5 minutes
ICOM6045 Internet Layer Security
Overview
Firewall
- definition
- a firewall is a combination of hardware and software that isolates an organization’s internal network from the Internet, allowing some packets to pass and blocking others
- functions
- firewall can also provide segmentation between internal resources
- in the simplest form, firewall control access to, from and between networks within the organization and the internet
- scenario
- the home router would have the functions of firewall, but it is only a little
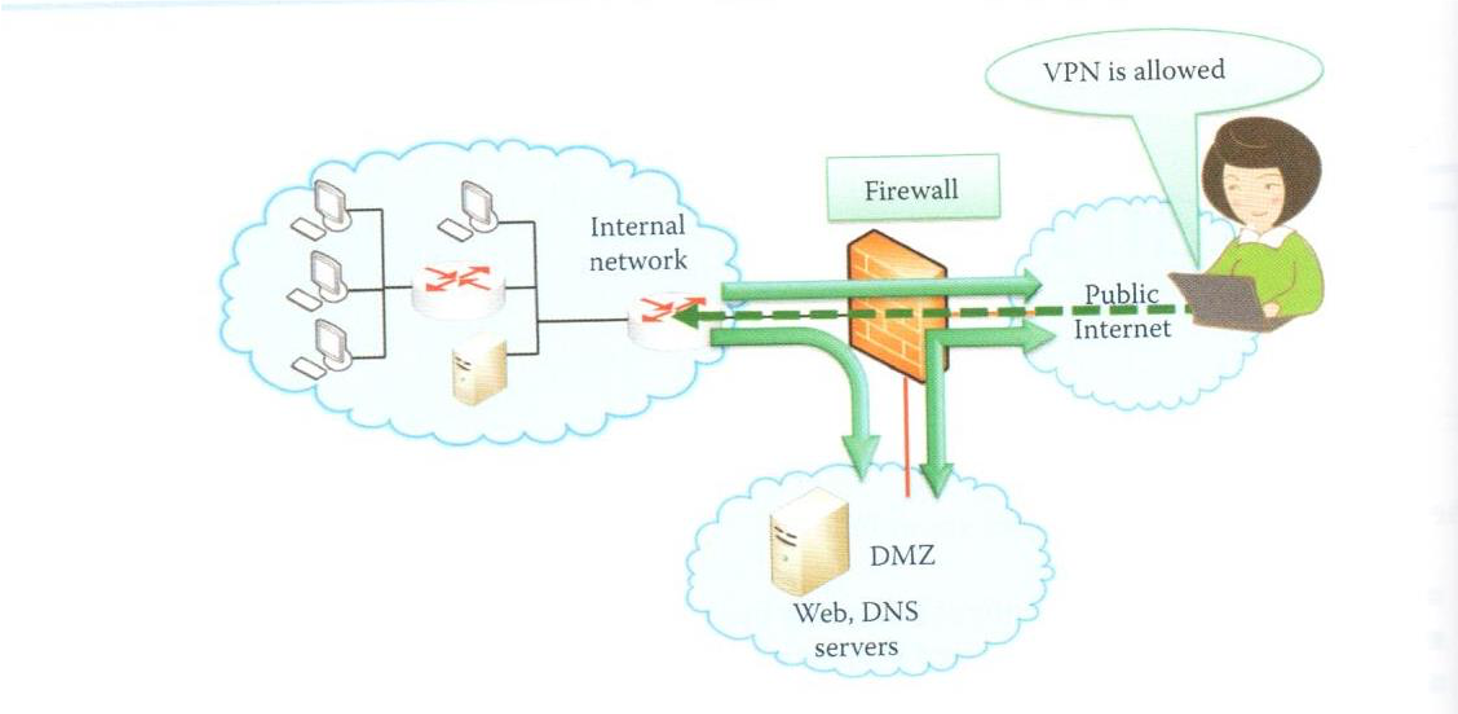
DMZ (Demilitarized Zone)
- definition
- a physical or logical subnetwork that contains and exposes an organization’s external services to the Internet
- functions
- the purpose of a DMZ is to add an additional layer of security to an organization’s local area network (LAN)
- an external attacker only has access to equipment in the DMZ, rather than any other part of the network
- typical services in DMZ
- web server
- proxy server
- email server
- reverse proxy server
- difference between firewall and DMZ
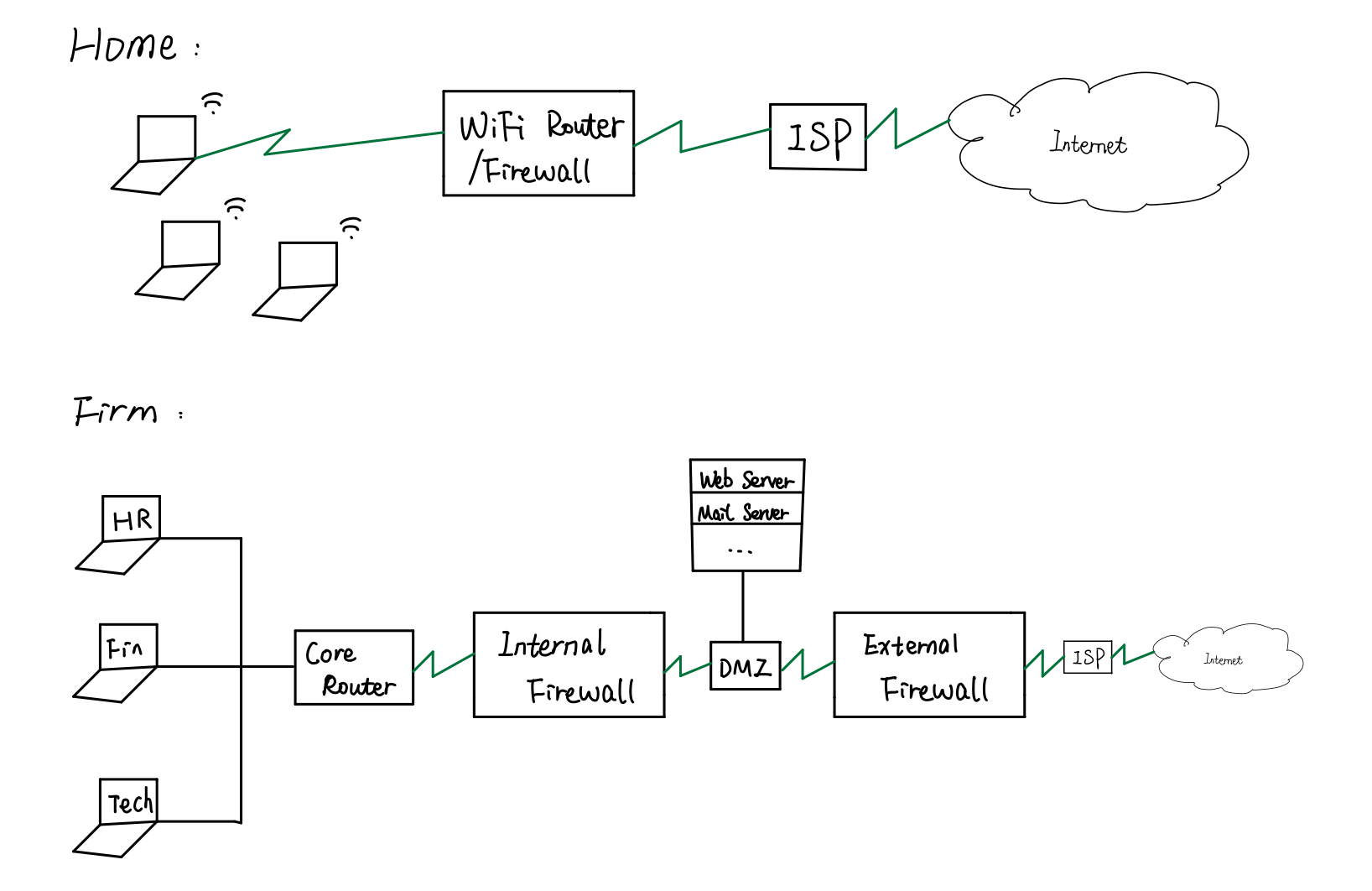
- commerical use
- because two firewalls are more expensive, using following method
- because two firewalls are more expensive, using following method
UTM (Unified Threat Management)
- contains up to 8 components
- firewall
- content filtering by proxy server
- network address translation (NAT)
- virtual private network (VPN)
- anti-virus
- anti-spam
- URL filtering
- intrusion detection/prevention system (IDS/IPS)
- advantage
- low cost all-in-one tools that are deployed to small to medium businesses: usually deployed at the edge of the enterprise network
Types of Firewalls
Overview
- packet filtering – network layer
- a multi-ported IP router that applies a set of rules to each incoming/outgoing IP packet and decides whether it is to be forwarded or not
- nowadays, almost home routers can do this
- proxy gateway – also known as application layer gateway, proxy server
- a gateway from one network to another for a specific network application, acts as a proxy on behalf of the network users
- circuit level inspection socks (i.e. sockets)
- a protocol that is application independent and transparent to user, performs filtering at the session layer (no content filtering)
Packet filtering
- stateless packet filtering
- process
- an organization usually has a router that connects its internal network to its ISP, then to the internet: all traffic leaving and entering the internal network passes through this router
- most router provides option for filtering, i.e. some data packets pass through the router and filter out other data packets
- typical filtering decision are based on
- source IP address
- destination IP address
- source port
- destination port
- other data fields that commonly used by hackers, e.g. TCP SYN or ACK bits
- example
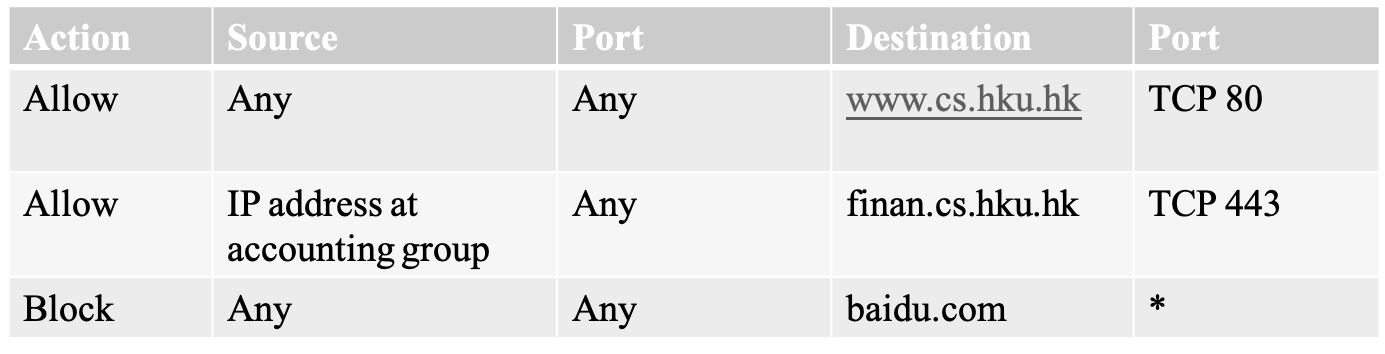
- problem
- IP fragmentation
- a TCP segment or a UDP datagram is too big to fit into one packet
- port numbers and TCP ACK flag can be obtained from the first fragment only
- impossible to filter except the first packet
- need to introduce states into packet filters
- commercial firewalls
- support packet filter per connection and service
- support actions other than “permit” and “deny”, such as user authentication and encryption, e.g. “perform FTP connection between any IP address and 123.14.6.23 if user authentication is successful”
- a TCP segment or a UDP datagram is too big to fit into one packet
- only control access based on source and destination information, do not monitor state of communication and application information
- e.g. unable to limit certain users to use some services such as telnet
- managing filtering rules is cumbersome, leading to simple mistakes
- such as giving access right to threatening packets
- having a poorly configured firewall is worse than having no firewall at all because it gives you a false sense of security
- IP fragmentation
- process
- filtering based on IP addresses
- example
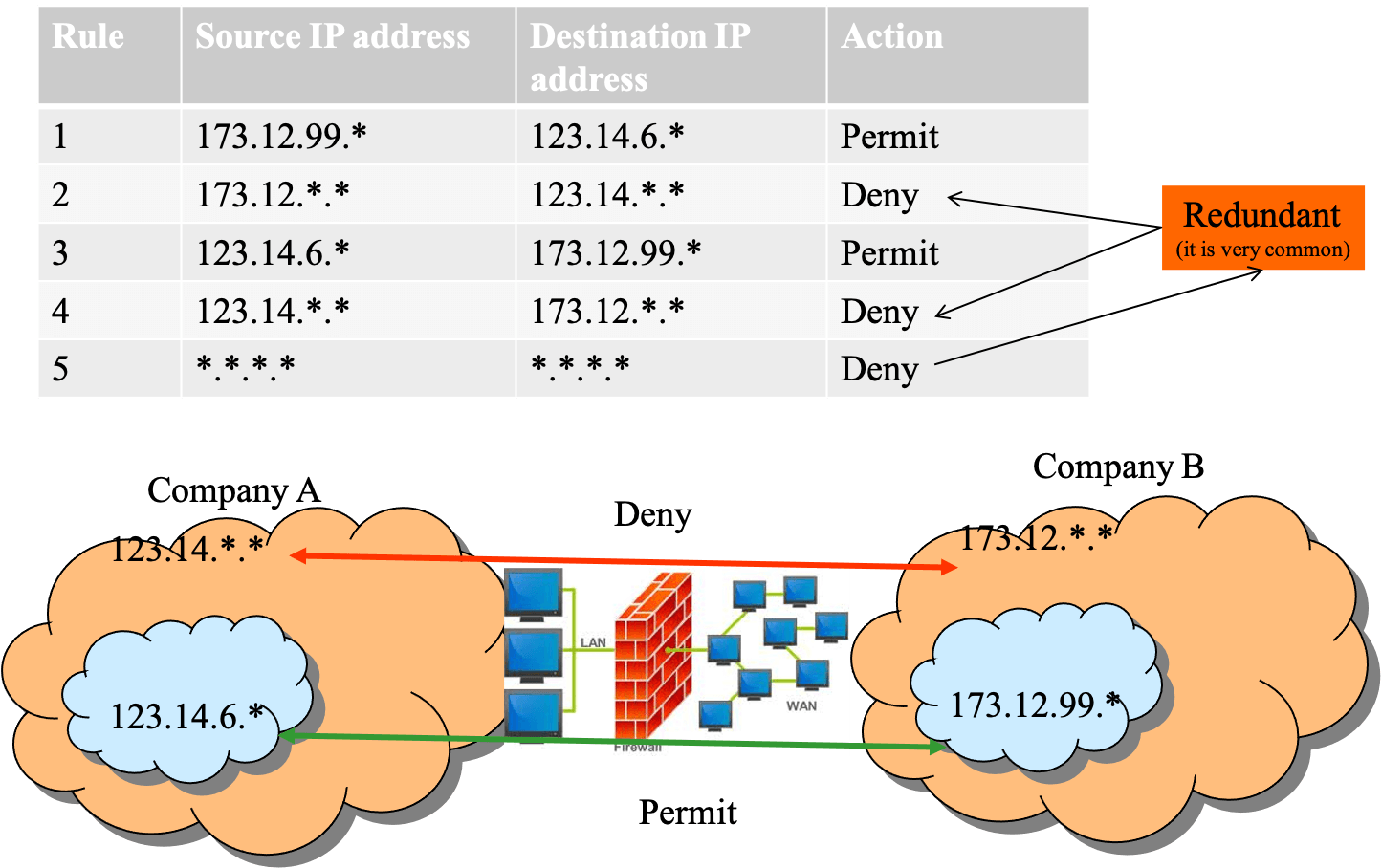
- example
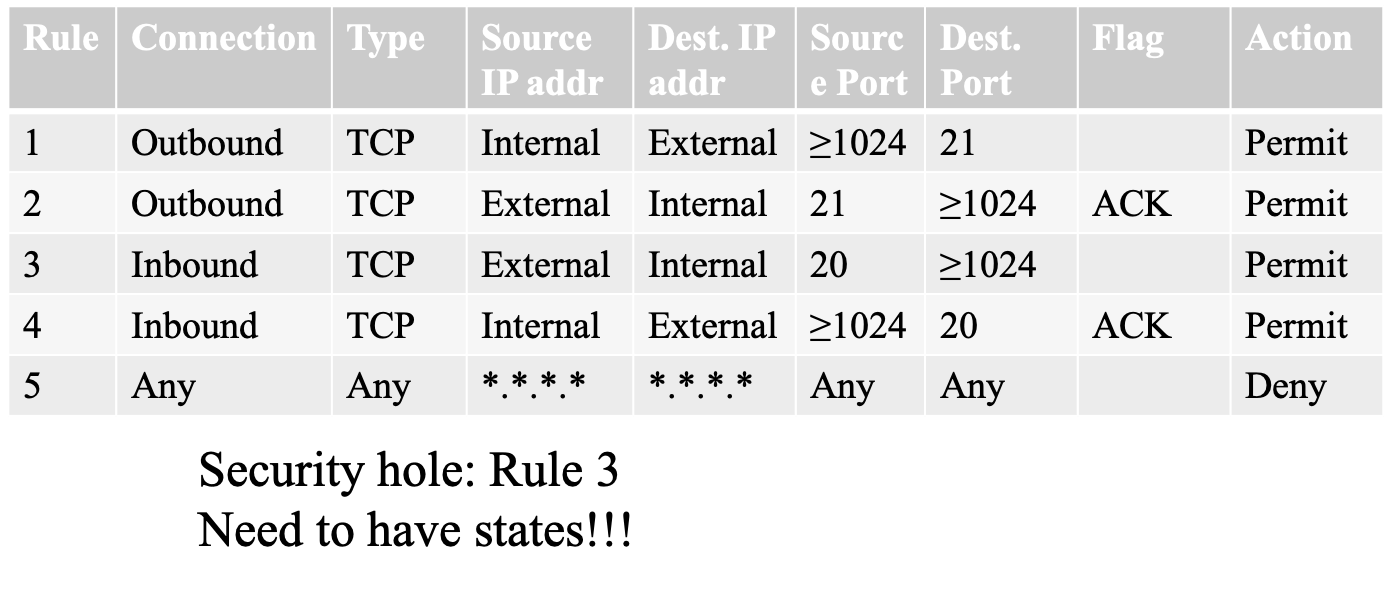
- filtering based on IP addresses and port numbers
- inbound and outbound connection
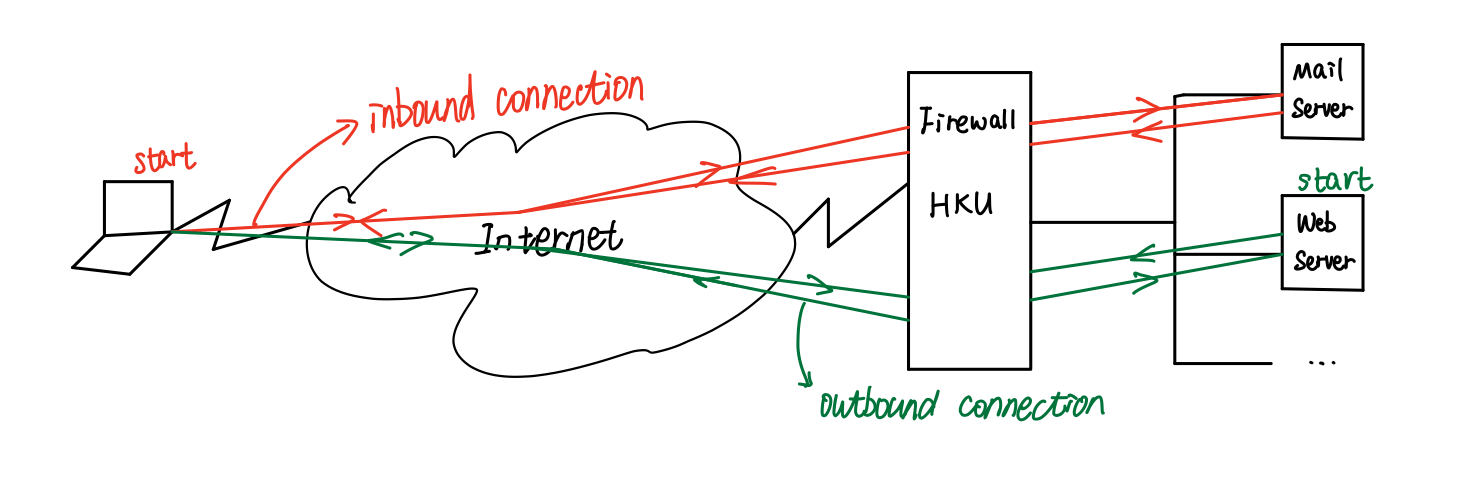
- example
- rule 3 and rule 4 are in pair, but rule 4 is not secure
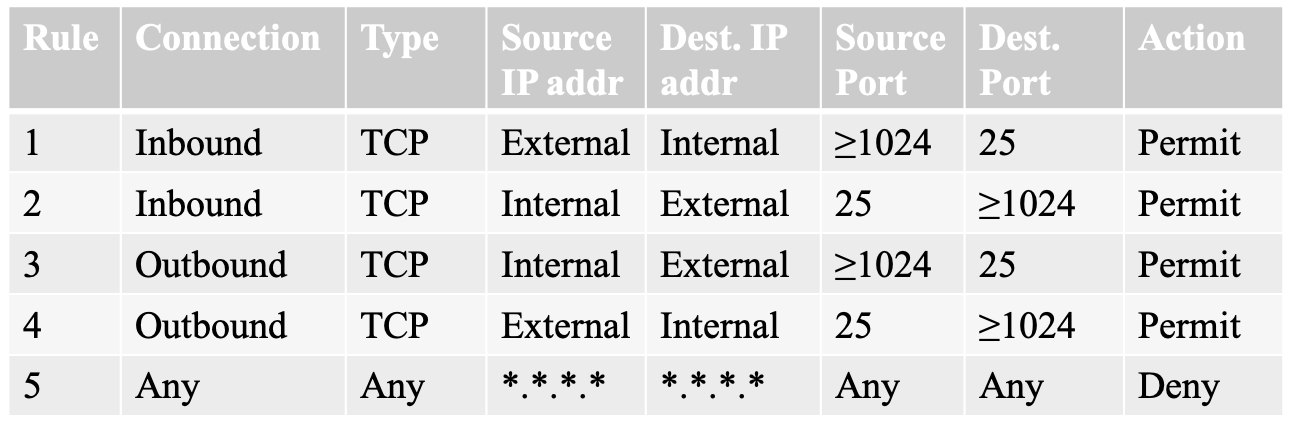
- rule 3 and rule 4 are in pair, but rule 4 is not secure
- inbound and outbound connection
- filtering with ACK flag
- example
- rule 1 starts the connection
- rule 2 is a trust packet
- rule 4 should apply only to established connections that are initiated by an internal client (no trust packets)
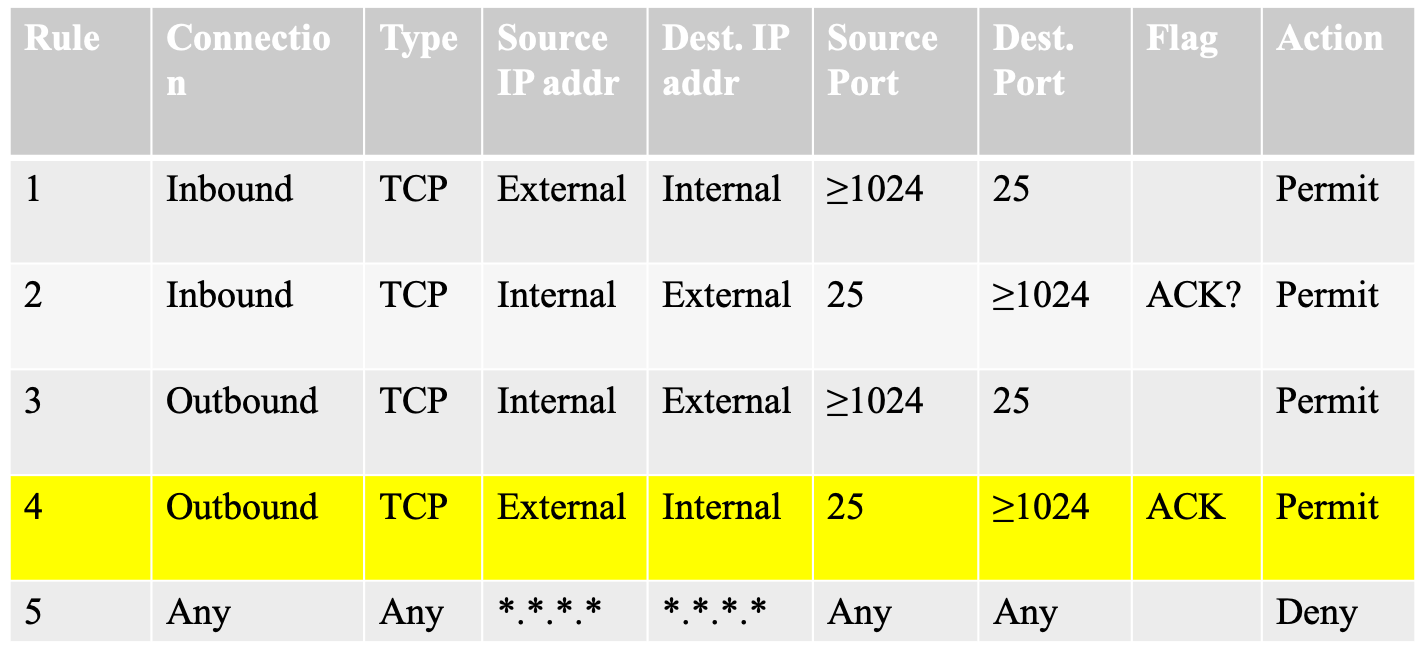
- problem -> FTP problem
- FTP uses multiple ports
- client (random port) initiates FTP connect to port 21 of the FTP server
- FTP data transfer on port 20, initiated by the FTP server to the client (another random port)
- FTP uses multiple ports
- example
Proxy gateway
- TCP 3-way handshake
- client to server: (SYN flag, SeqNumC)
- server to client: (SYN/ACK flag, AckNumS=SeqNumC+1, SeqNumS)
- client to server: (ACK flag, AckNumC=SeqNumS+1)
- SYN flooding
- send TCP connection requests faster than a system can process them
- exhaust states in the TCP/IP stack (only two handshakes, the third one may wait until timeout)
- cannot use packet filtering, because each request is compliant
- mechanism
- proxy gateway completes the 3-way handshake, if the process is finished, the client would be connected to the real server
- passive gateway (not widely used)
- similar to gateway mechanism except it does not send the ACK immediately, but with a shorter timeout period
- stateful packet filter (NAT)
- a medium translate the public IP address to the private IP address (dynamic), achieving the gateway function
- binding through not common used port numbers
- problems
- when port number cannot be changed, e.g. service supported by a server
- when an external server must distinguish between clients based on their IP addresses, e.g. peer-to-peer application
- methods in handling incoming requests in NAT
- application level gateways
- static port forwarding
- Universal Plug and Play (UPnP)
- Internet Gateway Device (IGD) protocol
- Traversal Using Relays around NAT (TURN)
Socket secure
- sockets sits at layer 5, which can handle several request types, including HTTP, HTTPS, POP3, SMTP and FTP
- it can be used for email, web browsing, peer-to-peer sharing, file transfers and more
Questions
Q: Why some companies purchase firewall software rather than UTM?
A: Although UTM is cheaper, considering the performance, some firms choose firewall eventually beacuse UTM puts a lot of functions together.