5 minutes
ECOM7123 Smart Environment and Energy
Overview
Smart environment
- objectives
- green & sustainable urban planning
- effective management and optimization of urban resources
- achieve energy saving and emission reduction
- scopes
- greening
- land use planning
- environmental protection & pollution control
- smart & green building
- smart waste management
- smart water management
- smart & renewable energy
Details of Smart Environment
Greening
- definition
- the process of making somewhere greener and environmental friendly by planting grass, trees and plants there
- benefits
- create fresh, beautiful, comfortable and elegant environment
- improve urban living conditions
- purify air, reduce pollution, adjust climate, improve soil quality and ecology
- enhance visual environment
- greening techniques
- skyrise greenery
- all greening at the buildings or other structures beyond the ground level
- roof greening (main approach)
- vertical greening (main approach)
- sky gardens
- terrace planting
- all greening at the buildings or other structures beyond the ground level
- skyrise greenery
- tree management
- strategies
- tree maintenance
- tree register, routine maintenance, rick assessment and management
- tree protection
- registration of heritage trees, tree preservation
- planning and tree planting
- green development plans required from developers, tree selection and planting
- training
- train tree management professionals
- public management
- tree maintenance
- strategies
Land use planning
- definition
- is defined as the process of protecting and improving the living, production and recreation environment in a city through the proper use and development of land
- technology adoption
- remote sensing
- acquiring information about an object without touching the object itself
- acquired data is digitized and processed into image
- captures spatial (area), spectral (color) and temporal (time) data with accuracy, speed & cost effective on a repetitive basis
- drone/UAV (Unmanned aerial vehicle)
- aircraft without human pilot aboard
- remote control
- mounted with cameras to capture ground images
- monitor land use
- illegal landfill detection
- LiDAR (Light Detection And Ranging)
- measures distance to a target by illuminating that target with a laser light
- scan ground surface/objects
- monitor landscape changes and illegal dumping
- 3D modelling
- developing digital representation of any 3D surface of an object/landscape
- commonly used in urban planning
- visual impact analysis
- landscape analysis
- remote sensing
Pollution control
- Paris agreement
- came into force on 4 Nov 2016
- succeeding the Kyoto Protocol that expired in 2020
- signed by 197 countries in 2016 including China, and ratified by 185 as of Jan 2019
- carbon neutrality
- China - by 2060
- Hong Kong - before 2050
Smart & green building
- smart building - convenient direction
- definition
- deliver useful building services that make occupants more productive at the lowest cost and environmental impact over the building life cycle
- utilize integrated ICT technologies to operate & manage building services & functions
- require detailed planning during the inception stage as well as ensuring the longevity of the implemented technologies
- functions
- video surveillance
- access control
- power management
- programmable lighting
- facilities management
- data network and data center
- wireless systems
- building management system
- all integrated with IT
- definition
- green building - environmental direction
- definition
- the one that considers its impact on the environment and human health
- part of a global response to increasing awareness of the role of human activity in causing global climate change
- incorporates design, construction and operational practices that significantly reduce or eliminate the negative impact of development on the environment and people
- energy efficient, resource efficient and environmentally responsible
- measures
- reduce heat loads, maximize natural light, promote circulation of fresh air
- energy efficient air conditioning & lighting
- use environmentally friendly, non-toxic materials
- water efficient plumbing fittings and water harvesting
- using renewable energy sources
- sensitive to the impact to the environment
- definition
- smart building and green building have an intersection
Smart waste management
- examples
- clearbot, designed by HKU, HKUST & CityU
- effective waste recycling, Japan
- discarded plastic turns into jersey, Taiwan
- collecting food waste with IT, South Korea
- automatic vacuum waste collection system
- central compactor system
- smart rubbish bin
- reduce cost
- less truck
- less emission
- less fuel required
- less time
- eliminate overflow
- real-time waste tracking and monitoring
- GPS
- CCTV
- RFID for waste collection
- each bin tipping is recorded and used as basis of charging
- WTE (Waste to Energy)
- consist of waste treatment processes that produce energy in the form of electricity, heat, biogas, landfill gas or fuels from different waste sources
- energy is a by-product of waste treatment
- WTE technologies can be applied to sewage sludge and municipal solid waste
- amager bakke, Copenhagen, Denmark
- more than a WTE plant
- a landmark, a leisure facility
- the plant’s architecture includes a roof-wide artificial ski slope open to the public
Smart water management
- water intelligent network
- to manage and monitor water supply
- improve the efficiency, longevity, and reliability of the underlying physical water network by better measuring, collecting, analyzing, and acting upon a wide range of network events, e.g., leakage, blockage, etc.
- an integrated set of products, solutions and systems that enable utilities to remotely and continuously monitor and diagnose problems, prioritize and manage maintenance issues and use data to optimize all aspects of the water distribution network
- water network + sensors can generate data
- leakage management control
- identifies water leakage location
- analyze impact areas and affected customers
- implemented by GIS and dashboards
- AMR (Automatic Meter Reading) system’s advantages
- automatic reading of meters
- detection of abnormal water consumptions (e.g. leakage of inside service)
- better planning and management of water supplies
- availability of consumption data for resolving water charges disputes
- enhancing customer services through provision of Internet and mobile phone access to consumers for accessing their consumption data
- ideal platform for promotion of water conservation
Smart energy
- definition
- intelligent integration of decentralized renewable energy sources and power consumption to form the future energy ecosystem
- examples
- floating solar, Huainan City, Anhui Province, China
- panda solar farm, China
- through PV (Photovoltaic)
- smart lighting, Copenhagen
- wind energy
Trends for Smart Environment
Aspects and details
- smart metering
- citizens are encouraged to reduce energy consumption especially at peak level
- new micro-sources of power
- citizens use homes and offices to generate electricity
- smart & responsive appliances
- smart appliances can temporarily reduce energy consumption in peak energy demand periods
- self-healing grid
- IoTs are added to monitor real-time data
- able to detect & isolate faults & reconfigure the system to minimize impact on customers
- lower usage through gamification
- the data generated by smart meters can be used to create detailed insight into energy usage patterns
- localized environmental enforcement
- embedded sensor networks & intelligent algorithms can provide data to human analysts
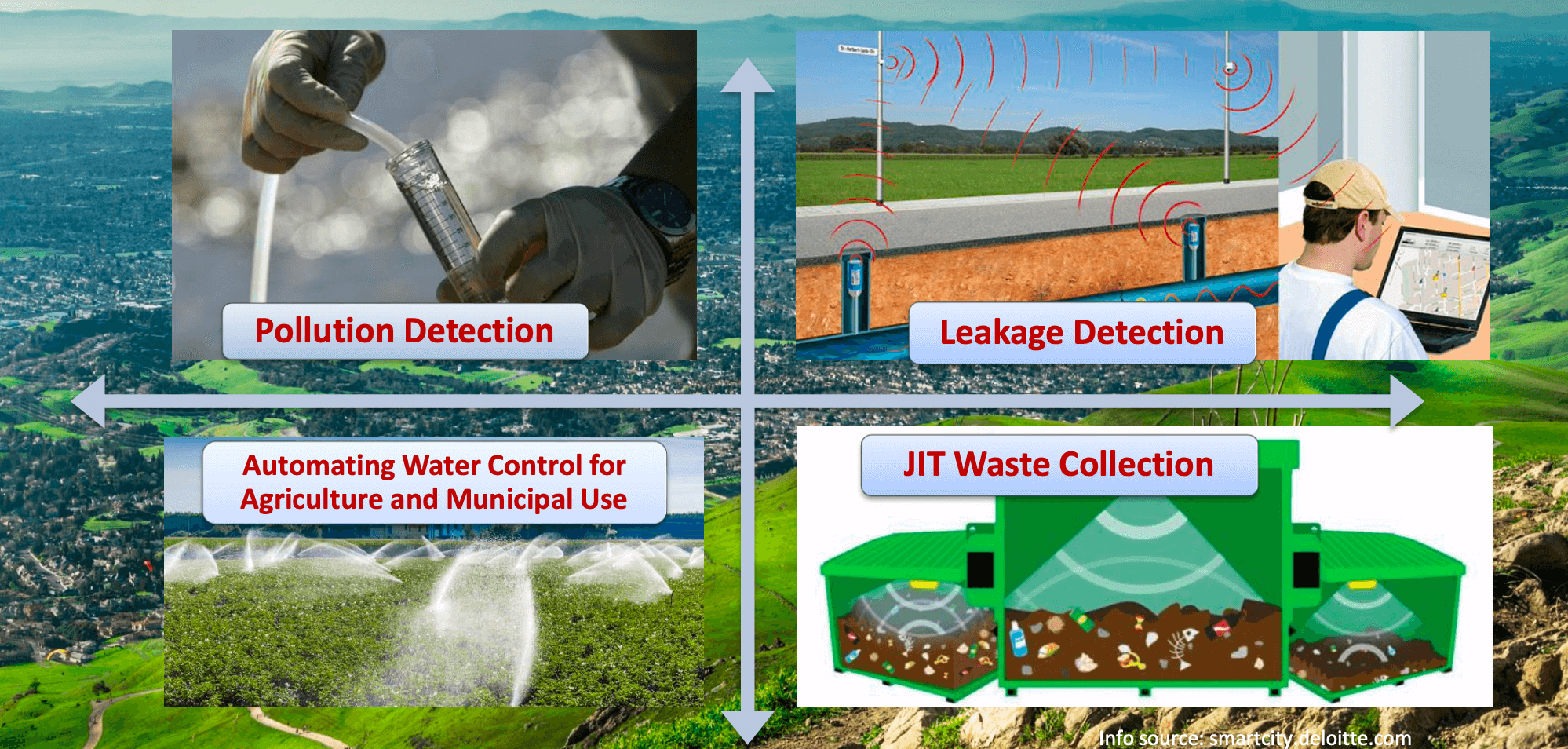
- embedded sensor networks & intelligent algorithms can provide data to human analysts
Additional Reading
ecom7123 building smart cities: an information system approach smart city smart environment smart energy
1017 Words
2021-01-14 09:24