4 minutes
ECOM7123 IoT, Big Data Analytics and AI

IoT
Overview
- features
- everything is connected
- tying together the physical, digital and analytic worlds
- connectivity and the “any” dimension
- IoT allows people & things to be connected anytime at anyplace with anything and anyone using any network and any service
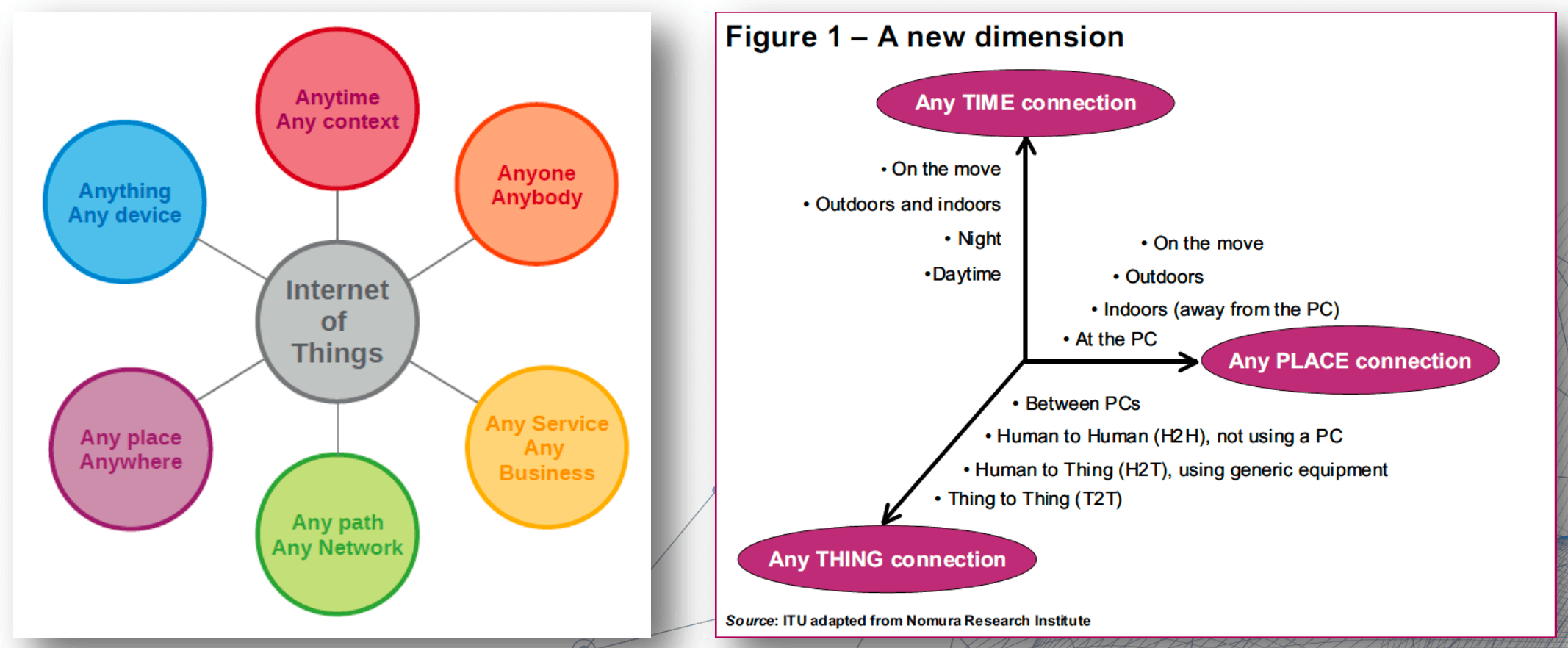
- IoT allows people & things to be connected anytime at anyplace with anything and anyone using any network and any service
Evolution
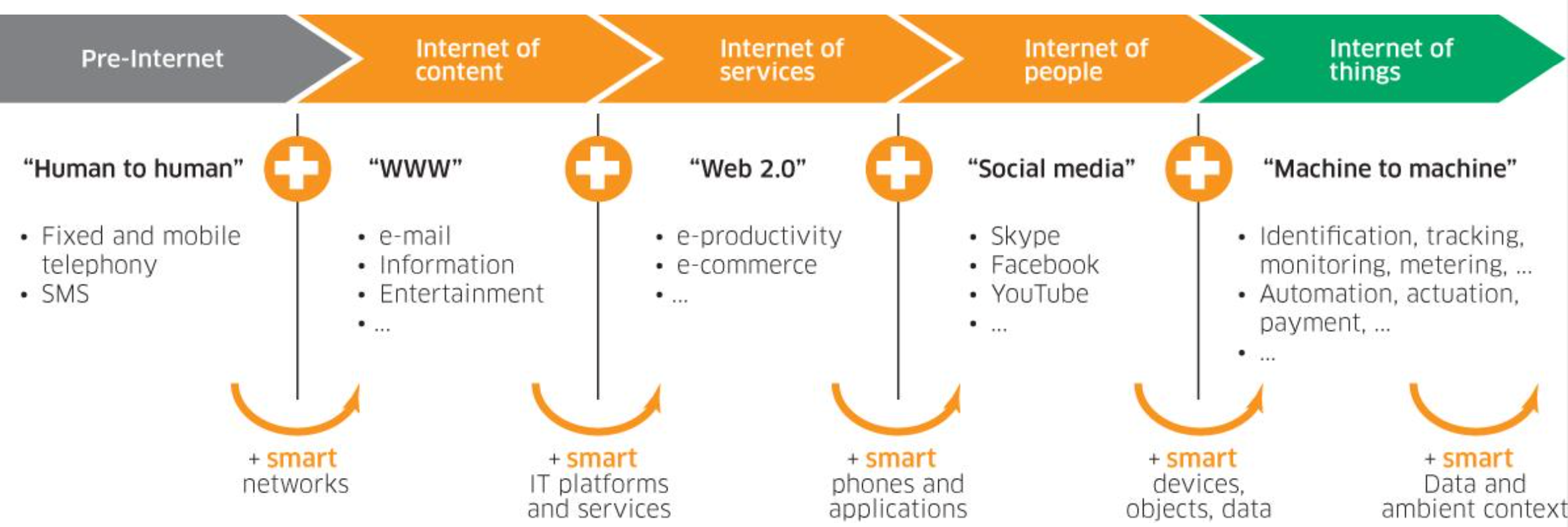
Characteristics
- dynamic changes
- heterogeneity
- things-related services
- inter-connectivity
- enormous scale
Architecture
- sensor and identification layer
- information generation
- lowest abstraction layer
- with sensors we are creating digital nervous system
- incorporated to measure physical quantities
- interconnects the physical and digital world
- collects and process the real time information
- examples
- barcode & QR code
- RFID
- smartphone sensor
- network construction layer
- information transmission
- robust and high performance network infrastructure
- supports the communication requirements for latency, bandwidth or security
- allows multiple organizations to share and use the same network independently
- examples
- telecommunication systems (e.g., GSM, UMTS, LTE)
- WLAN
- short range (e.g., bluetooth)
- NB-IoT (Narrowband Internet of Things) & LoRa (Long Range Radio)

- satellite systems
- broadcast systems
- fixed wireless access
- SNs (Sensor Networks)
- consist of a certain number of sensing nodes communicating in a wireless multi-hop fashion
- SNs generally exist without IoT but IoT cannot exist without SNs
- applications
- environmental monitoring
- agriculture
- medical care
- event detection
- 5G
- dramatically increase
- speed of data transfer
- response time
- capacity for billions of devices to be connected
- dramatically increase
- management layer
- information processing
- capturing of periodic sensory data
- data analytics
- streaming analytics (process real time data)
- ensures security and privacy of data
- integrated application layer
- information application
- provides a user interface for using IoT
- different applications for various sectors like transportation, healthcare, agriculture, supply chains, government, retail, etc.
Challenges
- lack of standardization
- addressing issues
- new network traffic patterns to handle
- device level energy issues
- security concerns
- privacy issues
Summary
- with billions of devices connected, vast amount of data can be generated
- data sharing/exchange among the devices will generate new data as well
- data analytics is necessary to analyze the data to acquire insights and trends
Big Data
Overview
- sources
- users
- applications
- systems
- sensors
- structure
- unstructured
- data that has no inherent structure and is usually stored as different types of files
- e.g., PDFs, images
- quasi-structured
- textual data with erratic formats that can be formatted with effort and software tools
- e.g., clickstream data
- semi-structured
- textual data files with an apparent pattern, enabling analysis
- e.g., spreadsheets and XML files
- structured
- data having a defined data model, format, structure
- e.g., database
- unstructured
- tradition data vs big data
- traditional data
- large scale
- highly centralized
- structured
- files
- records
- databases
- sequential
- indexed
- processing transactions
- big data
- massive scale
- highly distributed
- unstructured
- emails
- audio/video
- blogs, etc.
- random
- looking for patterns and relationships
- traditional data
Characteristics
- volume
- the vast amounts of data generated every second
- velocity
- the speed at which new data is generated and the speed at which data moves around
- veracity
- the messiness or trustworthiness of the data
- variety
- the different types of data can now be used
- value
- having access to big data is no good unless we can turn it into value
Types
- activity data
- conversation data
- photo & video image data
- sensors data from IoT devices
- real time data
- spatial data
- spatiotemporal data
- is an extension of spatial database
- captures spatial and temporal aspects of data and deals with geometry changing over time and location of objects moving over invariant geometry
Big data and location
- all IoT sensors have loactions
- the most common IoT sensors in smartphones - GPS receiver
- all posts, photos and messages are tagged with phone or IP locations in social media
- geospatial big data analytics
- requires new science of spatial statistics
- GIS as a tool for spatial statistical analysis
- aggregate data
- join data
- summarize data
- calculate data
- find hot spots
Issues
- data privacy
- data security
- data discrimination
- data accuracy
- data existence
AI
Overview
- relationship
- IoT is the “senses” (connect devices and collect data)
- big data is the “fuel” (capture, storage, analysis of data)
- AI is the “brain” (data-based learning, analytics, automation)
- AI & ML & DL
- AI
- board definition
- building machines that learn & think like people
- ML
- ability to learn & improve its performance without human interaction
- DL
- solve any problem which requires “thought”
- feed a lot of data
- learn from its mistakes
- AI
Development
- basic (weak AI)
- specialize in a certain scope
- advanced (strong AI)
- think & operate like a human being
- super advanced (Artificial Superintelligence)
- smarter than the best human brains
The rules for success
- computing power
- data
- algorithms and architecture
8 ways AI will transform our cities smarter by 2030
- transportation
- education
- healthcare
- public safety
- home & service robots
- employment & workplace
- entertainment
- low-resource communities
Additional Reading
ecom7123 building smart cities: an information system approach smart city iot big data ai
750 Words
2021-01-09 09:23