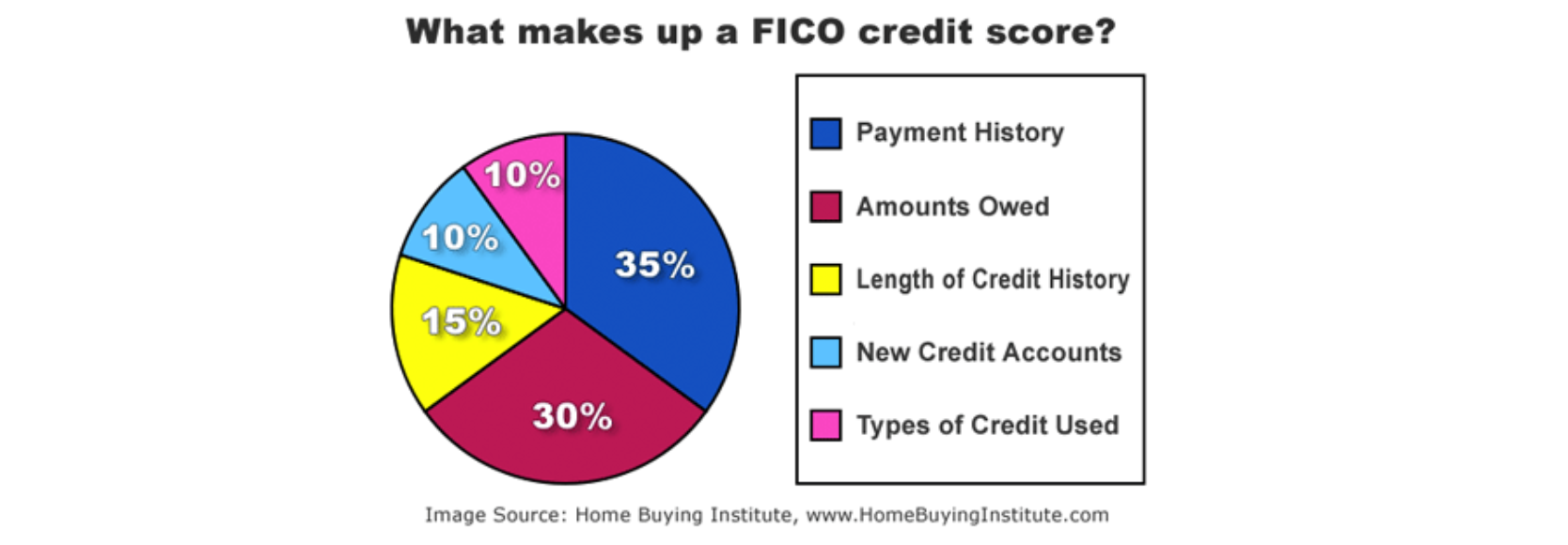
- Fair Isaacs Corporation created FICO, a credit scoring system used in the US
- consider age
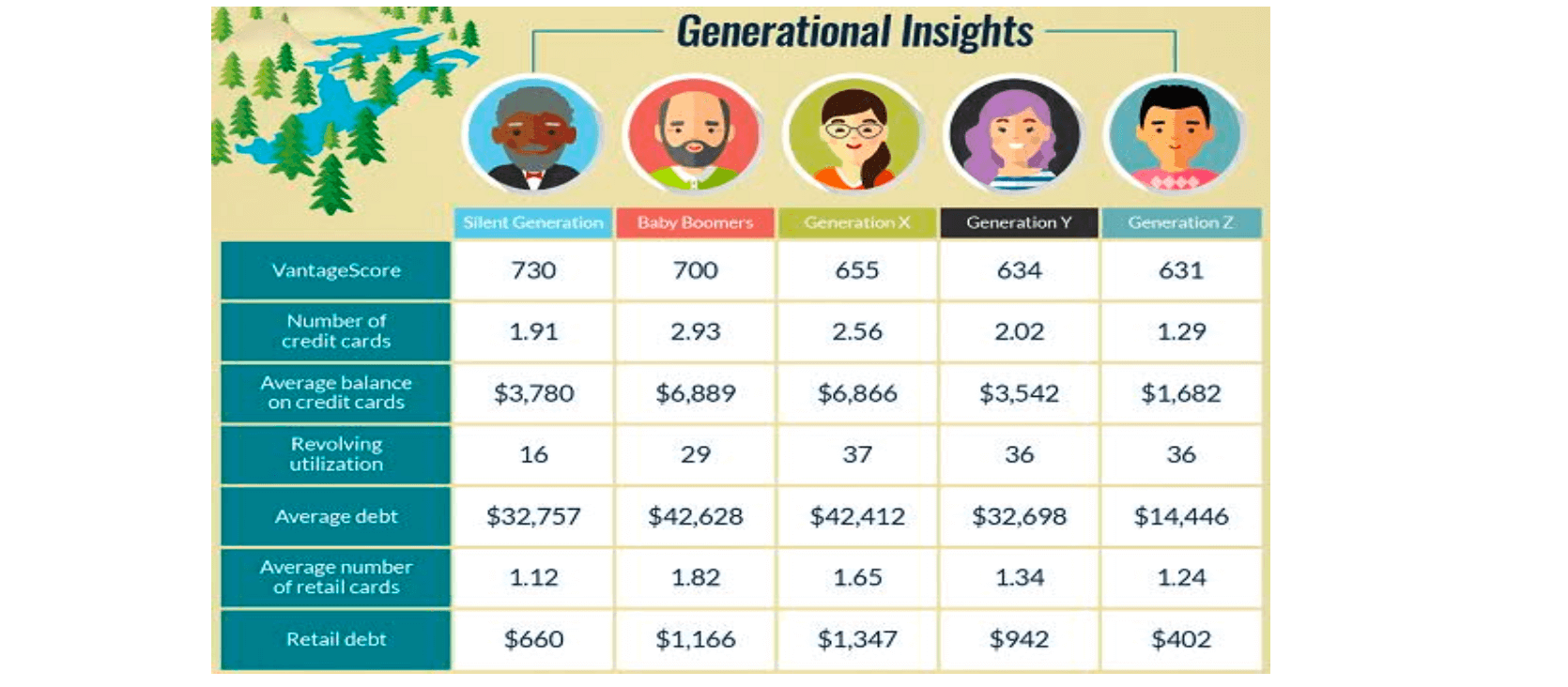
- yong or low-income families pay more to buy a house, with a higher mortage interest rate
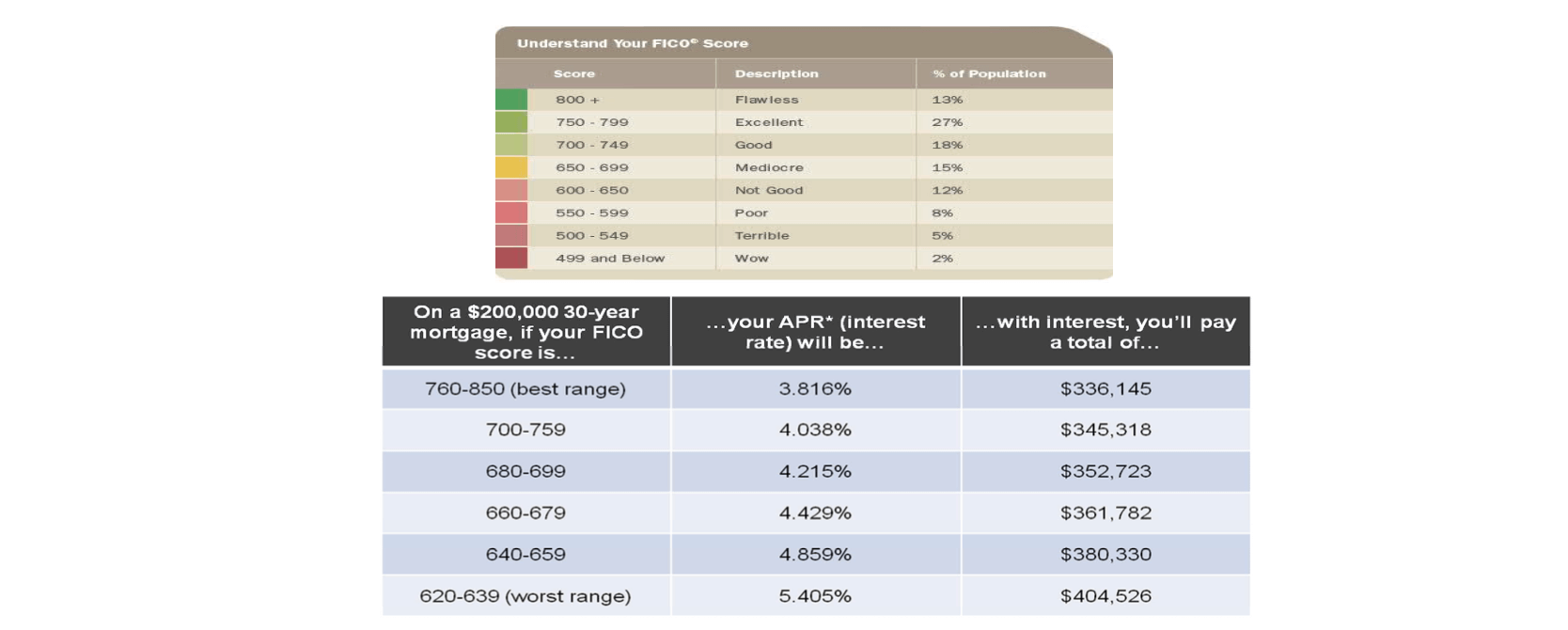
- if this was a Covid-fatality risk calculator, who would you vaccinate first & why
- FinTech - the disrupting force
- different data sources
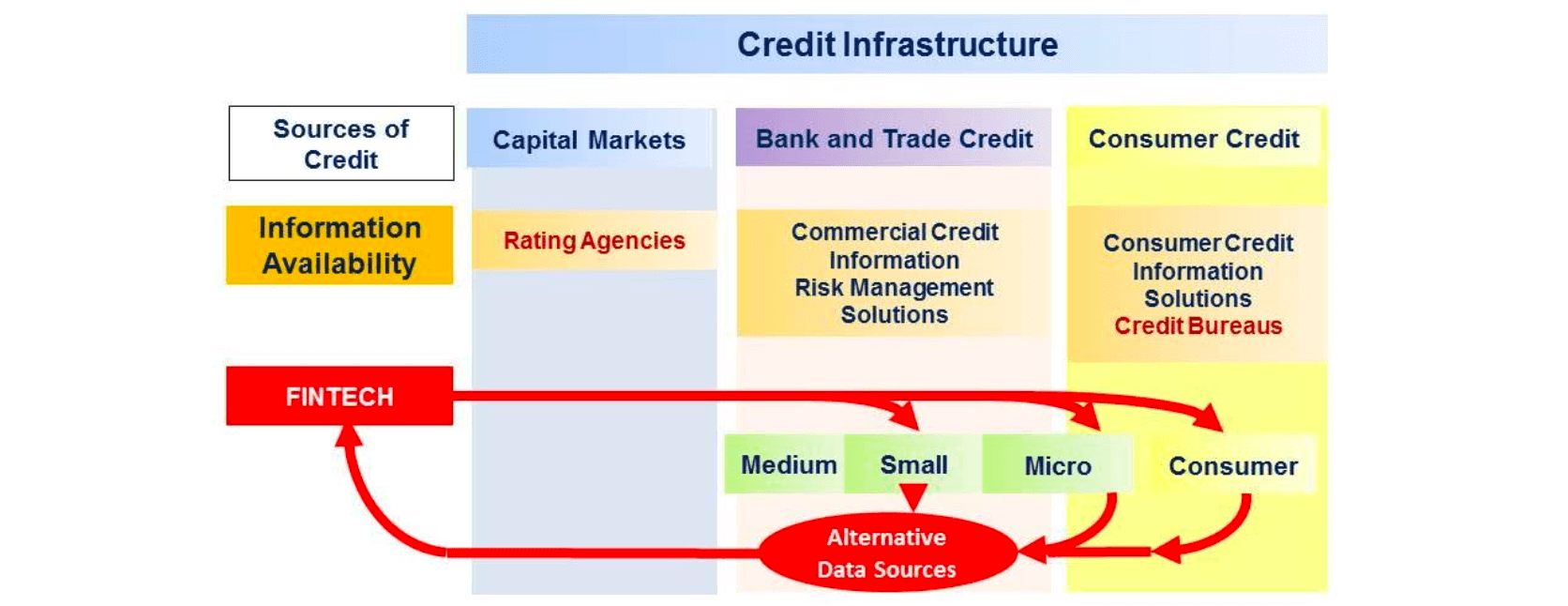
- applying AI, machine learning and predictive analytics for credit scoring
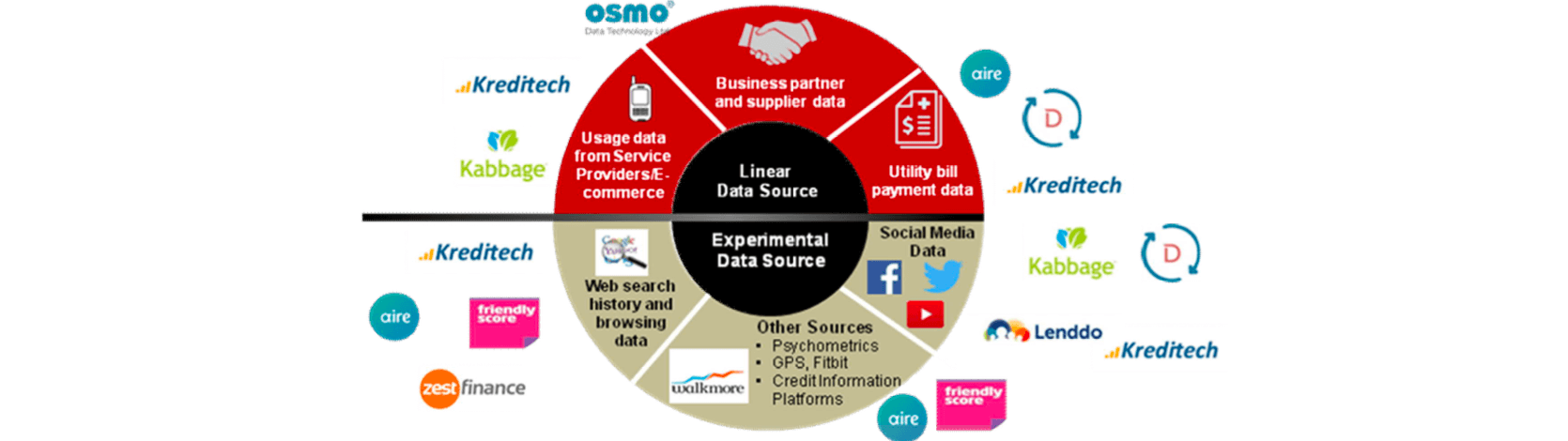
- different data sources
Bank loans & credit in China
- history
- 1949 all FIs nationalized -> People’s Bank of China
- 1980s Bank of China, Agricultural Bank of China, China Construction Bank, Industrial & Commercial Bank of China established for loans to SOEs
- 2010 all listed on stock exchange, largest banks in the world by market cap, 1⁄2 of total assets in China
- regulatory control of interest rates for insurance and mutual fund products
- 20% of SMEs had access to credit, 60% GDP
- private micro-enterprises of < 10 employees, no credit access
- 2008 PBOC and CBRC microfinance defined
- 2013 village and town 7839 microfinance companies with $131B in loan balance
- CreditEase
- poor talented students seeking vocational training at Ning Tang’s (the founder) school
- problem - students can’t afford tuition
- need - speedy credit approval for tuition loan
- risk — default, not paying back
- reward— better-paying jobs increase likelihood of payback
- proxies — grades, attendance, teacher recommendations
- credit rating system
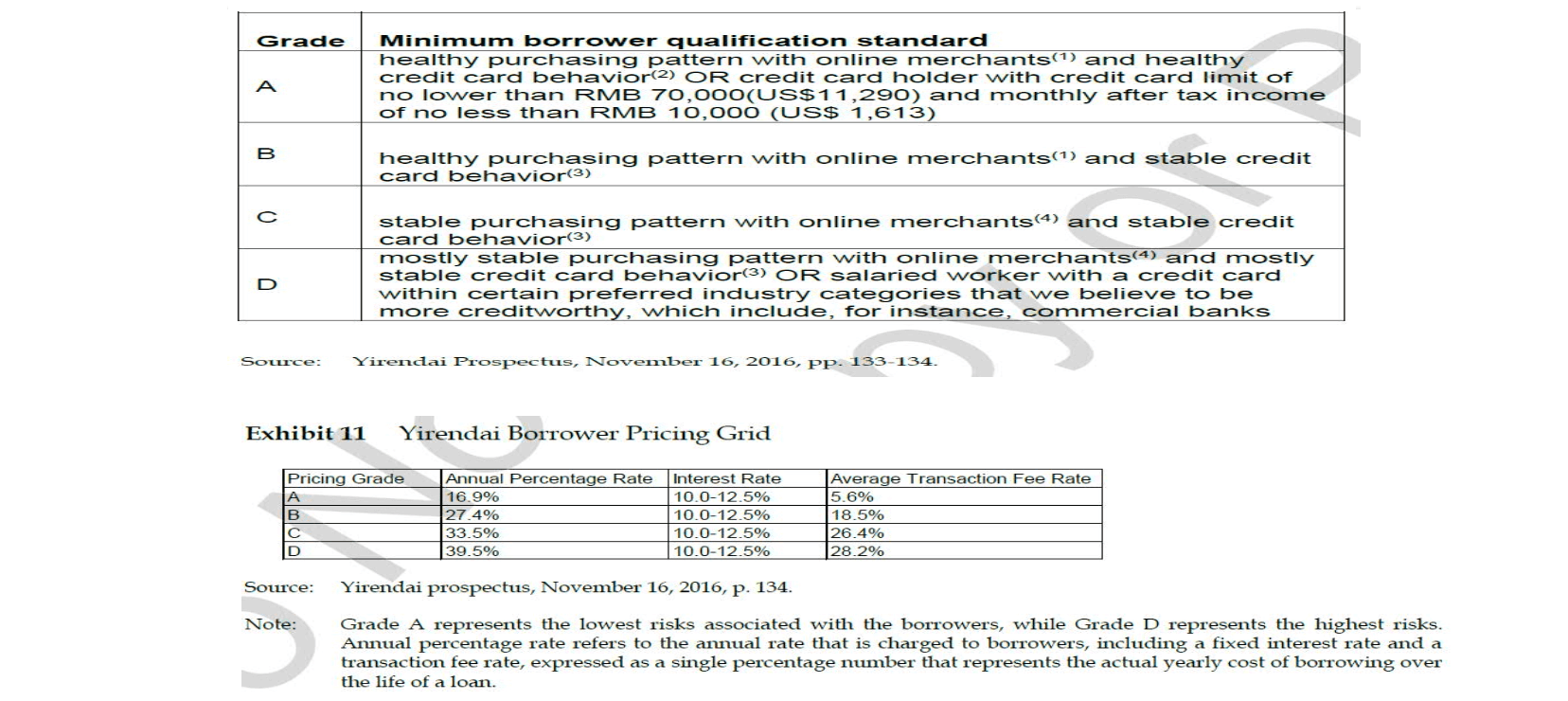
- P2P lending
- the importance of credit-scoring
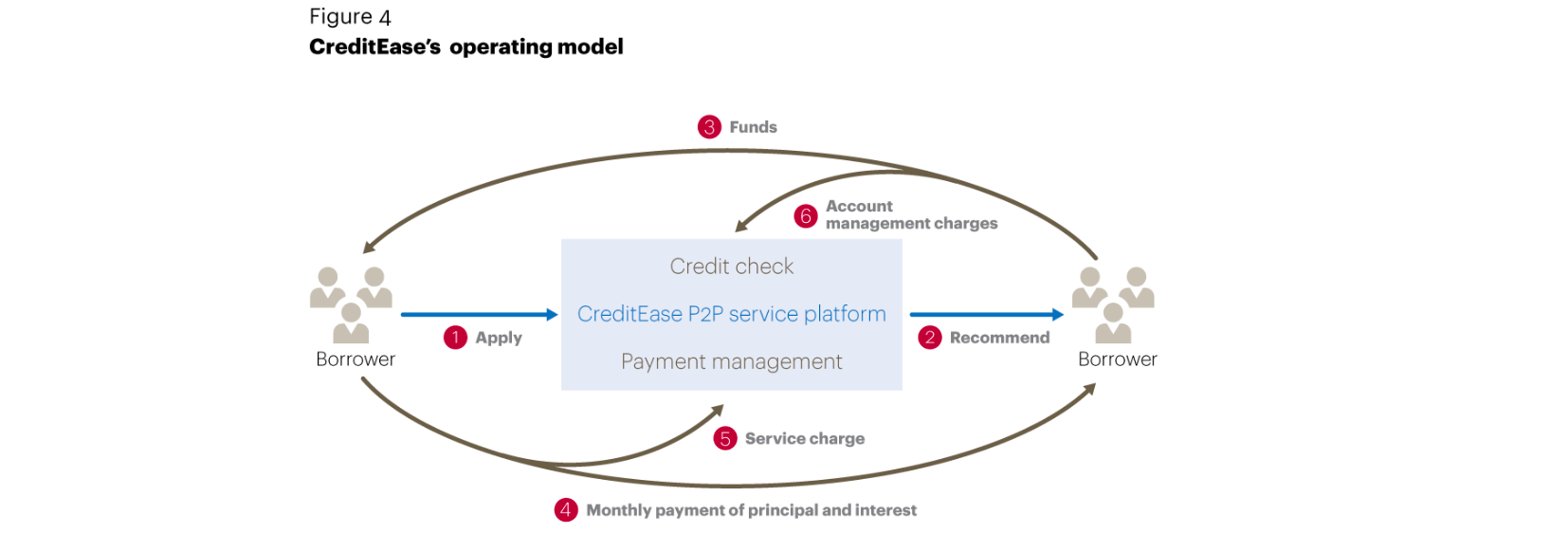
- the importance of credit-scoring
- bank loans vs P2P lending
- the source of money is different
- the risk control of traditional bank is better than that of P2P platform
- Dianrong & sesame credit
- using alternative data - “data exhaust”
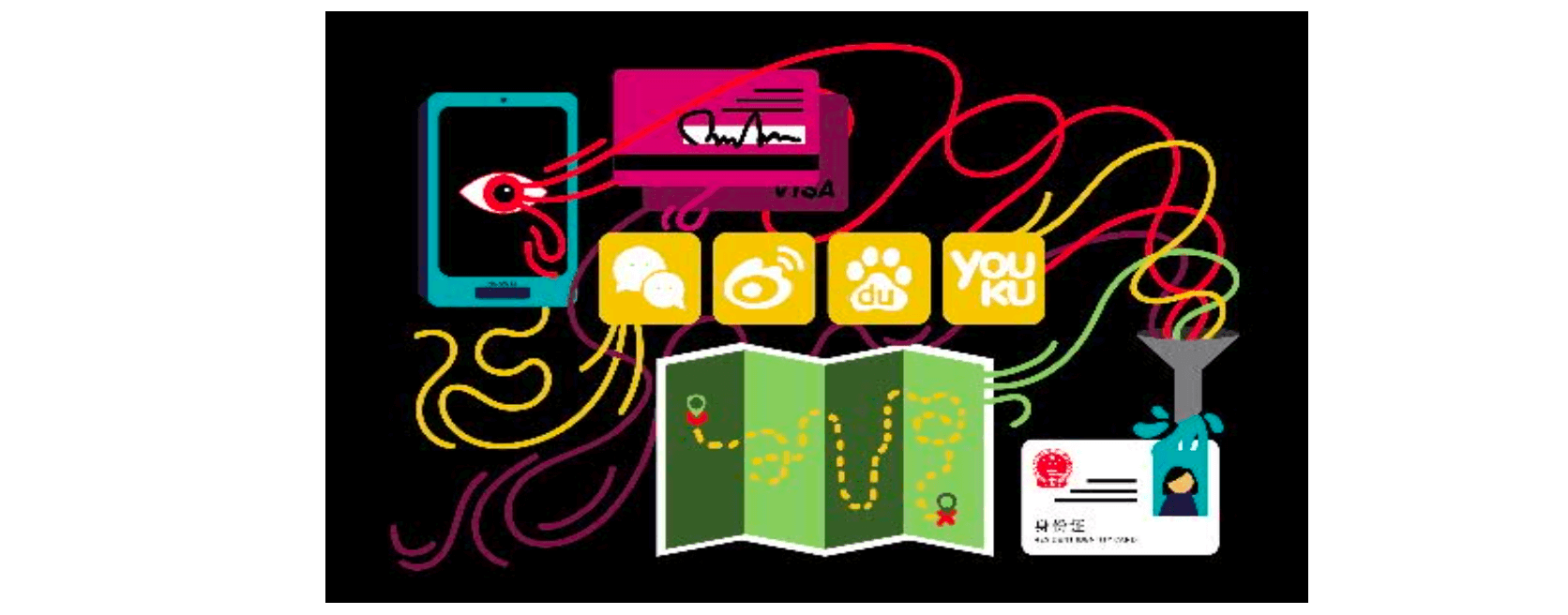
- using alternative data - “data exhaust”
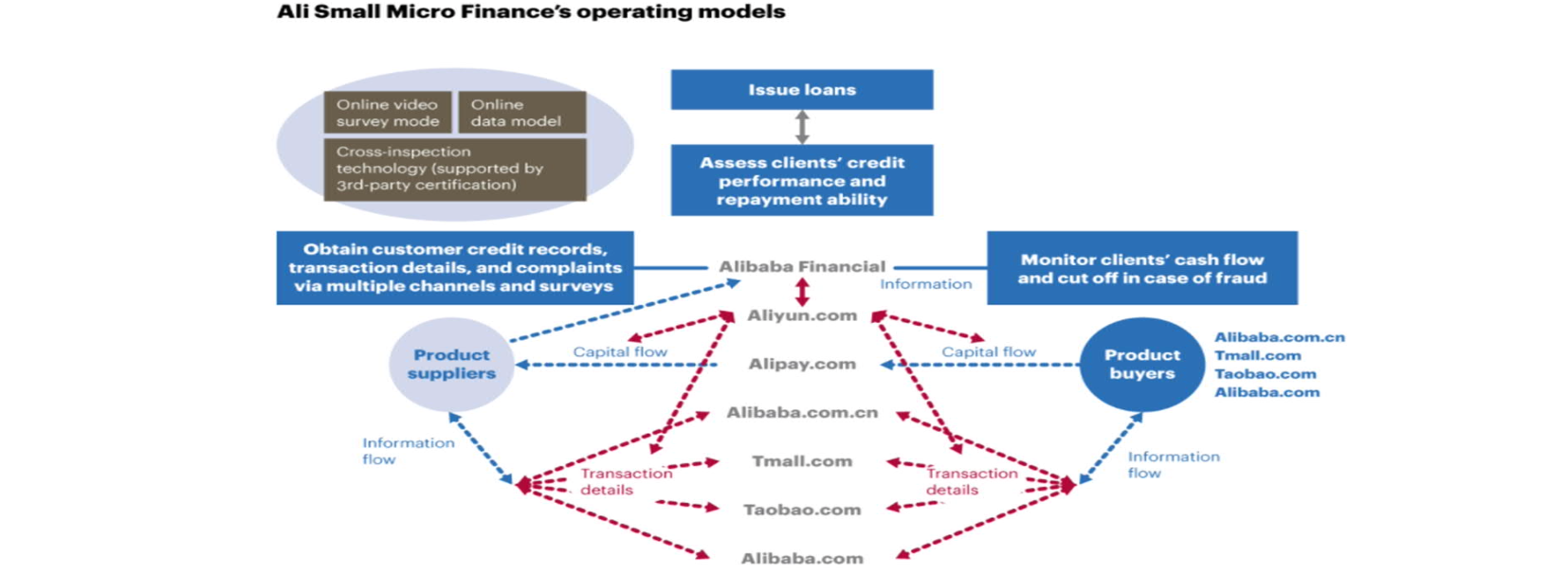
- Ant Financial & sesame credit
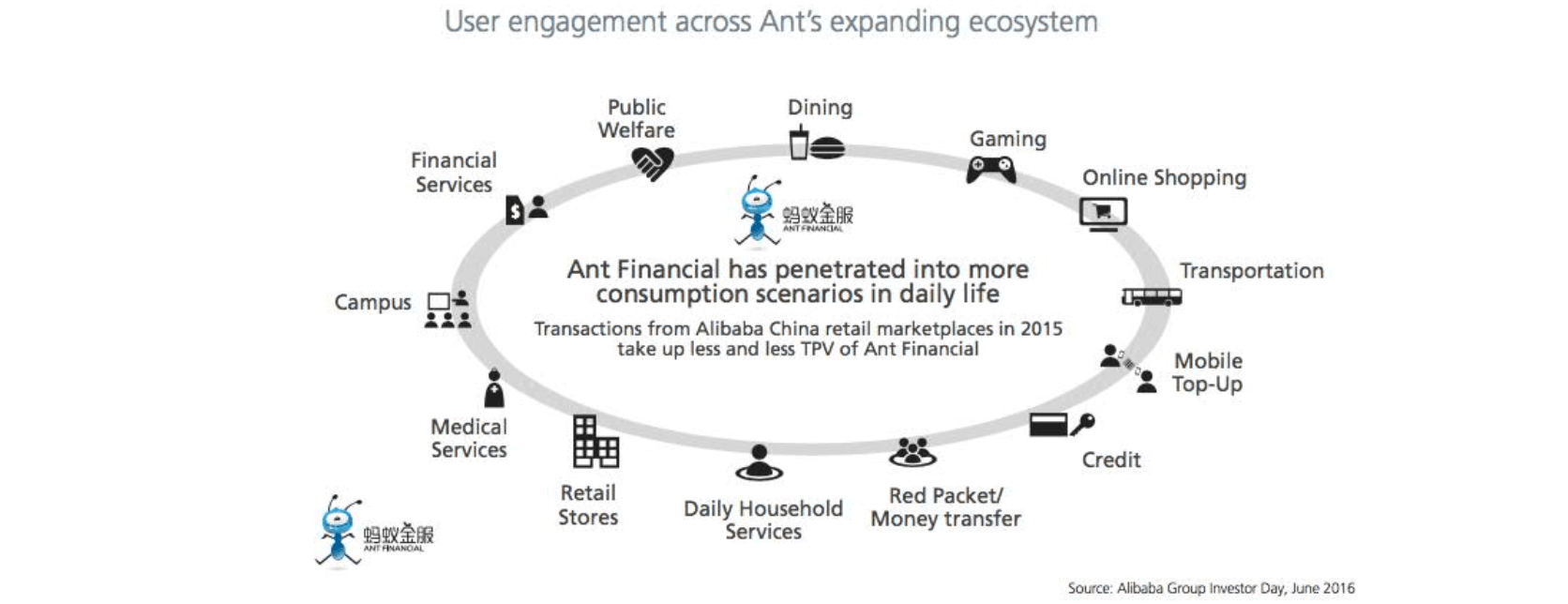
- consumption scenarios
- creating real-time datastreams
- consumption scenarios
AI-Enabled Insurance
Overview
- insurance technology
- is an important sector of the financial services industry
- the reason of using InsurTech
- more accurate
- better predictions and better at spotting claims fraud via video, e.g. Lemonade 1 min. claim
- “unbiased”
- reduced agent favoritism or outright corruption, e.g. Ping An Medical Insurance/OneConnect
- fast
- speeds the application and ID verification & approval process and the customer experience, e.g. Ant Financial auto 6 seconds vs 6 days for claims reimbursement
- cheap
- more accessible medical care and emergency payment for rural and underserved areas, e.g. The Good Doctor telemedicine one-minute clinic
- more accurate
Lemonade’s AI bot is easy and fast
-
video description
-
top 5 data questions
- home address
- own or rent
- roommates, fire alarm, burglar alarm
- birthdate
- active renter’s insurance
Ethical Considerations
Assessing the risk of an automated decision making system
- beneficiary
- who is going to gain from the decision being made
- high risk from high benefits for the decision maker
- low risk from low benefits for the individual
- because of a unbalanced situation
- data immutability
- if decisions are made on the basis of characteristics people are born with such as age and ethnic origin
- this is higher risk and more controversial than lifestyle choices such as the music people like or what they watch on TV
- impact
- what effect is a decision going to have
- a life or death decision about cancer treatment is much more important than whether or not to send someone a 10% coupon for frozen pizza
Approaches of using predictive models for “high risk” decisions
- try to identify at risk groups
- separate score distribution reports can be compared to see if certain groups will be adversely treated
- a more fair treatment
- for lower than average scoring groups, constraints and over-ride rules as well as different cut-offs can be set
- continue to monitor the situation once the decision making system goes live
- review score profile and decision rules for key groups
- fine tune cut-offs, constraints, and over-rides
InsurTech
-
Axa - $10k large-loss claims
- video description (until 9'20'')
-
ethical considerations for Axa
- what are the automated decision rules that will use the predictions of the large-claim predictive model
- who might be at-risk groups
- what constraints, over-ride, cut-offs should be set for risk groups
- how to monitor
- how to protect reputation if the large-claim predictive model is used to “screen out” undesirable drivers
-
different legislative regimes
- US utilitarian approach
- personal data can be harvested for business goals
- if there is a problem using a specific type of data, unacceptable bias against a specific group, legislation is enacted to address that concern
- European Union rights based approach
- personal ownership of data, companies have no right to hold or use personal data unless the individual gives permission
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulations) for EU citizens and transactions, “right to erase”
- US utilitarian approach
Additional Reading
ecom7122 entrepreneurship development and fintech ventures in asia entrepreneurship fintech machine learning insurance technology ethical considerations
874 Words
2021-03-23 17:07