5 minutes
ECOM7123 Smart Mobility
Overview
Mobility
- definition
- mobility describes the ability of people and goods to move around an area, and in doing so to access the essential facilities, communities & other destinations that are required to support a decent quality of life & a buoyant economy
- mobility incorporates the transport infrastructure & services that facilitate these interactions
- challenges of urban mobility
- overview
- congestion
- energy crisis
- pollution
- climate change
- details
- increasing demand for travel in city centers, suburbs & between the two areas
- increasing demand for improved intercity mobility
- requiring faster & more direct connectivity between destinations
- increasing city traffic, pollution, waste production & CO2 emission
- overview
Smart Mobility
Goals
- contents
- optimise traffic flow & increase connectivity
- operational efficiency
- managing capacity & efficient use of existing physical infrastructure
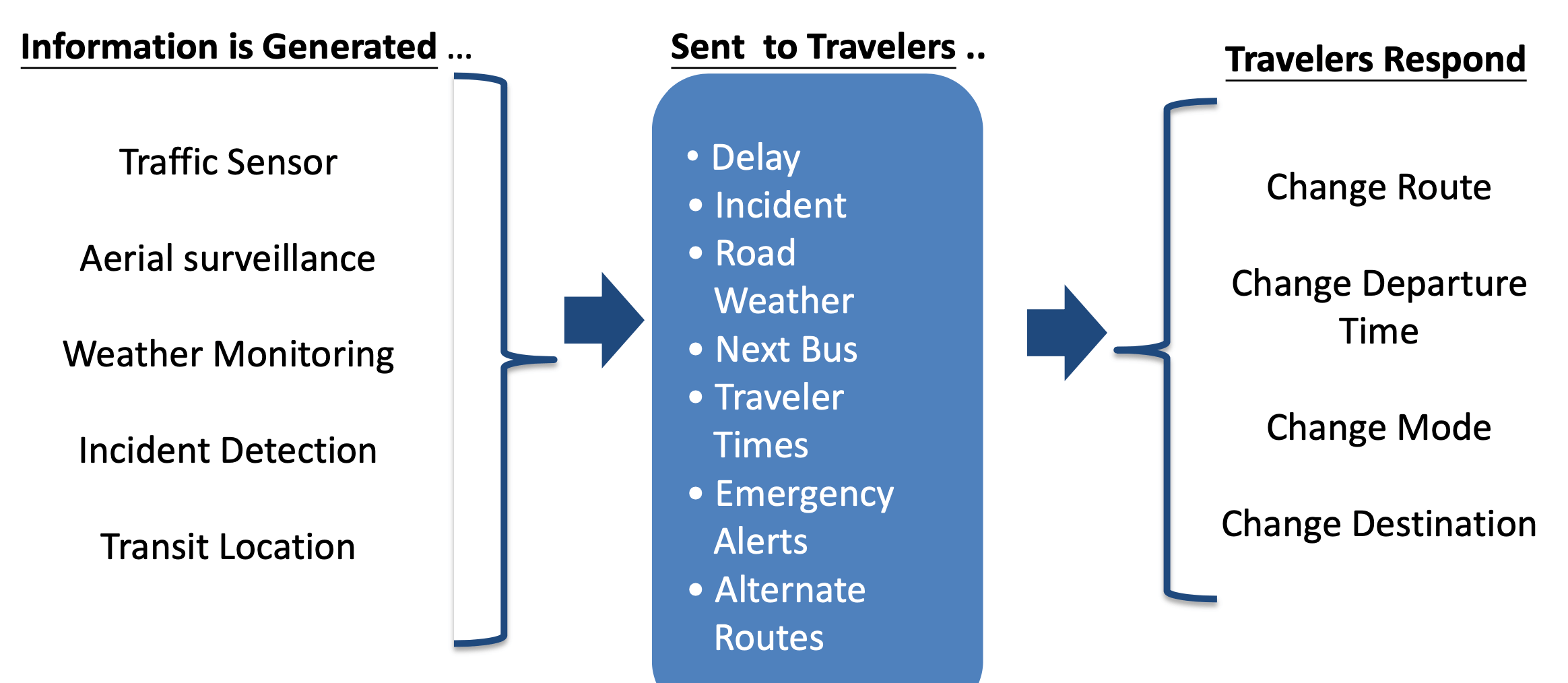
- distribute information to travelers about the benefits of different travel options
- reduce pollution, traffic congestion and costs
- improve people safety, transfer speed and efficiency
Structure
- overview
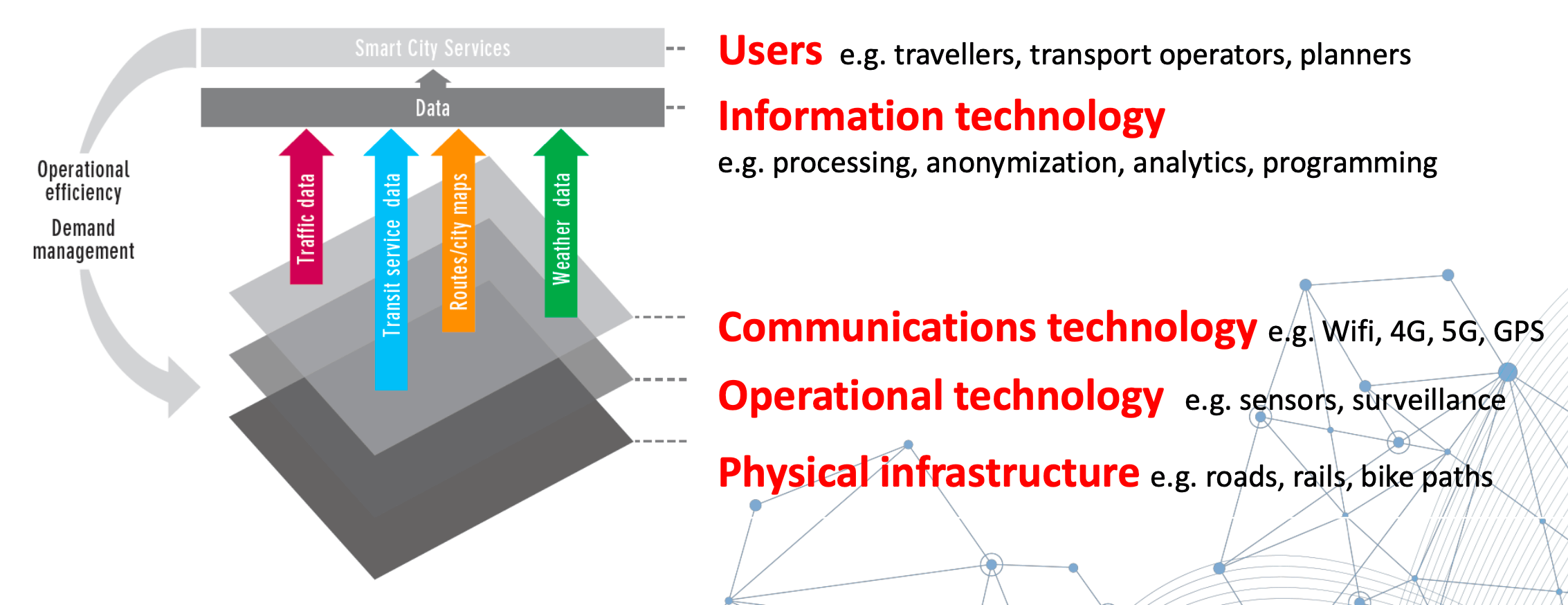
- physical infrastructure
- including
- pedestrian pathways
- walkability - the friendliness of walking, pedestrian pathway design
- provide health, economic & environmental benefits
- technology of walkability
- site selection to identify walkability zones
- walkability zones mapping
- walking network modelling
- apps for multi-model network routing analysis
- design criteria
- close to city center
- close to public transport
- close to walkable streets
- close to shops, restaurants, culture
- close to parks
- close to water
- perimeter block shape
- walkability - the friendliness of walking, pedestrian pathway design
- bicycle lanes
- enable bicycle commuting
- for short distance travel
- bicycle sharing system
- e.g., Amsterdam, Budapest, Paris, San Francisco, Barcelona and China
- railways (mass transit)
- fast & efficient
- high capacity
- economical for travelers
- environmental friendly by eletrified trains
- achieved by high speed trains (> 200km/h)
- high speed train systems around the world
- China, Taiwan, Japan, France, Italy, South Korea, etc.
- pedestrian pathways
- aims
- optimize journeys, traffic within & between cities
- save energy
- reduce carbon emissions
- including
Technology and usage
- GPS (Global Positioning System)
- operate by 24 satellites orbiting around the earth
- broadcast signals for location fixing
- vehicle location fixing and tracking
- real time positioning & navigation
- communication technologies
- wireless communications
- wifi
- radio modem: UHF, VHF
- 3G, 4G, 5G
- 5G
- the speeds & data processing capabilities support autonomous vehicles
- 4G: travel 60cm before it can stop
- 5G: travel 7cm before it can stop
- high speed (at least 10 times faster than 4G)
- extremely low latency
- the speeds & data processing capabilities support autonomous vehicles
- 5G
- real time data collection
- remote control
- GIS (Geographic Information System)
- a system designed to capture, store, manipulate, analyze, manage, & present spatial or geographical data
- digital maps to illustrate locations
- provide functions for location based analysis
- routing analysis: best route
- buffer analysis: crash analysis
- integrate with GPS for vehicle tracking & navigation
- usage
- understand travel patterns
- project capital improvement
- manage roadside assets
- share real time collected travel data
- improve ove rall safety and security
- help response to crisis and traffic incidents
- coordinate between travel agencies and entities
- identify ways for cost saving during journey
- assist in planning, managing and growing ITS
- help avoid congestion
- AI
- reduce vehicle emission in car park
- reduce time to find parking space
- avoid accident caused during parking
- increase parking space utilization
- drivers no need to memorize parking location
- secure & safe
- Geo.AI (Geospatial + AI) to predict traffic conditions
- surveillance technologies
- CCTV
- real time monitoring on traffic and road conditions
- road safety monitoring
- sensing technologies
- vehicle based & infrastructure based
- collect real time data / traffic conditions
- sends back to control centers for decision making & traffic management (IoT)
- avoid vehicle collision
- auto payment
- electric car
- use electrical energy stored in rechargeable batteries
- reduce air pollution cased by traditional automobiles
- infrastructure required – build charging station at convenience places
- connected car
- a car with devices that connects to other devices within or outside the car, such as other cars, home, office or infrastructure
- equipped with internet access to share information outside the car
- advantages
- infotainment
- safety
- diagnostics efficiency
- navigation
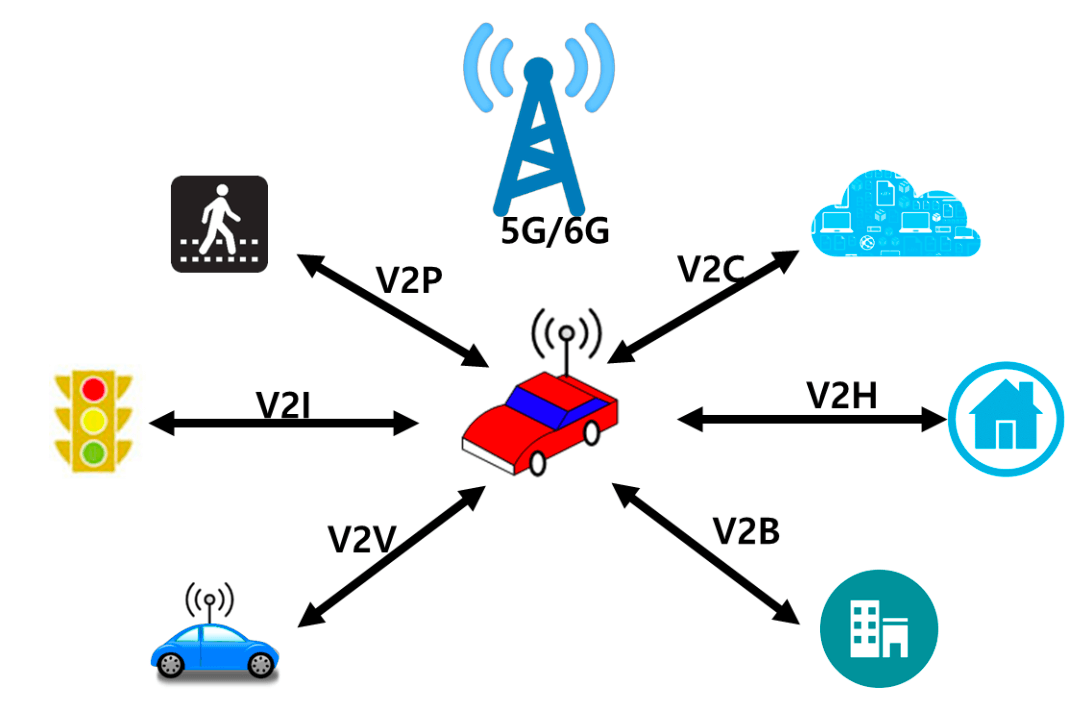
- vehicle to everything (V2X)
- the passing of information from a vehicle to any entity that may affect the vehicle, and vice versa
- all vehicles and infrastructure systems are interconnected with each other
- provide more precise knowledge of the traffic situation across the entire road network
- advantages
- optimize traffic flows
- reduce accident numbers
- reduce congestion
- minimize emissions
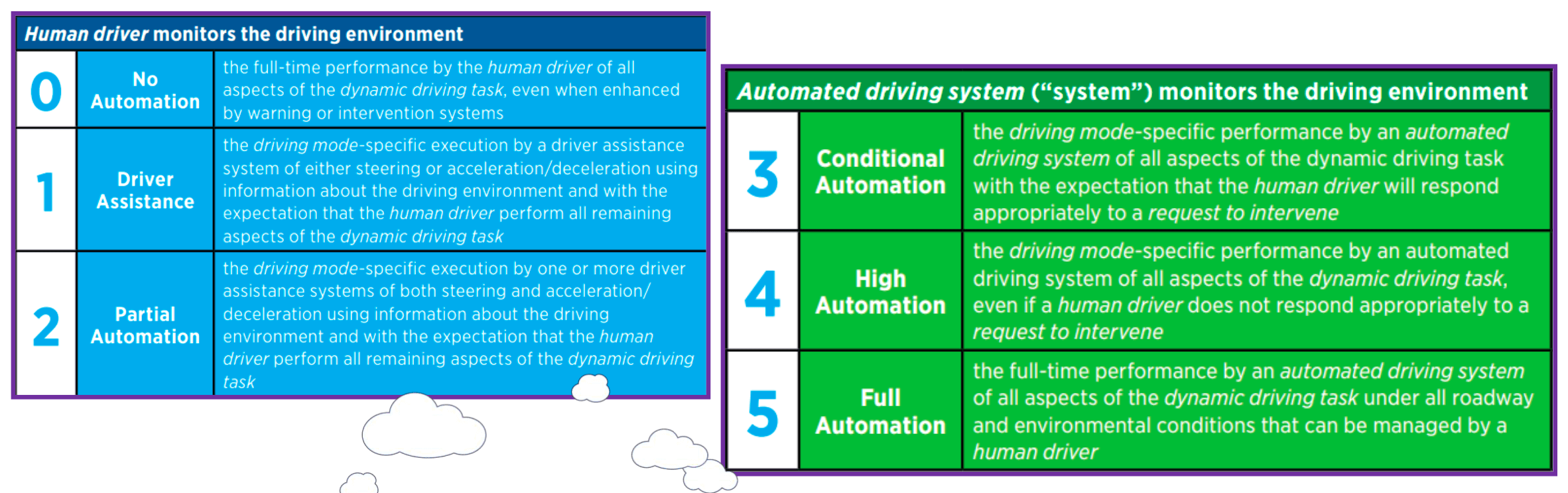
- autonomous car
- driverless car
- run on electricity or hybrids
- equipped with autopilot computer systems and cameras to monitor car’s surroundings
- under trial and technology is in preliminary stages
- 6 levels of automation by SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers)
- bicycle sharing system
- allow people to borrow a bike at a location & return at specified collection points
- infrastructure required – bicycle lanes
- help reduce carbon emission and road congestion
- ITS (Intelligent Transport System)
- integrated application of advanced technologies using electronics, computers, communications & advanced sensors
- these applications provide important information to travellers while improving the safety & efficiency of the transportation system
- smartphone & mobile apps technologies
- mobile apps for transportation
- user based
- disseminate traffic data
- analysis and convert traffic data to meaningful applications
- change user behavior to utilize road network resources
- example - arrival time estimation apps
- end user based
- assist journey time planning
- change user behavior to use public transport
- avoid congestion and peak
- ERP (Electronic Road Pricing)
- a traffic management tool to tackle road traffic congestion
- rationalize traffic flow in targeted areas where severe traffic congestion occurs
- based on the “user pays” principle
- technologies
- ANPR (Automatic Number Plate Recognition)
- use cameras to capture the images of license number plates
- DSRC (Dedicated Short-ranged Radio Communication)
- pre-install an in-vehicle unit for information exchange with the equipment mounted on ERP pole using wireless communication
- geofencing (a GIS application)
- delineate a virtual boundary / area
- when object goes in or leave the area, alert / message / action will be generated
- ANPR (Automatic Number Plate Recognition)
- IVU (In-Vehicle Unit)
- using RFID tag
- payment
- FFTS (Free-Flow Tolling System)
- ERP
- parking
- real-time traffic data collection
- traffic management
- big data analysis
- source data inputs
- smartphone partners
- automotive OEM partners
- mobile apps
- telematics
- portable navigation devices
- fleet management systems
- then
- to utilize these data can promote efficiency and create opportunities to the community at large
- inspire people to innovate solutions to deal with traffic is sues such as congestion and accidents
Transportation of tomorrow
- ultimate goals
- future
- data-rich
- high accuracy
- real-time
- high-speed
- trusted & secure
- resilient
Additional Reading
ecom7123 building smart cities: an information system approach smart city smart mobility
1017 Words
2021-01-07 09:44